Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vascular Diseases
Uploaded by
Windelyn GamaroCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Vascular Diseases
Uploaded by
Windelyn GamaroCopyright:
Available Formats
Vascular
Diseases
Vascular System Anatomy
Disorders
Aneurysm
Is a sac formed by
dilation of an
artery secondary
to weakness and
stretching of the
arterial wall.
The dilation may
involve one or all
layers of the
arterial wall
Risk Factors
Atherosclerosis
Age: 50-70 years old
Hypertension
Trauma
Syphilis
Infectious process
Classification
Fusiform
Saccular
Dissecting
False
Assessment
Early stage: often asymptomatic
Deep diffuse chest pain
Hoarseness, dysphagia, dyspnea
Pallor, diaphoresis
Distended neck veins, edema or hand and arms
Feeling of heart-beating in the abdomen (if
abdominal aortic aneurysm)
Nursing Intervention
Monitor and improve clients cardiopulmonary state
Record baseline BP (lying, sitting and standing)
in both arms
Provide dependent and other collaborative nursing
interventions
Give meds: antihypertensive drugs
Prepare for UTZ
Surgery: Resection of Aneurysm and
replacement with a Teflon/Dacron graft
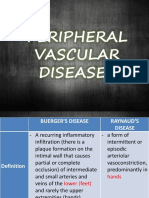
Buergers Disease
(Thromboangitis Obliterans)
and Raynauds Disease
Buergers Disease Raynauds Disease
Vasculitis of the small and
medium size veins and
arteries, usually in the lower
extremities.
More common in MEN
S&Sx: Pain; intermittent
claudication, tingling
sensation, impaired pulse,
hair loss in the legs
Leg angiography reveals
inflammatory lesions
Nrsg Dx: Altered peripheral
tissue perfusion
Intervention:
o Instruct the client to stop smoking
o Avoid trauma to affected extremity
o Maintenance of warmth during cold
weather
Vasospastic condition of
arteries of hands that occurs
with exposure to cold or
stress
More common in WOMEN
S&Sx: Cyanosis of fingers or
toes after exposure to cold,
numbness and tingling of
digits
Allens Test reveals
circulatory problems
Nrsg Dx: Altered peripheral
tissue perfusion
Intervention:
o Avoid cold weather
o Wear leather gloves when getting
anything from the refrigerator
o Stop smoking
o Administer vasodilators as ordered
Quick Recall
Manifestation Condition
1. Intermittent
claudication
2. Pain
3. Vasospasm
4. Inflamed blood
vessels
5. Intermittent
color changes of
the fingers
A. Buergers
Disease
B. Raynauds
Disease
C. Both
D. Neither
Thrombophlebitis and
Varicose Veins
Thrombophlebitis Varicose Veins
Clot in the vein with
inflammation of the wall of
the vein
S&Sx:
o Unilateral leg edema w/ (+) Homans
sign
o Severe pain at site
o Fever, chills, swelling and cyanosis
of site
Venography reveals a clot
N. Dx: Altered tissue
perfusion
Intervention:
o DO NOT MASSAGE THE
AFFECTED LEG
o Increase fluid intake
o Monitor leg edema
Weakening of the venous
valves leading to pooling of
blood
S&Sx:
o Tortuous vein
o Dull ache and heaviness in the legs
o Mild edema
o Itching of the skin over the affected
part
Doppler UTZ detects the
presence or absence of venous
reflux
N. Dx: Altered tissue
perfusion
Intervention
o Elevate the legs
o Avoid crossing of legs at knees
o Avoid prolonged sitting and standing
o Avoid constrictive clothing
o Prepare the client for surgery
Quick Recall
Manifestation Disease
1. Edema
2. Pain
3. Homans sign
4. Tortuous vein
5. Intermittent
claudication
A. Thrombophlebit
is
B. Varicose vein
C. Both
D. Neither
End
You might also like
- Heavy Equipment Operator Testing and CertificationDocument7 pagesHeavy Equipment Operator Testing and CertificationJaffer Rizvi0% (1)
- Peripheral Vascular Disease Arteries NHSDocument10 pagesPeripheral Vascular Disease Arteries NHSAdahl HetheringtonNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Vascular DiseaseDocument45 pagesPeripheral Vascular DiseaseKammoshi100% (4)
- Varicose Veins Treatment OptionsDocument49 pagesVaricose Veins Treatment OptionsYuli Setio Budi PrabowoNo ratings yet
- MS2 Chapter 24 Peripheral Vascular DiseasesDocument76 pagesMS2 Chapter 24 Peripheral Vascular DiseasesTatiana Leashe Wooten100% (1)
- Deep Vein ThrombosisDocument42 pagesDeep Vein ThrombosisNsklm100% (7)
- Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesCirculatory SystemKumar Sujeet100% (1)
- Rife RatesDocument17 pagesRife RateszonetrekNo ratings yet
- Congenital Adrenal HyperplasiaDocument28 pagesCongenital Adrenal HyperplasiaWindelyn Gamaro0% (1)
- Disorders of The Peripheral Vascular SystemDocument17 pagesDisorders of The Peripheral Vascular SystemDardarConstantinoNo ratings yet
- The Ideal Heart Healthy Diet Cookbook; The Superb Diet Guide To Lower Your Blood Pressure And Cholesterol Levels With Nutritious Low Sodium Low Fat RecipesFrom EverandThe Ideal Heart Healthy Diet Cookbook; The Superb Diet Guide To Lower Your Blood Pressure And Cholesterol Levels With Nutritious Low Sodium Low Fat RecipesNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Vascular Disease-1Document52 pagesPeripheral Vascular Disease-1Johiarra Madanglog Tabigne100% (1)
- Mini Question Bank - Vety Sci - For Students PDFDocument106 pagesMini Question Bank - Vety Sci - For Students PDFRakesh Prajapati100% (3)
- PQA Summary FinalDocument25 pagesPQA Summary FinalWindelyn GamaroNo ratings yet
- The Sacred Mushroom "Reishi"-A ReviewDocument4 pagesThe Sacred Mushroom "Reishi"-A ReviewDinesh Babu PugalenthiNo ratings yet
- Case Digest For Legal ResearchDocument5 pagesCase Digest For Legal ResearchWindelyn GamaroNo ratings yet
- In Re - Kay Villegas Kami 35 SCRA 429 (1970)Document1 pageIn Re - Kay Villegas Kami 35 SCRA 429 (1970)Windelyn GamaroNo ratings yet
- Varicose Veins, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandVaricose Veins, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Vascular Disease NursingDocument13 pagesPeripheral Vascular Disease NursingCatlyn Chatpman100% (1)
- Robin Williams Case of Acute Depression Leading To Suicide From Point of View of AstrologyDocument5 pagesRobin Williams Case of Acute Depression Leading To Suicide From Point of View of AstrologyJatinder Sandhu100% (1)
- Phlebitis and ThrombophlebitisDocument27 pagesPhlebitis and ThrombophlebitisMaría Fernanda RíosNo ratings yet
- Ectropion & EntropionDocument2 pagesEctropion & EntropionAhmed ShafikNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Vascular DiseaseDocument32 pagesPeripheral Vascular DiseaseShy PatelNo ratings yet
- Vascular Disorders Guide Covering Thrombophlebitis, DVT, Varicose Veins, PAD, AneurysmsDocument7 pagesVascular Disorders Guide Covering Thrombophlebitis, DVT, Varicose Veins, PAD, Aneurysmskevin_manansala_1No ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Adults With Vascular ProblemsDocument54 pagesNursing Care of Adults With Vascular ProblemsTraci Ann NewberryNo ratings yet
- VASCULARDocument32 pagesVASCULARnixsieNo ratings yet
- Vascular Diseases: Kibrom Gebreselassie, MD, FCS-ECSA Cardiovascular and Thoracic SurgeonDocument57 pagesVascular Diseases: Kibrom Gebreselassie, MD, FCS-ECSA Cardiovascular and Thoracic SurgeonVincent SerNo ratings yet
- Nursing Managment For DVTDocument23 pagesNursing Managment For DVTgvs5zdbcsfNo ratings yet
- Managemnet Arterial UlcersDocument24 pagesManagemnet Arterial UlcersMohamad Zulfikar100% (1)
- Peripheral-Vascular-Disease 2ndDocument84 pagesPeripheral-Vascular-Disease 2ndAb BabyNo ratings yet
- Phlebitis and ThrombophlebitisDocument27 pagesPhlebitis and ThrombophlebitisSushant SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Phlebitis and ThrombophlebitisDocument27 pagesPhlebitis and ThrombophlebitisMaría Fernanda Ríos100% (1)
- PERIPHERALDocument7 pagesPERIPHERALhakky gamyNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Klinis Vaskuler 1,0Document39 pagesPemeriksaan Klinis Vaskuler 1,0Bobby PrayogoNo ratings yet
- Penyakit VenaDocument37 pagesPenyakit VenaSarah JR Nur AzizahNo ratings yet
- 10 Arterial UlcersDocument29 pages10 Arterial Ulcerskim suhoNo ratings yet
- Varicose Vein & DVT (Surgery II) .Document24 pagesVaricose Vein & DVT (Surgery II) .selormniiqNo ratings yet
- Arterial Stenosis or OcclusionDocument83 pagesArterial Stenosis or OcclusionMuhammad Umer Farooq NadeemNo ratings yet
- Prevention of DVTDocument49 pagesPrevention of DVTMariya DantisNo ratings yet
- NCM 103 Report .Paod - Aneurysm.buergersDocument72 pagesNCM 103 Report .Paod - Aneurysm.buergersArlyn Padua OlivasNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument25 pagesUntitledAlthea Sachi Cruz100% (1)
- 115-NCLEX-RN Review Made Incredibly Easy, Fifth Edition (Incredibly Easy Series) - Lippincott-16083 - p87Document1 page115-NCLEX-RN Review Made Incredibly Easy, Fifth Edition (Incredibly Easy Series) - Lippincott-16083 - p87MuhNatsirNo ratings yet
- VHD-to-DVTDocument55 pagesVHD-to-DVTShiehan Mae ForroNo ratings yet
- EDEMADocument36 pagesEDEMAGeetanjali MiglaniNo ratings yet
- Leg UlcerDocument26 pagesLeg UlcerBhuiyan Ma Yousuf100% (1)
- Crs Peripheral Artery Disease - Billi Brian GeniroDocument21 pagesCrs Peripheral Artery Disease - Billi Brian Genirofathiya nurkhalisaNo ratings yet
- Ischaemia of Lower Limbs: by Dr. ShampileDocument46 pagesIschaemia of Lower Limbs: by Dr. ShampileFreeburn SimunchembuNo ratings yet
- Referat Ulkus DMDocument33 pagesReferat Ulkus DMAisyah Fatinah AgamNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Conditions (20 HRS) - 1Document79 pagesCardiovascular Conditions (20 HRS) - 1staceyatienoomaNo ratings yet
- Vascular SystemDocument33 pagesVascular SystemCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (3)
- Haemodynamic DisordersDocument27 pagesHaemodynamic DisordersHareem FatimaNo ratings yet
- Raynaud Disease ReportingDocument20 pagesRaynaud Disease ReportingShimri MagsicoNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument33 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic FeverCharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer Internist ApproachDocument57 pagesDiabetic Foot Ulcer Internist ApproachSandip DNo ratings yet
- Infectious EndocarditisDocument4 pagesInfectious EndocarditisKhalid Mahmud Arifin100% (1)
- Peripheral Vascular DiseaseDocument52 pagesPeripheral Vascular DiseaseEbiNo ratings yet
- Gangrene of ExtremitiesDocument31 pagesGangrene of ExtremitiesUsaid SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Listeriosis - O&G SeminarDocument17 pagesListeriosis - O&G SeminarFaris Mohd NasirNo ratings yet
- Definition of Terms Used in Medical NursingDocument15 pagesDefinition of Terms Used in Medical NursingKakuru Joseph mNo ratings yet
- Varicose VeinDocument22 pagesVaricose VeinArslan KhanNo ratings yet
- Aortic AneurysmDocument60 pagesAortic AneurysmSantosh NaliathNo ratings yet
- Kuliah DVTDocument29 pagesKuliah DVTluluksNo ratings yet
- +oleksandr Chaika Theme 15 Varicose Veins.Document19 pages+oleksandr Chaika Theme 15 Varicose Veins.Oussama ANo ratings yet
- 8 EndocarditisDocument19 pages8 EndocarditisdaisyNo ratings yet
- Thrombophlebitis & Thrombosis o An Inflammatory Process That Causes A Blood Clot To Form and Block One orDocument8 pagesThrombophlebitis & Thrombosis o An Inflammatory Process That Causes A Blood Clot To Form and Block One orJannah Marie A. Dimaporo100% (1)
- Varicose Vein Anatomy, Causes, and TreatmentDocument34 pagesVaricose Vein Anatomy, Causes, and TreatmentirfanNo ratings yet
- MEDIATRIXDocument67 pagesMEDIATRIXMaria Consuelo LingcasoNo ratings yet
- CCSNH MLC Habits of Mind Costa-Kallick DescriptionDocument14 pagesCCSNH MLC Habits of Mind Costa-Kallick DescriptionPusti AlaufaNo ratings yet
- CA upholds conviction of man for double murder, attempted murderDocument16 pagesCA upholds conviction of man for double murder, attempted murderWindelyn GamaroNo ratings yet
- Persons and Family Relations - Case DigestDocument3 pagesPersons and Family Relations - Case DigestWindelyn GamaroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Reviewer Statutory ConstructionDocument3 pagesChapter 3 - Reviewer Statutory ConstructionWindelyn GamaroNo ratings yet
- Sample Learning Plan in English: Time Topic/s Learning Outcomes Methodologies/Strategies Resources AssessmentDocument1 pageSample Learning Plan in English: Time Topic/s Learning Outcomes Methodologies/Strategies Resources AssessmentWindelyn GamaroNo ratings yet
- Vascular DiseasesDocument17 pagesVascular DiseasesWindelyn GamaroNo ratings yet
- Oncology NursingDocument32 pagesOncology NursingWindelyn GamaroNo ratings yet
- Paulo Coelho's The Fifth Mountain: A Novel About Prophet Elijah's Life LessonsDocument5 pagesPaulo Coelho's The Fifth Mountain: A Novel About Prophet Elijah's Life LessonsWindelyn GamaroNo ratings yet
- Emergency and Disaster Nursing ReviewDocument40 pagesEmergency and Disaster Nursing Reviewdecsag06No ratings yet
- 24 Hour PlannerDocument1 page24 Hour PlannerCheng KysonNo ratings yet
- Emerging Philosophies Philippine EducationDocument4 pagesEmerging Philosophies Philippine EducationWindelyn GamaroNo ratings yet
- Paulo Coelho's The Fifth Mountain: A Novel About Prophet Elijah's Life LessonsDocument5 pagesPaulo Coelho's The Fifth Mountain: A Novel About Prophet Elijah's Life LessonsWindelyn GamaroNo ratings yet
- Capacity BuildingDocument10 pagesCapacity BuildingWindelyn GamaroNo ratings yet
- Emergency and Disaster Nursing ReviewDocument40 pagesEmergency and Disaster Nursing ReviewWindelyn GamaroNo ratings yet
- O Learning: Classical ConditioningDocument2 pagesO Learning: Classical ConditioningWindelyn Gamaro100% (1)
- South AfricaDocument47 pagesSouth AfricaWindelyn GamaroNo ratings yet
- Middle Adulthood Psychology ReportDocument29 pagesMiddle Adulthood Psychology ReportWindelyn GamaroNo ratings yet
- TURBT Procedure GuideDocument80 pagesTURBT Procedure GuideWindelyn GamaroNo ratings yet
- The Philippines Is A Unique Combination of Varied TopographyDocument1 pageThe Philippines Is A Unique Combination of Varied TopographyWindelyn GamaroNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Nursing DiscussionDocument69 pagesPsychiatric Nursing DiscussionWindelyn GamaroNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience ReviewerWindelyn GamaroNo ratings yet
- The Philippines Is A Unique Combination of Varied TopographyDocument1 pageThe Philippines Is A Unique Combination of Varied TopographyWindelyn GamaroNo ratings yet
- Meeting The Conditions of A PermitDocument2 pagesMeeting The Conditions of A PermitWindelyn GamaroNo ratings yet
- MCN Day 3Document27 pagesMCN Day 3Windelyn GamaroNo ratings yet
- MCN Day 2Document85 pagesMCN Day 2Windelyn GamaroNo ratings yet
- 01 M039 43754Document16 pages01 M039 43754DrDeepak PawarNo ratings yet
- Amir Bin Tamin 2Document3 pagesAmir Bin Tamin 2Akram KastiranNo ratings yet
- CPR and Aed: Quiz #2 ResultsDocument2 pagesCPR and Aed: Quiz #2 ResultsNathan WhiteNo ratings yet
- Atlas de Acupuntura (Ingles)Document16 pagesAtlas de Acupuntura (Ingles)Medicina Tradicional China - Grupo LeNo ratings yet
- Inamsc Literature Review Dg1fQQFe Guideline INAMSC 2018Document20 pagesInamsc Literature Review Dg1fQQFe Guideline INAMSC 2018DevinNo ratings yet
- Boys Centile ChartDocument1 pageBoys Centile ChartElma AprilliaNo ratings yet
- Reasoning BookDocument38 pagesReasoning BookAshish Sharma100% (1)
- Nuclear Associates User ManualDocument20 pagesNuclear Associates User ManualvandarsNo ratings yet
- The Welfare of Cattle Kept For Beef ProductionDocument150 pagesThe Welfare of Cattle Kept For Beef ProductionIsabel CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Cir 0000000000000899Document25 pagesCir 0000000000000899hanifa ambNo ratings yet
- What Is HumorDocument5 pagesWhat Is HumorWan Sek ChoonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6. FeverDocument19 pagesChapter 6. FeverMonica CiorneiNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology of AsthmaDocument8 pagesEpidemiology of AsthmaMaria Alejandra Siachoque JaraNo ratings yet
- Msds MgOHDocument5 pagesMsds MgOHCahyaGeriyanaNo ratings yet
- The Medication Order Unit 11Document10 pagesThe Medication Order Unit 11novie100% (2)
- BooksDocument11 pagesBooksChanfaithxiaAva P CabanosNo ratings yet
- Resp 1.02 Hierarchy of O2 Delivery MethodsDocument1 pageResp 1.02 Hierarchy of O2 Delivery MethodsVin Lorenzo CampbellNo ratings yet
- Guava Soap Cures AcneDocument10 pagesGuava Soap Cures AcneAubrey VaflorNo ratings yet
- New 5Document37 pagesNew 5rishi gupta100% (1)
- Stock 07 Oktober 2022Document19 pagesStock 07 Oktober 2022Dwi AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Showtime - Smilf 1x01 (Pilot)Document36 pagesShowtime - Smilf 1x01 (Pilot)Vishnu SinhaNo ratings yet
- IMSS Nursing Knowledge ExamDocument11 pagesIMSS Nursing Knowledge ExamScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- ECG Identification QuizDocument40 pagesECG Identification QuizRahul AudenesenNo ratings yet