Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Immunization Schedule, Japan Vaccination Japon
Uploaded by
BouissacCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Immunization Schedule, Japan Vaccination Japon
Uploaded by
BouissacCopyright:
Available Formats
ver. 2005.
02
IDSC
IDSC
Infectious Disease
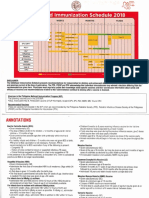
Immunization Schedule, Japan 2005 (Jan.-Mar.)
Surveillance C e n t e r
0 3 6 9 (yr)
(mo) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 60〜 65〜
Polio (OPV)
OPV: oral poliovirus
DTaP: diphtheria and tetanus toxoids
DTaP
Immunization Law
DT and acellular pertussis vaccine
DTaP/DT
Category I *1
DT: diphtheria and tetanus toxoids
BCG: bacille Calmette-Guérin
PPD: purified protein derivative
Measles
Rubella
Japanese
encephalitis
Category II
*2
annually 1dose
Influenza
*3
Tuberculosis BCG
Prevention
Law PPD (-) ve
Influenza annually, 2 doses 1-4 weeks apart annually, 1 or 2 doses 1-4 weeks apart
Varicella
Vaccination
(Chickenpox)
Voluntary
Mumps
3 times total (twice at interval of 4 weeks; the third 20-24 weeks later)
Hepatitis B
*4
Hepatitis A 3 times total (twice at interval of 2-4 weeks; the third 24 weeks later)
shot age regularly vaccinated age vaccination is regulated age vaccinated program of prevention of mother-to-child infection
*1 Category I : The objective is to protect the public health. Immunization is strongly *4 Newborn babies from HBs antigen positive mothers should receive anti-HBs human immunoglobulin
recommended by law. (HBIG) and HB vaccine. HBIG is intramauscularly injected to the neonates within 48 hr and 2-3 months
*2 Category II: The objective is to protect the individual's health. This is available on request. after birth, followed by hepatitis B vaccine starting at the time of the second immunoglobulin injection.
*3 60-64 year-old persons who have severe disorders of the heart, kidney, respiratory organs, or The vaccine is given three times; the first two doses at one month apart and the third one in three
from the human immunodeficiency virus months after the first dose. This is covered by health insurance.
○
C Copyright 2005 IDSC All Rights Reserved.
You might also like
- Vaccination ScheduleDocument1 pageVaccination ScheduleKrishanu BharNo ratings yet
- Vaccines Are For All AgesDocument34 pagesVaccines Are For All Agesmp1a1234No ratings yet
- Immunizations What Is Immunization?Document5 pagesImmunizations What Is Immunization?Bethrice MelegritoNo ratings yet
- Indiana School Required and Recommended ImmunizationsDocument1 pageIndiana School Required and Recommended ImmunizationsMesutNo ratings yet
- Childhood immunization schedule overviewDocument3 pagesChildhood immunization schedule overviewNiranjan HegdeNo ratings yet
- EPI Teaching DemoDocument32 pagesEPI Teaching DemoRommel G. Santiago100% (2)
- VaccineDocument5 pagesVaccinekhansa maryamNo ratings yet
- Vaccination EPI and Non EPIDocument19 pagesVaccination EPI and Non EPIRakhshanda khanNo ratings yet
- Green Book Chapter 11Document9 pagesGreen Book Chapter 11VergaaBellanyNo ratings yet
- The 7 Immunizable Diseases AreDocument6 pagesThe 7 Immunizable Diseases AreGladie Ann Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Expanded Program On Immunization With Pics - RHUBY ABENOJADocument8 pagesExpanded Program On Immunization With Pics - RHUBY ABENOJARHUBY ABENOJANo ratings yet
- Immunization Schedule for Infants and ChildrenDocument50 pagesImmunization Schedule for Infants and ChildrenElaine Frances IlloNo ratings yet
- Massachusetts immunization certificate guideDocument1 pageMassachusetts immunization certificate guidePrecilla Janet RosarioNo ratings yet
- Pms SummaryDocument40 pagesPms SummaryRoscelie KhoNo ratings yet
- Materi DR DR Ari Prayitno SpAK Typhoid Vaccine - Current and New PlatformDocument40 pagesMateri DR DR Ari Prayitno SpAK Typhoid Vaccine - Current and New PlatformMutiara UtiNo ratings yet
- 2022-2023 School ImmunizationsDocument1 page2022-2023 School ImmunizationsEmily FilipskiNo ratings yet
- Immunisation scheduleDocument1 pageImmunisation scheduleNitin AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Immunisation Schedule: Recommended Age Mandatory VaccinesDocument1 pageImmunisation Schedule: Recommended Age Mandatory VaccinessharanamayyappaNo ratings yet
- VacinationDocument10 pagesVacinationMostafa Ibrahim AhmedNo ratings yet
- VaccinationDocument2 pagesVaccinationOnn Swift EverbestNo ratings yet
- WHO Position Paper on Recommended Routine ImmunizationsDocument11 pagesWHO Position Paper on Recommended Routine ImmunizationsFrances Jean T. DoblasNo ratings yet
- DOH Programs Group 1 BSN 2L 1Document19 pagesDOH Programs Group 1 BSN 2L 1Jocelyn AtisNo ratings yet
- ROUTINE IMMUNIZATION SCHEDULE For INFANTSDocument7 pagesROUTINE IMMUNIZATION SCHEDULE For INFANTSJessica GlitterNo ratings yet
- EPI Vaccines and ScheduleDocument1 pageEPI Vaccines and ScheduleRukhsarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21Document8 pagesChapter 21daniphilip777No ratings yet
- Cte #2: Matrix of Communicable DiseasesDocument7 pagesCte #2: Matrix of Communicable Diseasesjoannamae molagaNo ratings yet
- Iap Guide Book On Immunization Iap Immunization Time Table 2011Document1 pageIap Guide Book On Immunization Iap Immunization Time Table 2011Gaurav GuptaNo ratings yet
- College Nursing Finals ModuleDocument15 pagesCollege Nursing Finals ModuleKeana BaganoNo ratings yet
- CHN 2Document12 pagesCHN 2Missy CookNo ratings yet
- Universal Immnunization ProgramDocument50 pagesUniversal Immnunization Programnamrata tiwariNo ratings yet
- Infant ImmunisationDocument1 pageInfant ImmunisationPaul GallagherNo ratings yet
- PEDIA Immunizations 2018Document4 pagesPEDIA Immunizations 2018Mary Christine IlangaNo ratings yet
- CHN Immunization Goals, Strategies & Vaccine ScheduleDocument28 pagesCHN Immunization Goals, Strategies & Vaccine ScheduleMARIA YVA SARITANo ratings yet
- Importance of VaccinationDocument46 pagesImportance of VaccinationTrixia Almiñe CervantesNo ratings yet
- How Long Vaccinations LastDocument1 pageHow Long Vaccinations LastJUNIE DAWN REYNONo ratings yet
- Baby Shots EngDocument2 pagesBaby Shots Engsunmo8217No ratings yet
- Philippines Vaccines ScheduleDocument3 pagesPhilippines Vaccines ScheduleKean KaiNo ratings yet
- USMLE Step 2 CK Pediatrics 2021Document1 pageUSMLE Step 2 CK Pediatrics 2021Asmaa SaraNo ratings yet
- National Immunization ProgramDocument9 pagesNational Immunization Programjuanamay30gmailcomNo ratings yet
- Peace Corps MTG 300 ImmunizationDocument199 pagesPeace Corps MTG 300 ImmunizationAccessible Journal Media: Peace Corps DocumentsNo ratings yet
- Sriphrapradang-Shantavasinkul2021 Article GravesDiseaseFollowingSARS-CoVDocument2 pagesSriphrapradang-Shantavasinkul2021 Article GravesDiseaseFollowingSARS-CoVBelajarNo ratings yet
- Sheen Ann John 1st Year PG Dept of PedodonticsDocument68 pagesSheen Ann John 1st Year PG Dept of PedodonticsSri MareesNo ratings yet
- Expanded Program On Immunization TrinalDocument2 pagesExpanded Program On Immunization Trinalagong lodgeNo ratings yet
- DR Kelvin Vaccine Schedule - Latest 2Document1 pageDR Kelvin Vaccine Schedule - Latest 2Komagal KunaisekaranNo ratings yet
- Immunization Division at Mohfw Universal Immunization Program (Uip)Document21 pagesImmunization Division at Mohfw Universal Immunization Program (Uip)Shekhar MishraNo ratings yet
- Fiolet, T., Kherabi, Y., MacDonald, C-J., & Ghosn, J. (2022) .Document21 pagesFiolet, T., Kherabi, Y., MacDonald, C-J., & Ghosn, J. (2022) .Yanreza Dwi HermawanNo ratings yet
- CHNDocument14 pagesCHNAi IrenNo ratings yet
- Adult Immunization ScheduleDocument5 pagesAdult Immunization Schedulejack01236No ratings yet
- Immunization AssignmentDocument4 pagesImmunization Assignmentgadoura95No ratings yet
- Policy Vaccination Record CardDocument2 pagesPolicy Vaccination Record CardGurpreetNo ratings yet
- Expanded Immunization Program EpiDocument22 pagesExpanded Immunization Program EpiGirome BairaNo ratings yet
- Effect of A Single Tetanus-Diphtheria Vaccine Dose On The Immunity of Elderly People in São Paulo, BrazilDocument5 pagesEffect of A Single Tetanus-Diphtheria Vaccine Dose On The Immunity of Elderly People in São Paulo, Brazilatika sgrtNo ratings yet
- Immunisation Schedule July 2018Document5 pagesImmunisation Schedule July 2018evatangNo ratings yet
- Universal Immunization ProgramDocument15 pagesUniversal Immunization Programsmruti ranjanNo ratings yet
- Parent Ver SCH 0 6yrs AafpDocument2 pagesParent Ver SCH 0 6yrs AafpcicitNo ratings yet
- COVID 19 A Year Later AutosavedDocument20 pagesCOVID 19 A Year Later AutosavedALEX CORPORALNo ratings yet
- Vaccine and ImmunizationDocument77 pagesVaccine and ImmunizationCarinaJongLeeNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Vaccines: A Review of The Safety and Efficacy of Current Clinical TrialsDocument28 pagesCOVID-19 Vaccines: A Review of The Safety and Efficacy of Current Clinical TrialsTien DangNo ratings yet
- Immunization UipDocument20 pagesImmunization Uipdevesh gargNo ratings yet
- Argumentative Essay (Yasmin Claire T. Navarro)Document2 pagesArgumentative Essay (Yasmin Claire T. Navarro)Yasmin Claire NavarroNo ratings yet
- Direct-To-Implant Breast ReconstructionDocument3 pagesDirect-To-Implant Breast ReconstructionCarlos Javier SolorzaNo ratings yet
- Xive - Dentsply Sirona ManualDocument120 pagesXive - Dentsply Sirona ManualPaula DumitracheNo ratings yet
- Donald A. Neumann-Kinesiology of The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument607 pagesDonald A. Neumann-Kinesiology of The Musculoskeletal SystemLuciano Klapisch81% (16)
- What Are The Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Coal To Generate ElectricityDocument6 pagesWhat Are The Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Coal To Generate ElectricityArchie CuyacotNo ratings yet
- CyberneticsDocument3 pagesCyberneticsTanya ChawdaNo ratings yet
- Learning Kit - Q3W3 CeslDocument10 pagesLearning Kit - Q3W3 CeslJoselle Batas MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- Eclampsia Nursing Care Plan - Altered Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesEclampsia Nursing Care Plan - Altered Tissue PerfusionCyrus De Asis84% (32)
- Warehouse Center Checklist 2Document5 pagesWarehouse Center Checklist 2Sankar ChinnathambiNo ratings yet
- Child Development A Cultural Approach 2nd Edition Arnett Solutions Manual DownloadDocument37 pagesChild Development A Cultural Approach 2nd Edition Arnett Solutions Manual DownloadMichael Pontius100% (24)
- Postnatal Assessment FormatDocument16 pagesPostnatal Assessment FormatValarmathi92% (13)
- HO#1.1 Caring For The BodyDocument7 pagesHO#1.1 Caring For The BodyGemma CanlapanNo ratings yet
- 16 Potential Key Performance Indicators For HospitalsDocument3 pages16 Potential Key Performance Indicators For HospitalsSyed Murtuza BakshiNo ratings yet
- Aiapget 2020 QPDocument29 pagesAiapget 2020 QPGanesh RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- "Classic" Technique Guide: Niti Rotary Instrumentation SystemDocument12 pages"Classic" Technique Guide: Niti Rotary Instrumentation SystemdrnikhilbobadeNo ratings yet
- ACTION PLAN FOR JUVENILE PRISONERS IN ILOILO CITYDocument22 pagesACTION PLAN FOR JUVENILE PRISONERS IN ILOILO CITYJohn Christian LopezNo ratings yet
- Nutraceutical Products in India Market ReportDocument7 pagesNutraceutical Products in India Market ReportMadan Mohan Sharan SinghNo ratings yet
- Surya Namaskar BenefitsDocument16 pagesSurya Namaskar BenefitsMillion Dollar KnowledgeNo ratings yet
- Uttarakhand Dealers Data, JanviDocument8 pagesUttarakhand Dealers Data, JanviVAISHNAVI TAYALNo ratings yet
- People Pleasing Patterns Are Learned When Needs Are Not Met PDFDocument10 pagesPeople Pleasing Patterns Are Learned When Needs Are Not Met PDFPamela RodriguezNo ratings yet
- The Perspective of Vat Concessions Regime in Tanzania PDFDocument32 pagesThe Perspective of Vat Concessions Regime in Tanzania PDFHandley Mafwenga SimbaNo ratings yet
- LESHKOWICH 2014 American EthnologistDocument20 pagesLESHKOWICH 2014 American EthnologistJuKaschuNo ratings yet
- Main - Factsheet Tacrolimus OintmentDocument4 pagesMain - Factsheet Tacrolimus OintmentSakuranbochanNo ratings yet
- Penicillin: Weird RPG Zine Issue 1 F A L L 2 0 1 9Document16 pagesPenicillin: Weird RPG Zine Issue 1 F A L L 2 0 1 9iNo ratings yet
- KOICA-Yonsei Master's Program in Infectious Disease ControlDocument28 pagesKOICA-Yonsei Master's Program in Infectious Disease ControlBIDAN KSANo ratings yet
- Modern Language Aptitude Test Ethics in Assessing Foreign Language Learning DisabilityDocument11 pagesModern Language Aptitude Test Ethics in Assessing Foreign Language Learning DisabilitypirhotmuntheNo ratings yet
- OD-PRO-HSE-032 Safety To Work at Height - Rev.01Document31 pagesOD-PRO-HSE-032 Safety To Work at Height - Rev.01aymenmoataz100% (1)
- TRS 957 (2010) - Annex 3 - WHO GMP For Pharmaceutical Products Containing Hazardous SubstancesDocument17 pagesTRS 957 (2010) - Annex 3 - WHO GMP For Pharmaceutical Products Containing Hazardous SubstancesQuang Hiếu NgôNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 WINS OrientationDocument2 pagesGrade 4 WINS OrientationChristine FranciscoNo ratings yet
- SJCTs Pilot Examination Information & InstructionsDocument6 pagesSJCTs Pilot Examination Information & InstructionsSkep100% (1)