Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.6 One SidedLimits&Continuity
Uploaded by
bd87glOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1.6 One SidedLimits&Continuity
Uploaded by
bd87glCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
6 One-Sided Limits & Continuity
One-sided limits: If f(x) approaches L as x tends toward c from the left (x < c), then lim f (x) = L . If f(x) approaches M as x tends toward c from the right (c < x), then x c lim f (x) = M . Continuity: A continuous function has no holes or gaps. To ensure that +
x c
f(x) does not have a hole or gap at x = c; the function must be defined at x = c, it must have a finite, two-sided limit at x = c; and lim f ( x) must equal f(c). If f(x) is not x c continuous at c, it is said to have a discontinuity there. Existence of a limit: The twosided limit lim f ( x) exists if and only if the two one-sided limits exist and are equal: x c
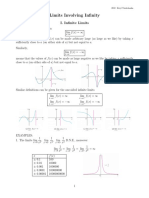
lim f ( x) = lim f ( x) = lim f ( x) . A polynomial or rational function is continuous wherever it x c x c x c+ is defined. Continuity on an interval: A function f(x) is continuous on an open interval a < x < b if it is continuous at each point x = c in that interval; it is continuous on the lim closed interval a x n if it is continuous on the open interval and x a+ f ( x) = f ( a) and lim lim Use the graphs to find the one-sided limits x 2 f ( x) and x 2+ f ( x) and lim f ( x) , if it x 2 exists: lim lim lim (1) x 2 f ( x) = (2) x 2 f ( x) = , 3. x 2 f ( x) = , lim f ( x) = lim f (x) =
x 2+ x 2
lim f ( x) = f ( b) . x b
lim f ( x) = lim f (x) =
x 2+ x 2
lim f ( x) = lim f (x) =
x 2+ x 2
Find the indicated limits, if it exists: x2 + 4 lim 4. x 2 x 2
(5) lim x 5
+
2x 1 3 x 5
(6)
x 1
lim f ( x) and lim f ( x )
x 1 +
1 if x < 1 f ( x) = x 1 f ( x) = x2 + 2x if x 1
Decide if the function is continuous at the specified value of x:
(7) f(x) = 1 x + 2x2 3x3 at x = 81
(8) f ( x) =
1 3x3 at x = 3x 6
9.
x2 1 ,x < 1 f ( x) = x+ 1 at -1 f ( x) = x2 3,x 1
List all the values of x for which the given function is not continuous: 10.
f ( x) = x2 2x + 1 x2 x 2
11.
2 3x, x 1 f ( x) = 2 x x + 3, x > 1
Homework: 1-40,43,45,51-54, Pages 81-84
You might also like
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Differentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDifferentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Final Notes For AB and BCDocument16 pagesFinal Notes For AB and BCsapabapjava2012No ratings yet
- Math 180 Midterm Review: Chapter 2: Quick Response QuestionsDocument5 pagesMath 180 Midterm Review: Chapter 2: Quick Response QuestionsMario AgudeloNo ratings yet
- Sections 1.4 Continuity: F (X) Exists But F (1) Is Not DefinedDocument9 pagesSections 1.4 Continuity: F (X) Exists But F (1) Is Not DefinedQurban HanifNo ratings yet
- Third Quarter Examination Grade 11 - Basic Calculus NAME: - DATE: - SCORE: - General RulesDocument3 pagesThird Quarter Examination Grade 11 - Basic Calculus NAME: - DATE: - SCORE: - General RulesJeo HuminisNo ratings yet
- Calculus Cheat Sheet Limits ReducedDocument1 pageCalculus Cheat Sheet Limits ReducedΜικρός ΒίκτωραςNo ratings yet
- Calculus Cheat Sheet LimitsDocument2 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet Limitstasos_rex3139No ratings yet
- School of Mathematics and Physics, The University of QueenslandDocument1 pageSchool of Mathematics and Physics, The University of QueenslandVincent LiuNo ratings yet
- Calculus I Notes On Limits and Continuity.: Limits of Piece Wise FunctionsDocument8 pagesCalculus I Notes On Limits and Continuity.: Limits of Piece Wise Functionsajaysharma19686191No ratings yet
- Check Continuity of Functions and Determine DiscontinuitiesDocument3 pagesCheck Continuity of Functions and Determine Discontinuitiesksr131No ratings yet
- Math 130 Course ReviewDocument4 pagesMath 130 Course ReviewJasonNo ratings yet
- Limits: Calculus Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesLimits: Calculus Cheat SheetPratiksh PatelNo ratings yet
- Basic CalculusDocument7 pagesBasic Calculusagliamraniel03No ratings yet
- MTPDF2 Limits and Continuity PDFDocument37 pagesMTPDF2 Limits and Continuity PDFLuis FonbuenaNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Continuity and One-Sided Limits: This Will Test The "Limits" of Your Brain!Document12 pages1.4 Continuity and One-Sided Limits: This Will Test The "Limits" of Your Brain!EDNA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Limit LawsDocument9 pagesLecture 4 Limit LawsMrDubsterNo ratings yet
- Limits Involving InfinityDocument12 pagesLimits Involving InfinityAde RahmaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics CalculusDocument11 pagesMathematics CalculusAnish NaniNo ratings yet
- LAS BASIC CALCULUS WK5 Fo StudDocument12 pagesLAS BASIC CALCULUS WK5 Fo StudMariane ManalastasNo ratings yet
- BASCALC Lesson 1.1 - Limit of A FuncitonDocument82 pagesBASCALC Lesson 1.1 - Limit of A FuncitonRaymond James OconerNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus AB 1st Semester Final Test Review GuideDocument20 pagesAP Calculus AB 1st Semester Final Test Review GuidemayanbNo ratings yet
- Math 55 LE1 Reviewer NotesDocument6 pagesMath 55 LE1 Reviewer NotesJc QuintosNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To LimitsDocument10 pagesAn Introduction To LimitsPrabath Suranaga MorawakageNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: MTHE01P03Document15 pagesMathematics: MTHE01P03Mohamed FathyNo ratings yet
- Limits Exercises With AnswersDocument17 pagesLimits Exercises With Answersabd_93100% (3)
- Continuity: X A X ADocument16 pagesContinuity: X A X Aluis calderonNo ratings yet
- Calculus Exercise LimitDocument5 pagesCalculus Exercise LimitfrancisecabanogNo ratings yet
- Calculus 1 Practice Test 1 (With Solutions) : September 21, 2011Document2 pagesCalculus 1 Practice Test 1 (With Solutions) : September 21, 2011tribalchanterNo ratings yet
- $RJG38X3Document14 pages$RJG38X3husseinmarwan589No ratings yet
- ACQUIRE Module 3 Limits and ContinuityDocument6 pagesACQUIRE Module 3 Limits and Continuitybelle.tan1105No ratings yet
- Unit 05Document16 pagesUnit 05Hamdardvir Singh BoparaiNo ratings yet
- ContinuityDocument12 pagesContinuityUɐƃnqnlUoɹNo ratings yet
- Limits of FunctionsDocument31 pagesLimits of FunctionsMustafaNo ratings yet
- Class 16th OctDocument51 pagesClass 16th OctmileknzNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Maths Important Questions Limits and DerivativesDocument9 pagesClass 11 Maths Important Questions Limits and DerivativesRoy67% (6)
- Derivative Basic-Differentiation Rules Up Rates of Change from-SBDocument26 pagesDerivative Basic-Differentiation Rules Up Rates of Change from-SBFranz DularzaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Functions, Limits and ContinuityDocument16 pagesLecture 1 Functions, Limits and ContinuityLor JanNo ratings yet
- Ma1103 4THWDocument13 pagesMa1103 4THWDanur WendaNo ratings yet
- Limit Contion DifferDocument25 pagesLimit Contion DifferSayan Kumar KhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction, Function and Limits With Derivatives: Module OutlineDocument10 pagesIntroduction, Function and Limits With Derivatives: Module OutlineErn NievaNo ratings yet
- Calculus 1 Topic 4Document9 pagesCalculus 1 Topic 4muradNo ratings yet
- (Group C) : Matcts@nus - Edu.sgDocument23 pages(Group C) : Matcts@nus - Edu.sglzyabc597No ratings yet
- 151 Exam 1 Review AU10Document3 pages151 Exam 1 Review AU10Nathan W. SerafiniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1426864972Document58 pagesLecture 1426864972Watan SahuNo ratings yet
- LAS in Basic Calculus Week 1 8 v2 1Document68 pagesLAS in Basic Calculus Week 1 8 v2 1Marione LontokNo ratings yet
- Limits Intuitive Definition To The Limit:: Calculus DifferentialDocument10 pagesLimits Intuitive Definition To The Limit:: Calculus DifferentialMarcela CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Limit of A FunctionDocument30 pagesLimit of A FunctionDaaft Prick100% (1)
- Notes For Limits and Continuity'Document5 pagesNotes For Limits and Continuity'Plămădeală MaxNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 01 - LimitDocument25 pagesSheet - 01 - LimitMankirat SinghNo ratings yet
- Limits, Exponentials, and Logarithms: MAT 1300 B Fall 2011Document24 pagesLimits, Exponentials, and Logarithms: MAT 1300 B Fall 2011vahidNo ratings yet
- 2.5.4 Limits of Trigonometric FunctionsDocument5 pages2.5.4 Limits of Trigonometric Functionssolomon okechukwuNo ratings yet
- LimitsDocument6 pagesLimitsHarry PotterNo ratings yet
- 1.3 One Sided Limits0001Document18 pages1.3 One Sided Limits0001Carmille Paz SANGUILANo ratings yet
- Limit & Continuity (New Handout)Document9 pagesLimit & Continuity (New Handout)Siti Khadijah Mohd ZainNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On DifferentiationDocument12 pagesLecture Notes On DifferentiationMd Arif Ul Islam-KowshikNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Infinite Limits: Right X Approaches 1 From The LeftDocument3 pages1.3 Infinite Limits: Right X Approaches 1 From The LeftFrancis Rey Bactol PilapilNo ratings yet
- UGCM1653 - Chapter 2 Calculus - 202001 PDFDocument30 pagesUGCM1653 - Chapter 2 Calculus - 202001 PDF木辛耳总No ratings yet
- Homework #2 Solutions Problems: Math 19: Calculus Summer 2010Document6 pagesHomework #2 Solutions Problems: Math 19: Calculus Summer 2010AnaMendezNo ratings yet
- Simulation PDFDocument37 pagesSimulation PDFWellington GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Science in MathematicsDocument9 pagesBachelor of Science in Mathematicsbd87glNo ratings yet
- TP11 ImpulseDocument11 pagesTP11 Impulsebd87glNo ratings yet
- Introduction NotesDocument14 pagesIntroduction Notesbd87glNo ratings yet
- RB429Document4 pagesRB429bd87glNo ratings yet
- PreliminariesDocument1 pagePreliminariesbd87glNo ratings yet
- Spanneberg Rose ICMI15 PropDocument8 pagesSpanneberg Rose ICMI15 Propbd87glNo ratings yet
- Year 1 and 2Document19 pagesYear 1 and 2bd87glNo ratings yet
- Analytical Geometry: DC ABDocument13 pagesAnalytical Geometry: DC ABbd87glNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Computer Simulation and Modeling Class:-BEIT (A/B)Document41 pagesQuestion Bank Computer Simulation and Modeling Class:-BEIT (A/B)bd87glNo ratings yet
- CPSC 531 Systems Modeling and Simulation: ReviewDocument50 pagesCPSC 531 Systems Modeling and Simulation: Reviewbd87glNo ratings yet
- Important Alg1 CH 6 NotesDocument15 pagesImportant Alg1 CH 6 Notesbd87glNo ratings yet
- Simulation NotesDocument24 pagesSimulation Notesbd87glNo ratings yet
- Subject Description Form: Subject Code Subject Title Credit Value Level Pre-requisite/Co-requisite/Exclusion ObjectivesDocument3 pagesSubject Description Form: Subject Code Subject Title Credit Value Level Pre-requisite/Co-requisite/Exclusion Objectivesbd87glNo ratings yet
- NMDDocument19 pagesNMDbd87glNo ratings yet
- Worksheet ContinuityDocument2 pagesWorksheet Continuitybd87glNo ratings yet
- 03 LectureDocument4 pages03 Lecturebd87glNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Matrix AlgebraDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Matrix Algebrabd87glNo ratings yet
- 201 Problem Set 1Document1 page201 Problem Set 1masyuki1979No ratings yet
- Analytical Geometry: DC ABDocument13 pagesAnalytical Geometry: DC ABbd87glNo ratings yet
- Math 113Document1 pageMath 113bd87glNo ratings yet
- 11106Document3 pages11106bd87glNo ratings yet
- Analytical Geometry: DC ABDocument13 pagesAnalytical Geometry: DC ABbd87glNo ratings yet
- 201 Problem Set 1Document1 page201 Problem Set 1masyuki1979No ratings yet
- Problem 2Document3 pagesProblem 2bd87glNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Matrix AlgebraDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Matrix Algebrabd87glNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Matrix AlgebraDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Matrix Algebrabd87glNo ratings yet
- 11106Document3 pages11106bd87glNo ratings yet
- VectorsDocument30 pagesVectorsbd87glNo ratings yet