Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Winding Down - A Visual Review of The Lending Facilities Created by The Federal Reserve During The Credit Crisis
Uploaded by
jpkoningOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Winding Down - A Visual Review of The Lending Facilities Created by The Federal Reserve During The Credit Crisis
Uploaded by
jpkoningCopyright:
Available Formats
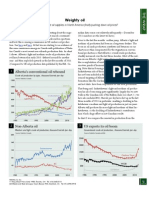
Winding Down
$1800
Financial Graph & Art
www.financialgraphart.com
John Paul Koning
A visual review of the lending facilities created by the Federal Reserve during the credit crisis
Oct 31, 2012
Source: Federal Reserve. Last data point is August 2012. Amounts are in billions of dollars
$150
9 Term Asset-Backed Secu100
rities Loan Facility (TALF)
10 ABCP MMMF Liquidity Facility (AMFL)
11 Primary Dealer
Credit Facility
12 Lending to American
International Group
1600
50
10
0 1400 $40 1200 0 $600
5 Maiden Lane LLC
6 Maiden Lane II LLC
7 Maiden Lane III LLC
8 AIA and ALICO holdings
1000
1
500 800 400 600
1 Central bank
liquidity swaps
2 Term Auction Facility
(TAF)
3 Commercial Paper Funding Facility (CPFF)
4 Discount lending
3
300
400
5
$200
2 8 4 12 6 7 9
200
11
100
0 2009 2010 2011 2012
2008
2008 09
10
11
12
2008 09
10
11
12
2008 09
10
11
12
2008 09
10
11
12
1 Central bank liquidity swaps initially expired in early 2010, but were reactivated in May 2010, and again in November 2011 to deal with credit market tightness. 2. The TAF auctioned credit to depository institutions on a collateralized basis for periods of 28 and 84-days. 3. The Federal Reserve lent to CPFF LLC so that the CPFF could purchase three month unsecured as well as asset-backed commercial paper from eligible issuers 4. Discount window lending is the traditional means by which the Federal Reserve lends to depository institutions. Usually provided on an overnight basis, terms were stretched to 30-days during the crisis. Unlike TAF, discount loans are provided not by auction, but at a penalty to the market rate 5. The Federal Reserve created and lent to Maiden Lane LLC so it could purchase certain assets of Bear Stearns so as to facilitate the purchase of Bear Stearns by JP Morgan 6. The Federal Reserve created and lent to Maiden Lane II LLC so it could purchase residential mortgage backed securities from American International Group (AIG). 7. The Federal Reserve created and lent to Maiden Lane III LLC so it could purchase
collateralized debt obligations on which AIG Financial Products had written credit default swaps. 8. The Federal Reserve received an interest in the common stock of two AIG insurance subsidiaries, American International Assurance Company Ltd. (AIA) and American Life Insurance Company (ALICO). In exchange, the outstanding loans to AIG (12) were reduced by $25 billion. 9. TALF lent for terms of up to five years, accepting as collateral asset-backed securities secured by student loans, auto loans, credit card loans, or small business loans 10 The Asset-Backed Commercial Paper Money Market Mutual Fund Liquidity Facility lent to depository institutions so they might finance purchases of commercial paper held by money market mutual funds 11 The PDCF provided overnight funds to primary dealers on a collateralized basis 12 The Federal Reserve opened a line of credit for AIG. This was in part reduced by the creations of Maiden Lane II and III, and the transfer of AIA and ALICO
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Money Fraud 101Document83 pagesMoney Fraud 101alexjamesinfo100% (3)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Federal Reserve: History of Lies, Thievery, and DeceitDocument9 pagesThe Federal Reserve: History of Lies, Thievery, and Deceitavatarz666No ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Letter of AdviceDocument3 pagesLetter of AdviceGreg Wilder100% (12)
- 07-17-12 Federal Reserve Bank Routing Numbers-May2009Document13 pages07-17-12 Federal Reserve Bank Routing Numbers-May2009thenjhomebuyer100% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- FDIC Core Deposits White PaperDocument18 pagesFDIC Core Deposits White PaperDouglas FunkNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- All Wars Are Bankers WarsDocument27 pagesAll Wars Are Bankers Warsgyrfalcon100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- 090 - IRS Levys and LiensDocument4 pages090 - IRS Levys and LiensDavid E RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Our Response Is Keyed To (1) Joint Stock Trust Act of 1873, (2) Federal Reserve System, (3) National Bank Acts, and (4) Canon Law.Document4 pagesOur Response Is Keyed To (1) Joint Stock Trust Act of 1873, (2) Federal Reserve System, (3) National Bank Acts, and (4) Canon Law.Gemini Research100% (2)
- New Ebook .How To Invest in Private Placement ProgramsDocument30 pagesNew Ebook .How To Invest in Private Placement ProgramsVicente Piqueras100% (2)
- Traders Mag GMBH August 2013Document84 pagesTraders Mag GMBH August 2013fredtag4393100% (1)
- Kaldor - 1939 - Speculation and Economic StabilityDocument28 pagesKaldor - 1939 - Speculation and Economic Stabilityjpkoning100% (1)
- Repos A Deep Dive in The Collateral PoolDocument7 pagesRepos A Deep Dive in The Collateral PoolppateNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Monetary Policy and Central BankingDocument6 pagesSyllabus - Monetary Policy and Central BankingLeanne Yumang60% (5)
- Clower - 1967 - A Reconsideration of The Microfoundations of Monetary TheoryDocument8 pagesClower - 1967 - A Reconsideration of The Microfoundations of Monetary TheoryjpkoningNo ratings yet
- Money in An Economy Without Banks - The Case of IrelandDocument10 pagesMoney in An Economy Without Banks - The Case of Irelandjpkoning100% (1)
- History of Bangladesh Bank & Central Banks Arount The WorldDocument7 pagesHistory of Bangladesh Bank & Central Banks Arount The WorldZahin SarwarNo ratings yet
- Silber - 1984 - Marketmaker Behavior in An Auction Market, An Analysis of Scalpers in Futures MarketsDocument18 pagesSilber - 1984 - Marketmaker Behavior in An Auction Market, An Analysis of Scalpers in Futures MarketsjpkoningNo ratings yet
- Lord Mansfield and The Law MerchantDocument19 pagesLord Mansfield and The Law MerchantjpkoningNo ratings yet
- Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe Monetary Policy Statement 2015Document73 pagesReserve Bank of Zimbabwe Monetary Policy Statement 2015Business Daily ZimbabweNo ratings yet
- White - 1984 - Competitive Payment Systems and The Unit of AccountDocument15 pagesWhite - 1984 - Competitive Payment Systems and The Unit of AccountjpkoningNo ratings yet
- Comment - 2011 - Revisiting The Illiquidity Discount For Private Companies, A SkepticalDocument14 pagesComment - 2011 - Revisiting The Illiquidity Discount For Private Companies, A Skepticaljpkoning100% (1)
- Wrap Sheet - Jun 17, 2011Document2 pagesWrap Sheet - Jun 17, 2011jpkoningNo ratings yet
- Alchian and Klein - 1973 - On A Correct Measure of InflationDocument20 pagesAlchian and Klein - 1973 - On A Correct Measure of Inflationjpkoning100% (1)
- Hertzel and Smith - Market Discounts and Shareholder Gains For Placing Equity PrivatelyDocument28 pagesHertzel and Smith - Market Discounts and Shareholder Gains For Placing Equity PrivatelyjpkoningNo ratings yet
- Wrap Sheet - Feb 14, 2012Document2 pagesWrap Sheet - Feb 14, 2012jpkoningNo ratings yet
- Simand and Caskey - 1994 - The Susan B. Anthony Dollar and The Theory of Coin-Note SubstitutionsDocument16 pagesSimand and Caskey - 1994 - The Susan B. Anthony Dollar and The Theory of Coin-Note SubstitutionsjpkoningNo ratings yet
- Liu - 2005 - A Liquidity Augmented Capital Asset Pricing ModelDocument41 pagesLiu - 2005 - A Liquidity Augmented Capital Asset Pricing ModeljpkoningNo ratings yet
- Lavoie - 1999 - The Credit Led Supply of Deposits and The Demand For Money, Kaldor's Reflux Mechanism As Previously Endorsed by Joan RobinsonDocument12 pagesLavoie - 1999 - The Credit Led Supply of Deposits and The Demand For Money, Kaldor's Reflux Mechanism As Previously Endorsed by Joan RobinsonjpkoningNo ratings yet
- Wrap Sheet - Oct 26, 2011Document2 pagesWrap Sheet - Oct 26, 2011jpkoningNo ratings yet
- Shiller - Fear of The Crash Caused The CrashDocument1 pageShiller - Fear of The Crash Caused The CrashjpkoningNo ratings yet
- Selgin - 1994 - On Ensuring The Acceptability of A New Fiat MoneyDocument20 pagesSelgin - 1994 - On Ensuring The Acceptability of A New Fiat MoneyjpkoningNo ratings yet
- Cowen - The New Monetary EconomcsDocument25 pagesCowen - The New Monetary EconomcsjpkoningNo ratings yet
- What Does Hyperinflation Feel Like?Document1 pageWhat Does Hyperinflation Feel Like?jpkoningNo ratings yet
- Wrap Sheet - July 12, 2012Document2 pagesWrap Sheet - July 12, 2012jpkoningNo ratings yet
- The Precipitation and Fall of Mess. Douglas, Heron and Co, Late Bankers in Air With The Causes of Their Distress and Ruin Investigated and ConsideredDocument180 pagesThe Precipitation and Fall of Mess. Douglas, Heron and Co, Late Bankers in Air With The Causes of Their Distress and Ruin Investigated and ConsideredjpkoningNo ratings yet
- Cowen and Kroszner - 1994 - Money's Marketability Premium and The Microfoundations of Keynes Theory of Money and CreditDocument12 pagesCowen and Kroszner - 1994 - Money's Marketability Premium and The Microfoundations of Keynes Theory of Money and CreditjpkoningNo ratings yet
- Monetary Explanations of The Weimar Republic's HyperinflationDocument17 pagesMonetary Explanations of The Weimar Republic's HyperinflationjpkoningNo ratings yet
- Deriving The Gold Lease RateDocument1 pageDeriving The Gold Lease Ratejpkoning100% (1)
- Pumphrey - The Exchange Equalization Account of Great Britain 1932-39Document15 pagesPumphrey - The Exchange Equalization Account of Great Britain 1932-39jpkoningNo ratings yet
- Managed Currency - The People's Bank of China Balance Sheet Since 2002Document1 pageManaged Currency - The People's Bank of China Balance Sheet Since 2002jpkoningNo ratings yet
- Wrap Sheet - Nov 23, 2009Document2 pagesWrap Sheet - Nov 23, 2009jpkoningNo ratings yet
- Bear Markets ComparisonsDocument1 pageBear Markets ComparisonsjpkoningNo ratings yet
- Chapter - IntroductionDocument6 pagesChapter - IntroductionNahidul Islam IUNo ratings yet
- MBA Intership Report On Liquidity Management Process of The City Bank Ltd-LibreDocument84 pagesMBA Intership Report On Liquidity Management Process of The City Bank Ltd-LibreGultekin Binte AzadNo ratings yet
- Finance 1Document12 pagesFinance 1Mary Ann AntenorNo ratings yet
- Questions For Articles On UnemploymentDocument2 pagesQuestions For Articles On UnemploymentMitch FallonNo ratings yet
- User's Guide - Bank Holding Co Performance RPTDocument148 pagesUser's Guide - Bank Holding Co Performance RPTRealcapitalNo ratings yet
- 1375781145binder1Document34 pages1375781145binder1CoolerAdsNo ratings yet
- Economic Implications of Brexit - Brookings InstitutionDocument6 pagesEconomic Implications of Brexit - Brookings InstitutionMaheswaran PandianNo ratings yet
- Wallstreetjournal 20171130 TheWallStreetJournalDocument36 pagesWallstreetjournal 20171130 TheWallStreetJournalsadaq84No ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document34 pagesChapter 15konosubaNo ratings yet
- Retail Bonds Trading Turnover and Trades 2015Document329 pagesRetail Bonds Trading Turnover and Trades 2015Sorken75No ratings yet
- Maximize shareholder wealth through EPS and stock priceDocument8 pagesMaximize shareholder wealth through EPS and stock pricergarbuz155No ratings yet
- 001 2013-01-09 Risk Perspectives V01 Stress Testing European EditionDocument126 pages001 2013-01-09 Risk Perspectives V01 Stress Testing European EditioncchimNo ratings yet
- Money Demand, The Equilibrium Interest Rate, and Monetary PolicyDocument29 pagesMoney Demand, The Equilibrium Interest Rate, and Monetary PolicyAbood AlissaNo ratings yet
- Oryza Rice: ExclusiveDocument8 pagesOryza Rice: ExclusiveMujahid AliNo ratings yet
- An Overview of The Financial System: ChoiceDocument32 pagesAn Overview of The Financial System: ChoiceHaris Fadžan0% (1)
- Using The Following Instructions, Perform Accuracy Check of Lecture SlideDocument3 pagesUsing The Following Instructions, Perform Accuracy Check of Lecture SlideAshish BhallaNo ratings yet
- ECB & Fed A Comparison A Comparison: International Summer ProgramDocument40 pagesECB & Fed A Comparison A Comparison: International Summer Programsabiha12No ratings yet