Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Conditions, Warranties & Innomiinate Terms by Komilla Chadha
Uploaded by
Komilla ChadhaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Conditions, Warranties & Innomiinate Terms by Komilla Chadha
Uploaded by
Komilla ChadhaCopyright:
Available Formats
Law of Obligations I: Express & Implied Terms Please note, that I have used Question & Answer: Contract
Law by Marina Hamilton 2012 to help me put this table together.
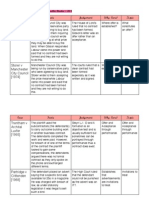
Classication Denition Condition Fundamental term determined at the time the contract is made. Innocent party can accept the repudiatory breach, treat the contract as discharged and claim. Warranty Minor term added to the root of the contract determined at the time the contract is made. Damages only. Innominate Term Determined by the consequences of the breach. Depends on seriousness of the breach as to whether remedy provided will be as for breach of contract. - Hong Kong Fir Shipping Co. Ltd v Kawasaki Ltd 1962: the loss of 20 weeks in a ships charter because of unreliable engines and staff breached a term as to being seaworthy. it was held that the effect of the breach had to be considered. The breach in this case did not deprive the whole benet of the contract and so there was no right of termination.
Effect of Breach
Cases
- Poussard v Spiers and Pond 1876: - Bettini v Gye 1876: a an actresss contract is terminated as performers contract could not she became ill and missed the be breached. As the term asking opening week which was deemed to him to coming six days before be a condition of the contract. for the rehearsals was said to be - Schuler AG v Wickman Machine Tool a warranty (he came three days Sales 1974 - where the interpretation late) of a condition would lead to - Acros Ltd v E.A. Ronaasen & unreasonable results so intention is Sons Ltd 1933- Section 15A of looked at. the Sale of Goods Act 1979, that - Lombard North Central plc v the terms regarding precise Buttterworth 1987- making a term of performance of goods are the essence to demonstrate the warranties. intention that a term be classied as a condition.
Classication Denition
Condition Fundamental term determined at the time the contract is made. - Legislation can be used to determine the classication of terms. For example, Sections 13-15 of the Sale of Goods Act 1979 imply that the terms are condition particularly where to do with goods corresponding to their description.
Warranty Minor term added to the root of the contract determined at the time the contract is made.
Innominate Term Determined by the consequences of the breach. - The effect of the breach of contract will only be known when the seriousness of the breach are known. This provides exibility and fairness but at the expense of certainity. - Flexibility has to be weighed with commercial certainity so caution must be given just incase it gives too wide an application - The Mihalis Angelos 1971
Further Notes
You might also like
- 07CASPart 4 Chart Practice IntroductionDocument3 pages07CASPart 4 Chart Practice IntroductionRajendra PrasathNo ratings yet
- Charter PartiesDocument7 pagesCharter PartiesJana KegaljNo ratings yet
- War Risk ClausesDocument4 pagesWar Risk Clausesxrobertk9073No ratings yet
- What Is A Ships Charterparty Agreement? - The ContractDocument5 pagesWhat Is A Ships Charterparty Agreement? - The ContractYugesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Liability of The Carrier - CMRDocument40 pagesThe Liability of The Carrier - CMRKwalar KingNo ratings yet
- Exclusion Clause:: 1 Maxine Footwear Co. Ltd. and Another. Appellants v. Canadian GovernmentDocument3 pagesExclusion Clause:: 1 Maxine Footwear Co. Ltd. and Another. Appellants v. Canadian GovernmentShweta AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Cos Charter PartyDocument61 pagesCos Charter PartyFroilan EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Impact On Blockage of Suez CanalDocument3 pagesImpact On Blockage of Suez CanalVishal SarkarNo ratings yet
- Off Hire Case StudiesDocument2 pagesOff Hire Case StudiesNikolay Petkov100% (1)
- LIMITATION OF LIABILITY (Print)Document7 pagesLIMITATION OF LIABILITY (Print)jacqNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document14 pagesChapter 12Krizza Ayenn MacutoNo ratings yet
- Marine Cargo Insurance GuideDocument209 pagesMarine Cargo Insurance GuideAwadhesh Yadav0% (1)
- Crew Structure On Board Merchant VesselsDocument3 pagesCrew Structure On Board Merchant VesselsArif Setyo PambudiNo ratings yet
- Cargo Insurance and Exclusion ClausesDocument21 pagesCargo Insurance and Exclusion ClausesManoj VarrierNo ratings yet
- Law Esaay Sample - Charter PartyDocument5 pagesLaw Esaay Sample - Charter PartyTommy TnpNo ratings yet
- Time CharterDocument23 pagesTime CharterAnkit MauryaNo ratings yet
- Judicial Sale ProcedureDocument12 pagesJudicial Sale ProcedureLyana SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Authority in Marine InsuranceDocument4 pagesAuthority in Marine Insuranceleslieaguilar7No ratings yet
- LO4 - 2d Insurance H&M-P&IDocument28 pagesLO4 - 2d Insurance H&M-P&ISapna DasNo ratings yet
- Voyage Charter ExplainedDocument12 pagesVoyage Charter ExplainedKwalar KingNo ratings yet
- Explaintory NotesDocument8 pagesExplaintory Notespgupta71No ratings yet
- Difference-CIF & FOBDocument4 pagesDifference-CIF & FOBVidhi ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Charter PartyDocument5 pagesCharter PartyIhtimam ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Clauses Applicable To Voyage and Time Charterparties: Practical Chartering Lecture 5 - Special Charterparty ClausesDocument7 pagesClauses Applicable To Voyage and Time Charterparties: Practical Chartering Lecture 5 - Special Charterparty ClausesMostafa Salah Eldin ZakyNo ratings yet
- Law of Carriage by Land, Sea and AirDocument35 pagesLaw of Carriage by Land, Sea and Airafifa_afrinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Shipping and LogisticsDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Shipping and LogisticsTambe Chalomine AgborNo ratings yet
- Liability for stevedore damageDocument16 pagesLiability for stevedore damagevidi68100% (1)
- Alternative Dispute ResolutionDocument24 pagesAlternative Dispute ResolutionpunithajobsNo ratings yet
- WAREHOUSE TO WAREHOUSE CLAUSESDocument5 pagesWAREHOUSE TO WAREHOUSE CLAUSEStinhcoonlineNo ratings yet
- General AverageDocument25 pagesGeneral AverageMohamed Salah El Din100% (1)
- Time Chartering eLearning CurriculumDocument4 pagesTime Chartering eLearning CurriculumshadmanNo ratings yet
- Cargo InsuranceDocument18 pagesCargo InsuranceYam ChaulagainNo ratings yet
- Charterparty CharterpartyDocument13 pagesCharterparty CharterpartyRAGIB SHAHRIAR RAFINo ratings yet
- International Cargo GuideDocument51 pagesInternational Cargo GuideBoxing GloveNo ratings yet
- Charterparty Bill of LadingDocument11 pagesCharterparty Bill of LadingTanvir HossainNo ratings yet
- LW3310 LW3311 Commercial LawDocument68 pagesLW3310 LW3311 Commercial Lawjason maoNo ratings yet
- Constractive Total LossDocument58 pagesConstractive Total LosskhannaparulNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document96 pagesLesson 2Trần Hữu Kỳ DuyênNo ratings yet
- AMWELSH 93 Charter PartyDocument8 pagesAMWELSH 93 Charter Partyahong1000% (1)
- Hague-Visby Rules - WikipediaDocument20 pagesHague-Visby Rules - WikipediaHarel Santos RosaciaNo ratings yet
- Carriage of Goods by Sea From Hague To R PDFDocument103 pagesCarriage of Goods by Sea From Hague To R PDFNidal AlsheikhNo ratings yet
- How To Handle Cargo ClaimsDocument3 pagesHow To Handle Cargo Claimspinko11No ratings yet
- Difference Between Hague Visby HamburgDocument16 pagesDifference Between Hague Visby HamburgAnil RainaNo ratings yet
- Marine Insurance Study MaterialDocument14 pagesMarine Insurance Study Materialsekkilarji100% (3)
- Unit 12Document12 pagesUnit 12Smarty AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Shipping Courses PDFDocument2 pagesShipping Courses PDFNico GoussetisNo ratings yet
- MARINE CARGO INSURANCE COVERAGEDocument72 pagesMARINE CARGO INSURANCE COVERAGEKhanh Duyen Nguyen HuynhNo ratings yet
- Introduction of CharteringDocument2 pagesIntroduction of CharteringUsuNorNo ratings yet
- Partial Loss Total Loss: Marine LossesDocument14 pagesPartial Loss Total Loss: Marine LossesseaguyinNo ratings yet
- Kenya Should Ratify the UN Convention on Contracts for International Sale of GoodsDocument18 pagesKenya Should Ratify the UN Convention on Contracts for International Sale of GoodseucaleaNo ratings yet
- Contract Carriage Liability SeaDocument15 pagesContract Carriage Liability SeaDevarajan GovindaswamyNo ratings yet
- Maritime Law Carriage GoodsDocument100 pagesMaritime Law Carriage GoodsmariaNo ratings yet
- Institute Cargo ClausesDocument20 pagesInstitute Cargo ClausesSathish Kumar JNo ratings yet
- Contrat of AffreightmentDocument29 pagesContrat of AffreightmentAnalisa Casanes PacunlaNo ratings yet
- Classification Society - Capt - Saujanya SinhaDocument3 pagesClassification Society - Capt - Saujanya SinhaJitender MalikNo ratings yet
- Introduction to P&I ClubsDocument6 pagesIntroduction to P&I ClubsSaulo GomesNo ratings yet
- Representations. The Consequences of Such Representations Being False Will Be ConsideredDocument39 pagesRepresentations. The Consequences of Such Representations Being False Will Be ConsideredkacaribuantonNo ratings yet
- Contract Law Lecture 4 - Terms of A Contract (PowerPoint)Document39 pagesContract Law Lecture 4 - Terms of A Contract (PowerPoint)Tosin YusufNo ratings yet
- Chapter Terms of ContractDocument9 pagesChapter Terms of ContractSheikh sNo ratings yet
- Law of Obligations Content & DischargeDocument47 pagesLaw of Obligations Content & DischargeAalif IbràhimNo ratings yet
- Common Law Constitutionalism & Human Rights Protection by Komilla ChadhaDocument4 pagesCommon Law Constitutionalism & Human Rights Protection by Komilla ChadhaKomilla ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Mix of Contract Cases by Komilla ChadhaDocument17 pagesMix of Contract Cases by Komilla ChadhaKomilla ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Game Theory PPT by Komilla ChadhaDocument15 pagesGame Theory PPT by Komilla ChadhaKomilla ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Theory of Production Decisions by Komilla ChadhaDocument3 pagesTheory of Production Decisions by Komilla ChadhaKomilla ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Adverse Possession Pack Komilla ChadhaDocument12 pagesAdverse Possession Pack Komilla ChadhaKomilla ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Monopolistic Comeptition by Komilla ChadhaDocument2 pagesMonopolistic Comeptition by Komilla ChadhaKomilla ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Contract Law: Breach Revision PackDocument8 pagesContract Law: Breach Revision PackKomilla ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Theory of Consumer Demand by Komilla ChadhaDocument6 pagesTheory of Consumer Demand by Komilla ChadhaKomilla ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Monopoly by Komilla ChadhaDocument3 pagesMonopoly by Komilla ChadhaKomilla ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Perfect Competition by Komilla ChadhaDocument7 pagesPerfect Competition by Komilla ChadhaKomilla ChadhaNo ratings yet
- KOMILLA CHADHA'S PROPERTY Full Mark (12) Answer Carbon Emission AS EconDocument2 pagesKOMILLA CHADHA'S PROPERTY Full Mark (12) Answer Carbon Emission AS EconKomilla ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Major Theories of Law by Komilla ChadhaDocument4 pagesMajor Theories of Law by Komilla ChadhaKomilla ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Limits To Growth and Development Pack by Komilla ChadhaDocument15 pagesLimits To Growth and Development Pack by Komilla ChadhaKomilla ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Virtue Theory Revision Pack by Komilla ChadhaDocument8 pagesVirtue Theory Revision Pack by Komilla ChadhaKomilla Chadha100% (1)
- Alcazar V AlcazarDocument2 pagesAlcazar V AlcazarsabethaNo ratings yet
- Case Digests 2 and 7Document5 pagesCase Digests 2 and 7Ren Concha100% (1)
- Class 22 SharesDocument59 pagesClass 22 SharesTimore FrancisNo ratings yet
- 11 - Pay V Vda de Palanca PDFDocument6 pages11 - Pay V Vda de Palanca PDFFrancisCarloL.FlameñoNo ratings yet
- Employment BondDocument5 pagesEmployment BondVad Mayores100% (1)
- PP Vs Dungo GR No 89420Document9 pagesPP Vs Dungo GR No 89420cashielle arellanoNo ratings yet
- 70-Philippine Pryce Assurance Corp. vs. Court of Appeals 230 SCRA 164Document5 pages70-Philippine Pryce Assurance Corp. vs. Court of Appeals 230 SCRA 164Jopan SJNo ratings yet
- GEPULLE-GARBO v. SPOUSES GARABATODocument2 pagesGEPULLE-GARBO v. SPOUSES GARABATOKaren TorresNo ratings yet
- VILLAR vs. INCIONGDocument2 pagesVILLAR vs. INCIONGBandar TingaoNo ratings yet
- GC 08-18 A2 CopsDocument1 pageGC 08-18 A2 CopsNikki MaxwellNo ratings yet
- ERMITA-MALATE HOTEL AND MOTEL OPERATORS ASSOCIATION, INC., HOTEL DEL MAR INC. vs. THE HONORABLE CITY MAYOR OF MANILADocument3 pagesERMITA-MALATE HOTEL AND MOTEL OPERATORS ASSOCIATION, INC., HOTEL DEL MAR INC. vs. THE HONORABLE CITY MAYOR OF MANILAJana GreenNo ratings yet
- A.M. No. 02-1-18-SCDocument12 pagesA.M. No. 02-1-18-SCmfv88No ratings yet
- Brian Dale Dubuc v. Tulsa County District Court, Tulsa County District Court, Oklahoma, Separately, and Clifford E. Hopper, Judge Tim Clark Tulsa County District Attorney's Office Ned Turnbull, Assistant District Attorney, Sued As: Ned Turnball Tulsa County Public Defender's Office, Separately and Sued As: Paula Alford and Ron Wallace, Assistants Tulsa Police Department, Sued As: Jeff Cash Derick Carlock Officer B. Finnly Officer McLanahan Officer D. Elliott Ron Fields, Sued as an Officer of the Tulsa Police Department Bill Ward, Sued as an Officer of the Tulsa County Sheriff's Department, 110 F.3d 73, 10th Cir. (1997)Document3 pagesBrian Dale Dubuc v. Tulsa County District Court, Tulsa County District Court, Oklahoma, Separately, and Clifford E. Hopper, Judge Tim Clark Tulsa County District Attorney's Office Ned Turnbull, Assistant District Attorney, Sued As: Ned Turnball Tulsa County Public Defender's Office, Separately and Sued As: Paula Alford and Ron Wallace, Assistants Tulsa Police Department, Sued As: Jeff Cash Derick Carlock Officer B. Finnly Officer McLanahan Officer D. Elliott Ron Fields, Sued as an Officer of the Tulsa Police Department Bill Ward, Sued as an Officer of the Tulsa County Sheriff's Department, 110 F.3d 73, 10th Cir. (1997)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Desistance AccidentDocument1 pageDesistance AccidentAnne Secretbox100% (9)
- 638 TRINIDAD Municipality of Sta Fe V Municipality of AritaoDocument2 pages638 TRINIDAD Municipality of Sta Fe V Municipality of AritaoCarissa CruzNo ratings yet
- Dispute between homeowners not an intra-corporate matterDocument6 pagesDispute between homeowners not an intra-corporate matterHannah Keziah Dela CernaNo ratings yet
- The Commercial Facial Recognition Privacy ActDocument15 pagesThe Commercial Facial Recognition Privacy ActTechCrunchNo ratings yet
- United States v. Berrill, 4th Cir. (1999)Document4 pagesUnited States v. Berrill, 4th Cir. (1999)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Moot Court & Court Management SyllabusDocument2 pagesMoot Court & Court Management SyllabusUtsav Anand MishraNo ratings yet
- Corruption of Courts Pro Se Beware!Document8 pagesCorruption of Courts Pro Se Beware!Colleen CollinsNo ratings yet
- Torts Case Digest 5Document13 pagesTorts Case Digest 5alyssamaesana100% (3)
- Insert Venue/Event Name: Artist AgreementDocument6 pagesInsert Venue/Event Name: Artist AgreementTheo AmadeusNo ratings yet
- People V Dela CernaDocument1 pagePeople V Dela CernaBGodNo ratings yet
- Court Docket 729Document13 pagesCourt Docket 729York Daily Record/Sunday NewsNo ratings yet
- DB 3 The Issues in Vehicle SearchesDocument1 pageDB 3 The Issues in Vehicle SearchesDanny ClintonNo ratings yet
- Admin Law Reviewer FINALDocument8 pagesAdmin Law Reviewer FINALRodrigoA.MapoyIIINo ratings yet
- TORT in IndiaDocument11 pagesTORT in IndiaTanisha MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Pre-Trial Brief: Legal Issues To Be Tried or ResolvedDocument3 pagesPre-Trial Brief: Legal Issues To Be Tried or ResolvedAnonymous h73ZG0No ratings yet
- Baer v. ChaseDocument19 pagesBaer v. ChaseValar JayaprakashNo ratings yet
- Foreign Court Disbarment Grounds for Reciprocal Discipline in PHDocument4 pagesForeign Court Disbarment Grounds for Reciprocal Discipline in PHAl Jay MejosNo ratings yet