Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Estructura y Funcion de La Hemoglobina
Uploaded by
willmedOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Estructura y Funcion de La Hemoglobina
Uploaded by
willmedCopyright:
Available Formats
Structure and
Structure and
function of
function of
Haemoglobin
Haemoglobin
Dr. Tariq M Roshan
Dr. Tariq M Roshan
Department of Hematology
Department of Hematology
PPSP
PPSP
The main function of red blood cell
The main function of red blood cell
Transfer of O Transfer of O2 2 from lungs to tissue from lungs to tissue
Transfer of O Transfer of O2 2 from tissue to lungs from tissue to lungs
To accomplish this function red cells
To accomplish this function red cells
has haemoglobin !Hb"
has haemoglobin !Hb"
#ach red cell has $%& million
#ach red cell has $%& million
molecules of Hb
molecules of Hb
'ntroduction
'ntroduction
'ntroduction
'ntroduction
Haemoglobin !Hb"( protein constituting )*+
Haemoglobin !Hb"( protein constituting )*+
of the red blood cells
of the red blood cells
Synthesis begins in proerythroblast
Synthesis begins in proerythroblast
$,- at erythroblast stage $,- at erythroblast stage
+,- at reticulocyte stage +,- at reticulocyte stage
T.o parts
T.o parts
Haem Haem
/lobin /lobin
Synthesis of Haemoglobin
Synthesis of Haemoglobin
!Hb"
!Hb"
Haem 0 globin produced at t.o
Haem 0 globin produced at t.o
di1erent sites in the cells
di1erent sites in the cells
Haem in mitochondria Haem in mitochondria
/lobin in polyribosomes /lobin in polyribosomes
2ell synchroni3ed
2ell synchroni3ed
Synthesis of Haemoglobin
Synthesis of Haemoglobin
Synthesis of Haem
Synthesis of Haem
Protoporphyrin ring .ith an iron atom
Protoporphyrin ring .ith an iron atom
in centre
in centre
The main site is mitochondria as it
The main site is mitochondria as it
contains 454S
contains 454S
Mature red cell does not contain
Mature red cell does not contain
mitochondria
mitochondria
Structure of Haem
Structure of Haem
Synthesis of globin
Synthesis of globin
Synthesis of globin
Synthesis of globin
6arious types of globin combines .ith
6arious types of globin combines .ith
haem to from di1erent haemoglobin
haem to from di1erent haemoglobin
#ight functional globin chains(
#ight functional globin chains(
arranged in t.o clusters the
arranged in t.o clusters the
7 cluster ! 7 cluster !
( (
( (
and and
globin genes" on the globin genes" on the
short arm of chromosome )) short arm of chromosome ))
7 cluster ! 7 cluster !
and and
globin genes" on the short globin genes" on the short
arm of chromosome )$ arm of chromosome )$
/lobin gene clusters
/lobin gene clusters
/lobin synthesis( starts at +
/lobin synthesis( starts at +
rd rd
.ee8 of
.ee8 of
gestation
gestation
#mbryonic
#mbryonic
Haemoglobin /o.er ' !
Haemoglobin /o.er ' !
2 2
2 2
"
"
Haemoglobin Portland !
Haemoglobin Portland !
2 2
2 2
"
"
Haemoglobin /o.er '' !
Haemoglobin /o.er '' !
2 2
2
2
"
"
9etal : Hb9 !
9etal : Hb9 !
2 2
2 2
"( Hb4 !
"( Hb4 !
2 2
2 2
"
"
4dult : Hb4( Hb42 !
4dult : Hb4( Hb42 !
2 2
2 2
"( Hb9.
"( Hb9.
Synthesis of globin
Synthesis of globin
/lobin chain s.itch
/lobin chain s.itch
4lpha 0 beta chains
4lpha 0 beta chains
Hb 4
Hb 4
Hb 4
Hb 4
2 2
Hb 9
Hb 9
structure
structure
2 2
2 2
2 2
2 2
2 2
2 2
;ormal -
;ormal -
<$7<= -
<$7<= -
).,7+.2 -
).,7+.2 -
&.,7&.= -
&.,7&.= -
4dult haemoblobin
4dult haemoblobin
9unctions of Haemoglobin
9unctions of Haemoglobin
O>ygen deli?ery to the tissues
O>ygen deli?ery to the tissues
Reaction of Hb 0 o>ygen
Reaction of Hb 0 o>ygen
O>ygenation not o>idation O>ygenation not o>idation
One Hb can bind to four O One Hb can bind to four O2 2 molecules molecules
5ess than .&) sec required for o>ygenation 5ess than .&) sec required for o>ygenation
chain mo?e closer .hen o>ygenated chain mo?e closer .hen o>ygenated
2hen o>ygenated 2(+7DP/ is pushed out 2hen o>ygenated 2(+7DP/ is pushed out
chains are pulled apart .hen O chains are pulled apart .hen O2 2 is is
unloaded( permitting entry of 2(+7DP/ unloaded( permitting entry of 2(+7DP/
resulting in lo.er a@nity of O resulting in lo.er a@nity of O2 2
O>y 0 deo>yhaemoglobin
O>y 0 deo>yhaemoglobin
O>ygen7haemoglobin
O>ygen7haemoglobin
dissociation cur?e
dissociation cur?e
O
O2 2
carrying capacity of Hb at
carrying capacity of Hb at
di1erent Po
di1erent Po2 2
Sigmoid shape
Sigmoid shape
Ainding of one molecule facilitate the second Ainding of one molecule facilitate the second
molecule binding molecule binding
P P ,& ,& !partial pressure of O !partial pressure of O2 2 at .hich Hb is at .hich Hb is
half saturated .ith O half saturated .ith O2 2" 2$.$mmHg " 2$.$mmHg
Hb7o>ygen dissociation
Hb7o>ygen dissociation
cur?e
cur?e
The normal position of cur?e
The normal position of cur?e
depends on
depends on
oncentration of 2(+7DP/ oncentration of 2(+7DP/
H H
B B
ion concentration !pH" ion concentration !pH"
O O
2 2
in red blood cells in red blood cells
Structure of Hb Structure of Hb
Hb7o>ygen dissociation
Hb7o>ygen dissociation
cur?e
cur?e
Right shift !easy o>ygen deli?ery"
Right shift !easy o>ygen deli?ery"
High 2(+7DP/ High 2(+7DP/
High H High H
B B
High O High O
2 2
HbS HbS
5eft shift !gi?e up o>ygen less readily"
5eft shift !gi?e up o>ygen less readily"
5o. 2(+7DP/ 5o. 2(+7DP/
Hb9 Hb9
Hb7o>ygen dissociation
Hb7o>ygen dissociation
cur?e
cur?e
Summary
Summary
;ormal structure including the proportion of
;ormal structure including the proportion of
globin chains are necessary for the normal
globin chains are necessary for the normal
function of haemoglobin
function of haemoglobin
Reduced haemoglobin in the red blood cells
Reduced haemoglobin in the red blood cells
due to any abnormality of any of its
due to any abnormality of any of its
constituents result into a clinical situation
constituents result into a clinical situation
called anaemia
called anaemia
Metabolic 0 other abnormalities result into
Metabolic 0 other abnormalities result into
abnormal o>ygen supply to the tissue
abnormal o>ygen supply to the tissue
You might also like
- Hemoglobin Structure and FunctionDocument42 pagesHemoglobin Structure and Functionniveendaoud100% (1)
- Hemoglobin: Ahmad Sh. Silmi MSC Haematology, FIBMSDocument52 pagesHemoglobin: Ahmad Sh. Silmi MSC Haematology, FIBMSPunit DwivediNo ratings yet
- Haemoglobin: Hiroshani Kulatunga BSC (Hons) MlsDocument36 pagesHaemoglobin: Hiroshani Kulatunga BSC (Hons) MlsNipun ShamikaNo ratings yet
- Structure, Types and Various Methods For Estimation of HaemoglobinDocument49 pagesStructure, Types and Various Methods For Estimation of HaemoglobinChandra ShekharNo ratings yet
- HaemoglobinDocument55 pagesHaemoglobinPhysiology by Dr RaghuveerNo ratings yet
- Hema 1 ErythropoiesisDocument20 pagesHema 1 Erythropoiesismarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Asif Zeb Lecturer Hematology Ipms - (Kmu)Document23 pagesMuhammad Asif Zeb Lecturer Hematology Ipms - (Kmu)MarcelliaNo ratings yet
- 1952uwu270191 H1827272u2bdbdbd017yfndnabab Structure and Fu37373nction Mbbs 2017 BatchDocument88 pages1952uwu270191 H1827272u2bdbdbd017yfndnabab Structure and Fu37373nction Mbbs 2017 BatchRed DiggerNo ratings yet
- 02 HemoglobinDocument78 pages02 HemoglobinpixiedustNo ratings yet
- Normal Hemoglobin Content: 1-Transport of Respiratory GasesDocument4 pagesNormal Hemoglobin Content: 1-Transport of Respiratory GasesDentistryNo ratings yet
- HAEMOGLOBINDocument8 pagesHAEMOGLOBINSenyonga EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- 4 HGBDocument38 pages4 HGBChona_Delos_Re_1233No ratings yet
- Blood6 OcaDocument7 pagesBlood6 Ocahydr.jNo ratings yet
- L11 Hemoglobin Structure-FunctionDocument26 pagesL11 Hemoglobin Structure-Functionziyad khalidNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of HaemoglobinDocument21 pagesStructure and Function of HaemoglobinEmily HoNo ratings yet
- Haemoglobin - Function, Variants, FateDocument27 pagesHaemoglobin - Function, Variants, FateXembergNo ratings yet
- Hgb Metabolism 1Document26 pagesHgb Metabolism 1MARTINEZ JUSTINENo ratings yet
- Heme and Hemoglobin SynthesisDocument5 pagesHeme and Hemoglobin Synthesiskep1313No ratings yet
- Hemoglobinopatzhy PDFDocument16 pagesHemoglobinopatzhy PDFJoy CuanoNo ratings yet
- Hemoglobin & Derivatives: DR. S. Irfan RazaDocument30 pagesHemoglobin & Derivatives: DR. S. Irfan RazaSyed Irfan RazaNo ratings yet
- C10 Hemoglobin MetabolisnmDocument60 pagesC10 Hemoglobin MetabolisnmNoreen B. BañagadoNo ratings yet
- MED-1 Metabolismofoxygen binding proteinDocument40 pagesMED-1 Metabolismofoxygen binding proteinozerbilge24No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 HemaDocument3 pagesChapter 10 HemaJoannah MarieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27aDocument228 pagesChapter 27aMiaNo ratings yet
- Lec - 12 Hemoglobin-3Document20 pagesLec - 12 Hemoglobin-3andreaNo ratings yet
- Haemoglobin SynthesisDocument28 pagesHaemoglobin SynthesisUche EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة الثانية عمليDocument7 pagesالمحاضرة الثانية عمليAbduslam AlkholeediNo ratings yet
- HB Structure & Function 2008Document19 pagesHB Structure & Function 2008Rhomizal MazaliNo ratings yet
- Activity 8&9Document30 pagesActivity 8&9Loulou ApolloNo ratings yet
- Hemoglobin Determination Using SpectrophotometryDocument6 pagesHemoglobin Determination Using SpectrophotometryBabylavender100% (1)
- Chapter 10 (Hemoglobin Metabolism)Document3 pagesChapter 10 (Hemoglobin Metabolism)Joannah Marie100% (1)
- HB SynthesisDocument21 pagesHB SynthesisPutriNo ratings yet
- Hemoglobin Function and Variation in Wild PopulationsDocument21 pagesHemoglobin Function and Variation in Wild PopulationsXeyale QuliyevaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of BloodDocument73 pagesPhysiology of BloodAggamemnon populosNo ratings yet
- 7 HemoglobinopathiesDocument34 pages7 HemoglobinopathiesAhmad SobihNo ratings yet
- RBC, Structure and FunctionDocument17 pagesRBC, Structure and FunctionAsyha KantifaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of HaemoglobinDocument21 pagesStructure and Function of HaemoglobinSonam JoshiNo ratings yet
- Por Phy RinsDocument69 pagesPor Phy RinsedinapetermugaduiNo ratings yet
- Haemoglobin EstimationDocument20 pagesHaemoglobin Estimationanon_719505684No ratings yet
- 6.globular ProteinsDocument45 pages6.globular ProteinsAhmad SobihNo ratings yet
- Hemoglobin and Its Types: DR Roomi Aijaz Memon Department of Phusiology Isra University HyderabadDocument14 pagesHemoglobin and Its Types: DR Roomi Aijaz Memon Department of Phusiology Isra University HyderabadUSAMA AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Globin Synthesis PDFDocument6 pagesGlobin Synthesis PDFmanoj_rkl_07100% (1)
- C7 (Gaseous Exchange)Document16 pagesC7 (Gaseous Exchange)nurhasinahabrahimNo ratings yet
- 1 Blood: Composition of Blood (Viva)Document21 pages1 Blood: Composition of Blood (Viva)Priyanka MhNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry SeminarDocument12 pagesBiochemistry SeminarPreeti GondNo ratings yet
- Topic: Structure and Function of Haemoglobin: GC University, LahoreDocument8 pagesTopic: Structure and Function of Haemoglobin: GC University, LahoreAbdullah MunawarNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of HemeDocument62 pagesStructure and Functions of HemeBrahmesh GuntamukkalaNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument24 pagesNotesSapna JainNo ratings yet
- HEMA 2Document4 pagesHEMA 2Alanah JaneNo ratings yet
- Hemoglobin: Portrait of A Protein in ActionDocument32 pagesHemoglobin: Portrait of A Protein in Actionraanja2No ratings yet
- Hemoglobin Electrophoresis: DR Nisha S Ahmad Chief of Lab Services Metropolis Health ServicesDocument63 pagesHemoglobin Electrophoresis: DR Nisha S Ahmad Chief of Lab Services Metropolis Health ServicescandiddreamsNo ratings yet
- Hemoglobin Determination: Cyanmethemoglobin MethodDocument31 pagesHemoglobin Determination: Cyanmethemoglobin Methodبراءة أحمد السلاماتNo ratings yet
- Structure, Function and Metabolism of Hemoglobin: Pavla BalínováDocument33 pagesStructure, Function and Metabolism of Hemoglobin: Pavla BalínováMamad GGNo ratings yet
- Formed Elements: Drsallama Hamid Consultant Lecturer DoctorDocument7 pagesFormed Elements: Drsallama Hamid Consultant Lecturer DoctorAhmed Ali AssafNo ratings yet
- Physiology of HemoglobinDocument15 pagesPhysiology of HemoglobinIbrahim YahyaNo ratings yet
- What Is The Function of Hemoglobin in The Human Body: February 2017Document8 pagesWhat Is The Function of Hemoglobin in The Human Body: February 2017AdriánNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument28 pagesBiochemistryPRAJWAL PES HDNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument5 pagesBloodAkachukwu ObunikeNo ratings yet
- 1 Abnormal HemoglobinDocument3 pages1 Abnormal Hemoglobinkep1313No ratings yet
- Structure and Function of HaemoglobinDocument21 pagesStructure and Function of HaemoglobinEmily HoNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Red Blood Cell Membranes: Yun Ge Supervisor: Dr. H.Jerry QiDocument9 pagesMechanical Properties of Red Blood Cell Membranes: Yun Ge Supervisor: Dr. H.Jerry QiwillmedNo ratings yet
- Blood and HemopoiesisDocument30 pagesBlood and HemopoiesiswillmedNo ratings yet
- Desordenes de Membrana InfDocument3 pagesDesordenes de Membrana InfwillmedNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of HaemoglobinDocument21 pagesStructure and Function of HaemoglobinEmily HoNo ratings yet
- Multilevel, Subdivision-Based, Thin Shell Finite Elements: Development and Application To Red Blood Cell Modeling Seth GreenDocument66 pagesMultilevel, Subdivision-Based, Thin Shell Finite Elements: Development and Application To Red Blood Cell Modeling Seth GreenwillmedNo ratings yet
- Desordenes de Membrana InfDocument3 pagesDesordenes de Membrana InfwillmedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Red Cell Defects FinalDocument28 pagesLecture 5 Red Cell Defects FinalwillmedNo ratings yet
- Bses Moleculares PDFDocument5 pagesBses Moleculares PDFwillmedNo ratings yet
- Red Cell Disorders GuideDocument49 pagesRed Cell Disorders GuideGeraldine AgpesNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of HaemoglobinDocument21 pagesStructure and Function of HaemoglobinEmily HoNo ratings yet
- Membrane The Molecular Basis of Disorders of The Red Cell: J. Clin. PatholDocument5 pagesMembrane The Molecular Basis of Disorders of The Red Cell: J. Clin. PatholwillmedNo ratings yet
- Estudio de Casos Xe Vs XN PDFDocument29 pagesEstudio de Casos Xe Vs XN PDFwillmedNo ratings yet
- Desordenes de Membrana InfDocument3 pagesDesordenes de Membrana InfwillmedNo ratings yet
- Red Cell Disorders GuideDocument49 pagesRed Cell Disorders GuideGeraldine AgpesNo ratings yet
- Estandarizacion de Muestra de Medula OseaDocument16 pagesEstandarizacion de Muestra de Medula OseawillmedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Red Cell Defects FinalDocument28 pagesLecture 5 Red Cell Defects FinalwillmedNo ratings yet
- Membrane The Molecular Basis of Disorders of The Red Cell: J. Clin. PatholDocument5 pagesMembrane The Molecular Basis of Disorders of The Red Cell: J. Clin. PatholwillmedNo ratings yet
- Estudio de Casos Xe Vs XNDocument29 pagesEstudio de Casos Xe Vs XNwillmedNo ratings yet
- Evaluacion de La Leucocitosis PDFDocument23 pagesEvaluacion de La Leucocitosis PDFwillmedNo ratings yet
- Velocidad de Sedimentacion PDFDocument8 pagesVelocidad de Sedimentacion PDFwillmedNo ratings yet
- Parametros Hematologicos SepsisDocument28 pagesParametros Hematologicos SepsiswillmedNo ratings yet
- Roussel Et Al-2012-Cytometry Part A PDFDocument10 pagesRoussel Et Al-2012-Cytometry Part A PDFwillmedNo ratings yet
- EsquistocitosDocument10 pagesEsquistocitoswillmedNo ratings yet
- EsquistocitosDocument10 pagesEsquistocitoswillmedNo ratings yet
- Organizacion Mayor de La Membrana EritrocitoDocument6 pagesOrganizacion Mayor de La Membrana EritrocitowillmedNo ratings yet
- XN 2000Document20 pagesXN 2000willmedNo ratings yet
- 497.full Evaluacion Del Celldyn 4000Document9 pages497.full Evaluacion Del Celldyn 4000willmedNo ratings yet
- JApplHematol44137-8138261 223622Document8 pagesJApplHematol44137-8138261 223622willmedNo ratings yet
- Physio Chapter 11 30Document30 pagesPhysio Chapter 11 30willmedNo ratings yet
- Mec 224 Properties of Mat TheoryDocument73 pagesMec 224 Properties of Mat TheoryNoreliana Md Sharif100% (5)
- Water/Cement Ratio LawDocument16 pagesWater/Cement Ratio LawNArendra REddyNo ratings yet
- Rock Mechanics Calculations: Wood-Biot-Gassmann EquationsDocument20 pagesRock Mechanics Calculations: Wood-Biot-Gassmann EquationsHcene HcenNo ratings yet
- Submerged PumpDocument8 pagesSubmerged Pumpbramantiya100% (1)
- Gmaw STTDocument4 pagesGmaw STTAnonymous 0rt9KWmNNo ratings yet
- R&AC Assigment-cum-Turorial Questions - Unit-V - 2017Document6 pagesR&AC Assigment-cum-Turorial Questions - Unit-V - 2017sivakrishna100% (1)
- Fire Retardant Finishes ExplainedDocument26 pagesFire Retardant Finishes Explainedrahul raj100% (1)
- Baroid SOPsDocument131 pagesBaroid SOPsLeo Wijaya0% (1)
- NOV Bolt Torque ValuesDocument14 pagesNOV Bolt Torque ValuesandreyengNo ratings yet
- Mohamed Abdel-Hameed Ahmed: Curriculum VitaeDocument3 pagesMohamed Abdel-Hameed Ahmed: Curriculum VitaeHatem HusseinNo ratings yet
- Heat Trace Fundamentals: Types, Monitoring, and Control OptionsDocument9 pagesHeat Trace Fundamentals: Types, Monitoring, and Control OptionsGanesh GanyNo ratings yet
- Air Quality Guidelines For EuropeDocument288 pagesAir Quality Guidelines For EuropeAlex OliveiraNo ratings yet
- GAMSAT TopicsDocument7 pagesGAMSAT TopicsSewon KimNo ratings yet
- CC Cerritos Recrystallization LabDocument2 pagesCC Cerritos Recrystallization LabJamieNo ratings yet
- Reverse Osmosis and ElectrodeionizationDocument124 pagesReverse Osmosis and ElectrodeionizationHamza RaoNo ratings yet
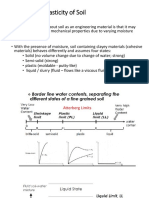
- Chapter 4 - Plasticity of SoilDocument15 pagesChapter 4 - Plasticity of SoilHussein EssaNo ratings yet
- Zam Brochure 0cef0f7dd4Document6 pagesZam Brochure 0cef0f7dd4Ivens LealNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument18 pagesChemistry Investigatory ProjectDinesh Singh Choudhary0% (1)
- Is 6396 - 2000 De-CarburisationDocument10 pagesIs 6396 - 2000 De-CarburisationDheeraj Chavan100% (1)
- Industrial Crops & ProductsDocument11 pagesIndustrial Crops & ProductsAleksandrs ArnautovsNo ratings yet
- Piping Spring HangersDocument2 pagesPiping Spring HangersyogacruiseNo ratings yet
- Uee Notes-1Document292 pagesUee Notes-1Mary Morse100% (1)
- 1 4713 4724 4742 4762Document4 pages1 4713 4724 4742 4762Ján KožičkaNo ratings yet
- Collection of Surface Wipe Samples For Analysis of Semi Volatile Organic Compounds (SVOCs)Document2 pagesCollection of Surface Wipe Samples For Analysis of Semi Volatile Organic Compounds (SVOCs)Berkeley AnalyticalNo ratings yet
- Application of Taguchi Method to Optimize Electro-Cyclone Separator ParametersDocument30 pagesApplication of Taguchi Method to Optimize Electro-Cyclone Separator ParametersAniruddha DasNo ratings yet
- Separations and Reactors Design Project Production of Allyl ChlorideDocument8 pagesSeparations and Reactors Design Project Production of Allyl ChloridefathiNo ratings yet
- USP-NF 857 Ultraviolet-Visible SpectrosDocument12 pagesUSP-NF 857 Ultraviolet-Visible SpectrosAbsheen ZamanNo ratings yet
- 2605 Sa 1Document3 pages2605 Sa 1vitalstyleNo ratings yet
- Pressure Relief ValvesDocument6 pagesPressure Relief ValvesShashank Sudhakar PathakNo ratings yet
- Aqsiq Notice No.151 (2012)Document16 pagesAqsiq Notice No.151 (2012)arbor02No ratings yet