Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Curie: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
Uploaded by
jamessonianOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Curie: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
Uploaded by
jamessonianCopyright:
Available Formats
Curie - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Page 1 of 1
Curie
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The curie (symbol Ci) is a unit of radioactivity, defined as 1 Ci = 3.71010 decays per second. This is roughly the activity of 1 gram of the radium isotope 226Ra, a substance studied by the pioneers of radiology, Marie and Pierre Curie, for whom the unit was named.[1][2] In addition to the curie activity can be measured using an SI derived unit, the becquerel (Bq), which equates to one decay per second. Therefore: 1 Ci = 3.71010 Bq = 37 GBq (100 mCi = 3.7 GBq) and 1 Bq 2.701011 Ci
A radiotherapy machine may have roughly 1000 Ci of a radioisotope such as cesium-137 or cobalt-60. This quantity of nuclear material can produce serious health effects with only a few minutes of exposure. Also, a commonly-used measure of radioactivity is the microcurie: 1 Ci = 3.7104 disintegrations per second = 2.22106 disintegrations per minute The typical human body contains roughly 0.1 Ci of naturally occurring Potassium-40.
Name
The Curie unit has been in use since c. 1910, named after Pierre Curie (1859-1906), and/or his wife, Marie Curie (1867-1934), the discoverers of Radium and Polonium. [3]
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Curie
3/12/2011
You might also like
- RadioactivityDocument12 pagesRadioactivityEn CsakNo ratings yet
- Radionuklida Di Laut: Metodologi OseanografiDocument17 pagesRadionuklida Di Laut: Metodologi OseanografiKang MaromNo ratings yet
- Radiation QuantitiesDocument1 pageRadiation QuantitiesDave DaveNo ratings yet
- 2.units and Quantities of Radiation ProtectionDocument21 pages2.units and Quantities of Radiation Protectionwajira sanjaya pereraNo ratings yet
- Igcse 72 Radiation&HalflifeDocument32 pagesIgcse 72 Radiation&HalflifeHany ElGezawy50% (2)
- D OSE S and S Ources of Rad I AT I ON ExposureDocument47 pagesD OSE S and S Ources of Rad I AT I ON ExposureAinah CredoNo ratings yet
- Radiation Quantities & UnitsDocument31 pagesRadiation Quantities & Unitsdeshpanderavi31100% (2)
- 0x Radiasi - SatuanDocument20 pages0x Radiasi - Satuanmairina yulistianiNo ratings yet
- IGCSE 72 Radiation&HalfLifeDocument32 pagesIGCSE 72 Radiation&HalfLifedmtungstenNo ratings yet
- Quantity Special UnitDocument4 pagesQuantity Special UnitMegNo ratings yet
- Common UnitsDocument3 pagesCommon UnitsAnbarasan PerumalNo ratings yet
- NanoDocument13 pagesNanovamsi NathNo ratings yet
- Unit 2.3Document42 pagesUnit 2.3Gabriel FungNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Radiation: Radiation Units: ©health Physics SocietyDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Radiation: Radiation Units: ©health Physics SocietyAhmedAmer1No ratings yet
- RT SafetyDocument1 pageRT Safetyகோகுல் இராNo ratings yet
- Radiation UnitsDocument35 pagesRadiation UnitsZaraa AshrafNo ratings yet
- Cyclotron Production of Cu by Deuteron Irradiation of ZNDocument5 pagesCyclotron Production of Cu by Deuteron Irradiation of ZNFernando Sebastian HussNo ratings yet
- Physician Intro Rad Units V4Document9 pagesPhysician Intro Rad Units V4Lalit MohanNo ratings yet
- Measuring Radiation UnitDocument4 pagesMeasuring Radiation UnitAsif ImtiazNo ratings yet
- 01 Radiation UnitsDocument41 pages01 Radiation UnitsFakhrul SyukriNo ratings yet
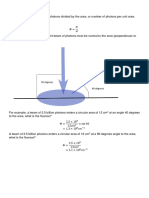
- Radiation - Quantities and Units of Ionizing RadiationDocument7 pagesRadiation - Quantities and Units of Ionizing RadiationjamessonianNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS PROJECT Half-TimeDocument7 pagesPHYSICS PROJECT Half-TimeanatoyosbenolielNo ratings yet
- University of Ghana: Answer Question 1 and Two Other QuestionsDocument2 pagesUniversity of Ghana: Answer Question 1 and Two Other Questionsanthony kingsleyNo ratings yet
- Becquerel and Sievert: Becquerel (BQ) Becquerel (BQ) Sievert (SV) Sievert (SV)Document10 pagesBecquerel and Sievert: Becquerel (BQ) Becquerel (BQ) Sievert (SV) Sievert (SV)Ahmed shabanNo ratings yet
- GEK1510 2015 Tutorial 01Document2 pagesGEK1510 2015 Tutorial 01WizardWannabeNo ratings yet
- Document 2Document2 pagesDocument 2asmaa.aboelaref7810100% (1)
- Calculations Using The First Order Rate EquationDocument4 pagesCalculations Using The First Order Rate EquationSandra LooNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint DoseDocument16 pagesPowerpoint DoselcsmfoxNo ratings yet
- Radiation Phys-Das 21Document38 pagesRadiation Phys-Das 21Amit PaulNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Chemistry and Applications of RadioactivityDocument7 pagesNuclear Chemistry and Applications of RadioactivityshikshitdheroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document4 pagesChapter 9Jerico LlovidoNo ratings yet
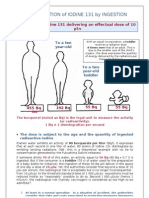
- Incorporation of Iodine 131 by Ingestion: To An Adult Toaten Year-OldDocument4 pagesIncorporation of Iodine 131 by Ingestion: To An Adult Toaten Year-Old7477aresNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Chemistry and Applications of RadioactivityDocument15 pagesNuclear Chemistry and Applications of RadioactivityAnusha KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Elements of Radiobiology and Radioprotection: Dr. A. Iftime, Dr. E. KatonaDocument12 pagesElements of Radiobiology and Radioprotection: Dr. A. Iftime, Dr. E. KatonaAlexandra StoikNo ratings yet
- Radiopharmaceutical NotesDocument6 pagesRadiopharmaceutical NotesARUN NTNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document8 pagesChapter 1fadilaNo ratings yet
- Rad (Unit) : Health Effects Material Effects Dose Examples History Radiation-Related Quantities See Also ReferencesDocument4 pagesRad (Unit) : Health Effects Material Effects Dose Examples History Radiation-Related Quantities See Also ReferencesLeandro BatistaNo ratings yet
- Sample Problems BDocument8 pagesSample Problems Bapi-308717184No ratings yet
- Efectos BiológicosDocument14 pagesEfectos BiológicosSari BustillosNo ratings yet
- Technical Tip: Irradiation Glossary of TermsDocument2 pagesTechnical Tip: Irradiation Glossary of TermsRakeshNo ratings yet
- Midterm 1 Additional Practice ProblemsDocument5 pagesMidterm 1 Additional Practice ProblemsKrage and JohnNo ratings yet
- Exercise Sheet - 5Document2 pagesExercise Sheet - 5Cristina MariaNo ratings yet
- Terminology For Service EngineersDocument24 pagesTerminology For Service EngineersOsmel HernandezNo ratings yet
- Radiation Safety Test-Aramco (Sample Q&a) 2 PDFDocument22 pagesRadiation Safety Test-Aramco (Sample Q&a) 2 PDFnidharshan69% (13)
- CT Radiation Dose and Image Quality: J. Thomas Payne, PHDTDocument10 pagesCT Radiation Dose and Image Quality: J. Thomas Payne, PHDTradiologi rsudNo ratings yet
- MSC Medical Physics Medical Imaging Exam 1Document9 pagesMSC Medical Physics Medical Imaging Exam 1Andy JohnstoneNo ratings yet
- Units and Quantities in Radiation ProtectionDocument35 pagesUnits and Quantities in Radiation ProtectionAlvin Garcia PalancaNo ratings yet
- 5 Activity and Half-Life: 5.1 The Law of Radioactive DecayDocument8 pages5 Activity and Half-Life: 5.1 The Law of Radioactive DecayNeill Zyrus DonNo ratings yet
- Industrial Radiography Health Physics ReviewDocument31 pagesIndustrial Radiography Health Physics ReviewHoang Diep PhanNo ratings yet
- Radiation Protection. DosimetryDocument6 pagesRadiation Protection. DosimetryCentral Asian StudiesNo ratings yet
- Dr. Rita Zahara, SP - OkDocument68 pagesDr. Rita Zahara, SP - OkRamadani NazarNo ratings yet
- 1 - Nuclear Chemistry PDFDocument51 pages1 - Nuclear Chemistry PDFSangga Buana Komara100% (1)
- HUGGINS Geometrical OpticsDocument61 pagesHUGGINS Geometrical Opticst6wtdpbg92No ratings yet
- 2023 - Tutorial - Radiation Measurement and Units - AnsDocument4 pages2023 - Tutorial - Radiation Measurement and Units - AnsmaddisonaturnerNo ratings yet
- Units of Radioactivity Measurements: Best AnswerDocument1 pageUnits of Radioactivity Measurements: Best AnswerSimi ChNo ratings yet
- Rad Safety Syllab For Radioactive MaterialsDocument25 pagesRad Safety Syllab For Radioactive MaterialsChad StrattonNo ratings yet
- Physics-Form One-Term 1 - MSDocument5 pagesPhysics-Form One-Term 1 - MSexan14431No ratings yet
- Mark Scheme Trial PHYSICS 2013 Sem 3Document6 pagesMark Scheme Trial PHYSICS 2013 Sem 3Zuraini ArshadNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - Early 20th Century MapDocument1 pageSouth East Europe History - Early 20th Century MapjamessonianNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - Early 14th Century MapDocument1 pageSouth East Europe History - Early 14th Century MapjamessonianNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - Early 12th Century MapDocument1 pageSouth East Europe History - Early 12th Century MapjamessonianNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - Early 14th Century MapDocument1 pageSouth East Europe History - Early 14th Century MapjamessonianNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - Early 13th Century MapDocument1 pageSouth East Europe History - Early 13th Century MapjamessonianNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - Early 11th Century MapDocument1 pageSouth East Europe History - Early 11th Century MapjamessonianNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - Early 15th Century MapDocument1 pageSouth East Europe History - Early 15th Century MapjamessonianNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - Early 13th Century MapDocument1 pageSouth East Europe History - Early 13th Century MapjamessonianNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - Early 12th Century MapDocument1 pageSouth East Europe History - Early 12th Century MapjamessonianNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - Early 19th Century MapDocument1 pageSouth East Europe History - Early 19th Century MapjamessonianNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - Early 9th Century MapDocument1 pageSouth East Europe History - Early 9th Century MapjamessonianNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - 6500 BC MapDocument2 pagesSouth East Europe History - 6500 BC MapjamessonianNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - Early 7th Century MapDocument1 pageSouth East Europe History - Early 7th Century MapjamessonianNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - Early 5th Century MapDocument1 pageSouth East Europe History - Early 5th Century MapjamessonianNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - 40000 BC MapDocument1 pageSouth East Europe History - 40000 BC MapjamessonianNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - Early 10th Century MapDocument1 pageSouth East Europe History - Early 10th Century MapjamessonianNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - Early 11th Century MapDocument1 pageSouth East Europe History - Early 11th Century MapjamessonianNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - 25000 BC MapDocument1 pageSouth East Europe History - 25000 BC MapjamessonianNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - Ealry 1st Century MapDocument1 pageSouth East Europe History - Ealry 1st Century MapjamessonianNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - 5500 BC MapDocument1 pageSouth East Europe History - 5500 BC MapjamessonianNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - 6000 BC MapDocument2 pagesSouth East Europe History - 6000 BC MapjamessonianNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - 10000 BC MapDocument1 pageSouth East Europe History - 10000 BC MapjamessonianNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - 5000 BC MapDocument1 pageSouth East Europe History - 5000 BC MapjamessonianNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - 5000 BC MapDocument1 pageSouth East Europe History - 5000 BC MapjamessonianNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - 4000 BC MapDocument2 pagesSouth East Europe History - 4000 BC MapjamessonianNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - 4500 BC MapDocument2 pagesSouth East Europe History - 4500 BC MapjamessonianNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - 1800 BC MapDocument1 pageSouth East Europe History - 1800 BC MapjamessonianNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - 3000 BC MapDocument1 pageSouth East Europe History - 3000 BC MapjamessonianNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - 2500 BC MapDocument1 pageSouth East Europe History - 2500 BC MapjamessonianNo ratings yet
- South East Europe History - 3500 BC MapDocument1 pageSouth East Europe History - 3500 BC MapjamessonianNo ratings yet