Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MIS-Komponen Elektronik 2011
Uploaded by
Anfield GeNk ToMiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MIS-Komponen Elektronik 2011
Uploaded by
Anfield GeNk ToMiCopyright:
Available Formats
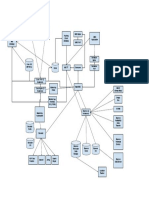
File and Database
Management Systems
File Concepts
Data Element or Field
Record
File
Primary Key
Secondary Key
File Structures
Sequential File Structure
Direct File Structure
Indexed Sequential File
Structure
Accessing Records
File Structures in on-Line, Real-
Time Processing
File Structures in Batch
Processing
File Management
Software
Commercially Prepared File
Management Software
File Management Programs
Developed in-House
Searching Files
Primary Keys
Secondary Keys
Search Parameters
Wild Cards
Database Concepts
Files vs. Databases
File Management Software vs.
Database Management
Software
Database Concepts
(Cont.)
Data Independence
Data Redundancy
Data Integrity
Database Management
Systems
Stores Data in a Uniform Way
Organizes Data Into Records in
a Uniform Way
Allows Access to Data in a
Uniform Way
Components of a
Database Management
System
Data Dictionary/Directory
Data Languages
Teleprocessing Monitor
Application Development
System
Security Software
Archiving and Recovery
Systems
DBMS Components
(cont.)
Report Writers
SQL and Other Query Languages
Microcomputer and
Minicomputer Versions of
Mainframe Databases
The Database Administrator
Views of the Database
The Conceptual View
The External View
The Internal View
Database Structures
Hierarchical Database Structure
Network Database Structure
Relational Database Structure
Object-Oriented Databases
Hierarchical Database
Structure
Inverted Tree
Root Record
Parent Record
Children Records
Nodes
Processing Is Done One Record
at a Time
Requires Explicit Links Between
Records
Less Flexibility in Ad Hoc
Queries
Network Database
Structure
Record Sets
Owner Records
Member Records
Processing Is Done One Record
at a Time
Less Flexibility in Ad Hoc
Queries
Requires Explicit Links Between
Records
Relational Database
Structure
Two-Dimensional Tables
Rows Are Records
Columns Are Data Elements or
Fields
Processing Can Be by Tables,
Rows, or Columns
doesn't Require Explicit Links
Between Records
Easy to Perform Ad Hoc Queries
Object-Oriented
Database Structure
Storing Documents, Images,
Drawings, Videos, and Other
Nontext Data
Complex Data Types That Vary
in Type, Length, Content, and
Form
Need Support for Cad,
Multimedia, and Other Systems
Object-Oriented
Databases
Objects and Attributes
Messages
Methods
Object Classes
Attribute and Behavior
Inheritance
Reusable Objects
Advantages of Database
Management Systems
Data Sharing
Reduced Data Redundancy
Improved Data Integrity
Data Independence
Increased Application
Programmer and User
Productivity
Improved Data Administration
and Control
Increased Emphasis on Data As
a Resource
Problems of Databases
Concurrency Problems
Ownership Problems
Resource Problems
Security Problems
Distributed Databases
Distributed Databases
Centralized Databases
Distributed Data Processing
Distributed Database Systems
Methods of Distributing
a Database
Replicated
Partitioned
Functional
Geographic
Hierarchical
On-Line Databases and
Information Utilities
Market Quotations
Market Information
General News and Information
Specific News and Information
Data Repositories
Data Repositories
Repository Managers
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Ani EmpatDocument9 pagesAni EmpatAnfield GeNk ToMiNo ratings yet
- Wash Plant GuideDocument2 pagesWash Plant GuideAnfield GeNk ToMiNo ratings yet
- Indonesia Research EducationDocument27 pagesIndonesia Research EducationGadzminSalisaNo ratings yet
- Improving Students' Speaking Through CLTDocument8 pagesImproving Students' Speaking Through CLTTuyet Quach AnhNo ratings yet
- Respect UDocument1 pageRespect UAnfield GeNk ToMiNo ratings yet
- Skripsi Produktifitas Belt Conveyor Pada CrusherDocument1 pageSkripsi Produktifitas Belt Conveyor Pada CrusherAnfield GeNk ToMiNo ratings yet
- Tam BangDocument158 pagesTam BangAnfield GeNk ToMiNo ratings yet
- Skripsi Produktifitas Belt Conveyor Pada CrusherDocument1 pageSkripsi Produktifitas Belt Conveyor Pada CrusherAnfield GeNk ToMiNo ratings yet
- Skripsi Produktifitas Belt Conveyor Pada CrusherDocument1 pageSkripsi Produktifitas Belt Conveyor Pada CrusherAnfield GeNk ToMiNo ratings yet
- 'E.txt' '-Ascii' 'N.TXT' '-Ascii' 'H.TXT' '-Ascii' 'K ' 'Selatan (M) ' 'Utara (M) ' 'Lokasi Survey'Document4 pages'E.txt' '-Ascii' 'N.TXT' '-Ascii' 'H.TXT' '-Ascii' 'K ' 'Selatan (M) ' 'Utara (M) ' 'Lokasi Survey'Anfield GeNk ToMiNo ratings yet
- I Am Citizen and I Respect To All Who Have A Respect.Document1 pageI Am Citizen and I Respect To All Who Have A Respect.Anfield GeNk ToMiNo ratings yet
- Nano-Minerals Identification by Different Physical TechniquesDocument6 pagesNano-Minerals Identification by Different Physical TechniquesAnfield GeNk ToMiNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Railway Reservation SystemDocument51 pagesRailway Reservation SystemVijendra SolankiNo ratings yet
- Port FlagsDocument2 pagesPort FlagsAndre CabeloNo ratings yet
- EBSPROD - Switchover - Switchback - Version 1.0Document20 pagesEBSPROD - Switchover - Switchback - Version 1.0Azeemahp PunekarNo ratings yet
- TR-4476-0716 Dedupe Compression CompactionDocument63 pagesTR-4476-0716 Dedupe Compression Compactionzaffa11No ratings yet
- A Simple MySQL Client in NBDocument12 pagesA Simple MySQL Client in NBDreamof JannahNo ratings yet
- Vijeo Citect User GuideDocument1,108 pagesVijeo Citect User GuideLucia Cosanzeana100% (1)
- SQL 1Document108 pagesSQL 1prkshjsNo ratings yet
- Analyzing ICMP traffic between hosts in Mininet and remote serverDocument13 pagesAnalyzing ICMP traffic between hosts in Mininet and remote serverJeelon MTNo ratings yet
- AT Command Set (MTK)Document170 pagesAT Command Set (MTK)ivankinoman387650% (2)
- 3 - Data Resource ManagementDocument43 pages3 - Data Resource ManagementSaba IlyasNo ratings yet
- Assign 1Document3 pagesAssign 1Tesfaye GemechuNo ratings yet
- HCP ReplicationDocument4 pagesHCP ReplicationLuis Moralez JimenezNo ratings yet
- SELECT UNION POWERS OPEN SQLDocument8 pagesSELECT UNION POWERS OPEN SQLcelsonnevesNo ratings yet
- VB Code to Populate FlexGrid from RecordsetDocument9 pagesVB Code to Populate FlexGrid from RecordsetMohd Gulfam100% (1)
- Tutorial - How To Use The MsiLockPermissionsEx Table (And CSI - GetSDDLFromObject Helper Script)Document14 pagesTutorial - How To Use The MsiLockPermissionsEx Table (And CSI - GetSDDLFromObject Helper Script)Firoz KhanNo ratings yet
- Commissioning FZCDocument187 pagesCommissioning FZCYen-Ting Chen100% (1)
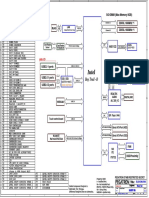
- Pegatron Iaxbt-Bl Rev Rev. 1.01 Acer Aspire Zc-606Document67 pagesPegatron Iaxbt-Bl Rev Rev. 1.01 Acer Aspire Zc-606Ban NeoNo ratings yet
- Search Database (MySQL) & App ArchitectureDocument1 pageSearch Database (MySQL) & App ArchitecturemrkaafNo ratings yet
- State Polytechnic of Jember: The Exercises of File System Chapter 10Document15 pagesState Polytechnic of Jember: The Exercises of File System Chapter 10Dwi Rifki NoviantoNo ratings yet
- HSN 0101Document130 pagesHSN 0101Jessica PerryNo ratings yet
- Web MiningDocument22 pagesWeb MiningPriya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Linux Networking Stack: Sending DataDocument151 pagesLinux Networking Stack: Sending DataAbdul HayeeNo ratings yet
- Token Bus (IEEE 802)Document9 pagesToken Bus (IEEE 802)anon_185146696No ratings yet
- Refresh Test Database from ProductionDocument5 pagesRefresh Test Database from ProductiongunalprasadgNo ratings yet
- Ts 72 Admin enDocument302 pagesTs 72 Admin enGautam PopliNo ratings yet
- CS411 HWDocument3 pagesCS411 HWJonathan MaresNo ratings yet
- Hardware Hacking 101 - Identifying and Dumping eMMC Flash - River Loop SecurityDocument32 pagesHardware Hacking 101 - Identifying and Dumping eMMC Flash - River Loop SecuritysopteaNo ratings yet
- MX29LV008C T/B 8M-BIT CMOS SINGLE VOLTAGE FLASH MEMORYDocument54 pagesMX29LV008C T/B 8M-BIT CMOS SINGLE VOLTAGE FLASH MEMORYAndre PinhoNo ratings yet
- 2.advanced ModelingDocument28 pages2.advanced ModelingMahdi MohamadZadeNo ratings yet
- PCD Filter ImageDocument16 pagesPCD Filter ImageTomi HartantoNo ratings yet