Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bils - Paper 1v
Uploaded by
legallyindiaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bils - Paper 1v
Uploaded by
legallyindiaCopyright:
Available Formats
EXAMINATION OF ARTICLED CLERKS PAPER IV Monday, 20th May, 2013 Tome: 3 hours [1.00 p.m. to 4.00 p.m.
] Total marks 100 Notes: (1) Figures in the bracket indicate full marks. (2) Answers should be legible, precise and to the point. (3) Answers to every question should be on afresh sheet of paper. (4) No tax computations are required under any of the questions. (5) Reference to the Act means Income Tax Act, 1961. 1 2(a) Discuss provisions relating to principles underlying capital expenditure and revenue expenditure Whether the following receipts are taxable under the head Salaries stating relevant provisions of the Act: a) Any arrears of salaries paid or allowed to an employee in a previous year by or on behalf of an employer or a former employer, if not charged to income tax for any earlier previous year? b) Any annuity or pension, c) Any gratuity any advance of salary, d) Any payment received by an employee in respect of any period of leave not availed by the employee, e) the contribution made by the employer in a previous year to the account of an employee under a pension scheme referred to in section 80CCD. Discuss provisions relating to gratuity received by an employee of private sector stating relevant provisions of the Act. Discuss provisions relating to relief when salary is paid in arrears stating relevant provisions of the Act. OR Discuss provisions relating to relief to an employee who receives house rent allowance from his employer stating relevant provisions of the Act and the Income Tax Rules, 1962. Discuss provisions relating to appeal before the Supreme Court of India under the Act. Discuss powers to admit additional evidence(s) under the Act: a) before the Tribunal, and b) before the High Court * How is the income from House Property determined? * What are the deductions permissible under this head of income? * What are the amounts that are not deductible from income under this head of income? OR Discuss the types of income of other persons that are to be included in MARKS 12 5
2(b) 2(c)
4 4
3(a) 3(b) 4
6 6 10
income of an assessee. Discuss whether the following receipts are taxable and also indicate the head of income under which the same is taxable: a) Bonus shares received by an equity shareholder. b) Loan advanced by a company in which public are not substantially interested to a person holding 15% of the beneficial ownership share capital of the Company. c) Medical allowance received by an employee, the entire amount of which has been spent by him for medical treatment. d) Receipt of a cash gift of Rs.60,000 from a friend on the occasion of wedding anniversary. e) Contribution to provident fund recovered from an employee by an employer. f) Gift of a plot of land given to a lawyer by one of his clients. The lawyer has been fully compensated for his services and this gift has been given in appreciation of his personal qualities. g) A lawyer closed down his profession. Subsequently he accepted a case on the insistence of his friend, but advised his friend to pay the fee payable to him directly to a charitable trust. h) Payment from an unrecognized provident fund at the time of retirement which consists of employers contribution and interest on both contributions. OR Discuss the taxability or otherwise of the following in the hands of recipient under section 56 of the Act: a. Ms. Dhillon purchased a land from ABC Co., a partnership concern, for Rs.5,50,000. The stamp duty value of the same was Rs.10,00,000. b. Patel HUF gifted a computer to the son of karta for scoring good marks in final LLB examination. The fair market value of the computer is Rs.60,000. c. Mr. Manmohan received 50 shares of XYZ Ltd. from his friend as a gift on the occasion of his birthday. The fair market value of these 50 shares on that date was Rs.300 per share. He had also received jewellery worth Rs.37,000 (fair market value) from his niece on the same day. d. Sharad, a member of his fathers HUF, transferred a house property to the HUF without consideration. The stamp duty value of this house property is Rs.12,00,000. e. Kamalakant HUF received Rs.1 lakh in cash from nephew of Kamalkant (i.e. son of Kamalkants sister). Kamalakant is the karta of the HUF. Write short notes on (any four): a) Tax planning v. tax avoidance. b) Rectification of mistake.
20
7.
8.
c) Dividend Distribution Tax. d) Agricultural income. e) Slump sale. f) Liability of directors of a private limited company in liquidation. g) Residence in India. Explain in brief: a) Under what circumstances certain transfers are regarded as void under section 281 of the Act. b) What are the exceptions to the said provisions? c) What are the safeguards to be adopted to avoid tax liability? Answer any three with reasons: 1) In A.Y. 2007-08, the assessee sold her residential property and from the sale proceeds, purchased residential property and bonds. The property and the bonds were purchased in the joint names of herself and her husband. Is the assessee entitled to the full benefit under Section 54 & 54 EC of the Act or 50% of the claim for direction? Advise the assessee 2) The assessee was an exporter and was eligible for deduction u/s. 10A. Due to diminution in rupee value, the assessee gained a higher sum in rupee value while earning the export income. The assessee claimed the deduction of the whole of the export profit u/s. 10A including the gains on account of fluctuation in rate of foreign exchange. The Assessing Officer disallowed the claim in respect of the gains on account of rate of foreign exchange. Please advise the assessee 3) Assessee was carrying on the business of conducting and managing a restaurant. Under an agreement, assessee had granted a license and permission to J to conduct and manage the restaurant business. Dispute arose between the assessee and J, which resulted in the filing of a suit before the City Civil Court, in which consent terms were arrived at and a decree was passed by consent. As per the consent decree, the assessee made payment to J which included settlement charges of Rs. 5,50,750/-. The assessee had also incurred legal expenditure of Rs.1,65,500/- in that respect. The assessee claimed both these amounts as deduction as revenue expenditure. The Assessing Officer disallowed the claim. Please advise the assessee 4) The assessee is in the business of manufacturing telecommunication and power cables. For the A.Y. 2001-02, the assessee claimed deduction of the software expenditure as revenue expenditure. The Assessing Officer disallowed the claim, holding it to be capital expenditure. Please advise the assessee.
10
15
You might also like
- Paper I PPDocument3 pagesPaper I PPlegallyindiaNo ratings yet
- Paper - Ii, CorporateDocument8 pagesPaper - Ii, CorporatelegallyindiaNo ratings yet
- Paper V MCLDocument3 pagesPaper V MCLlegallyindiaNo ratings yet
- Examination of Articled Clerks Paper II: Page - 1Document3 pagesExamination of Articled Clerks Paper II: Page - 1legallyindia100% (1)
- Paper III ConveyanceDocument4 pagesPaper III ConveyancelegallyindiaNo ratings yet
- Paper V - May 2013Document4 pagesPaper V - May 2013legallyindia0% (1)
- IBPS SO Previous Paper - Law Officer 2013Document11 pagesIBPS SO Previous Paper - Law Officer 2013ichchhit srivastavaNo ratings yet
- Important Questions From CS Exam From Company Law Part-I Dec 2015Document25 pagesImportant Questions From CS Exam From Company Law Part-I Dec 2015shivani jindal100% (1)
- One LinerDocument80 pagesOne LinerHarsh PrakashNo ratings yet
- Case LawsDocument32 pagesCase Lawssaurabh tomarNo ratings yet
- Taxability of GiftDocument9 pagesTaxability of GiftGaurav BeniwalNo ratings yet
- The JK Government Employees (Conduct) Rules, 1971 PDFDocument34 pagesThe JK Government Employees (Conduct) Rules, 1971 PDFAbdur Raouf100% (1)
- 34 - Appeal To CITDocument9 pages34 - Appeal To CITsanjay panjwaniNo ratings yet
- Arrangement of Section in Income Tax Act 1961Document8 pagesArrangement of Section in Income Tax Act 1961Jitendra VernekarNo ratings yet
- Set-Off and Carry ForwardDocument3 pagesSet-Off and Carry ForwardAnu KNo ratings yet
- .. STDocs Tender TND 095158 181863Document28 pages.. STDocs Tender TND 095158 181863Abhijor KoliNo ratings yet
- Drafting & Pleading: (Question Bank)Document49 pagesDrafting & Pleading: (Question Bank)Gaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- The Suits Valuation ActDocument4 pagesThe Suits Valuation ActShabnam BarshaNo ratings yet
- @CACell Inter Income Tax Important Sections List Nov22Document8 pages@CACell Inter Income Tax Important Sections List Nov22Srushti AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Adjournment Proceedings Under CPCDocument3 pagesAdjournment Proceedings Under CPCIrene OlomiNo ratings yet
- Ibc - Question Bank DTQ AnsDocument31 pagesIbc - Question Bank DTQ AnsShekhar PanseNo ratings yet
- Legality of Object & ConsiderationDocument26 pagesLegality of Object & Considerationjjmaini13100% (1)
- L16 ProspectusDocument9 pagesL16 ProspectusSagar MurtyNo ratings yet
- Moot PropositionDocument3 pagesMoot PropositionAbhinavParashar100% (1)
- Syllabus For PS Group BDocument6 pagesSyllabus For PS Group Brakesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Name of The Co.Document89 pagesName of The Co.gaurav100% (1)
- Model Agreement Provided Under The Maharashtra Ownership of Flats Act (Mofa)Document10 pagesModel Agreement Provided Under The Maharashtra Ownership of Flats Act (Mofa)vidya adsule100% (1)
- Code OF Civil Procedure II: First Appeals & Powers AND Duties OF Appellate CourtDocument58 pagesCode OF Civil Procedure II: First Appeals & Powers AND Duties OF Appellate CourtDaniyal SirajNo ratings yet
- Drafting Previous Year Question PaperDocument8 pagesDrafting Previous Year Question PaperRVNo ratings yet
- DPC MCQDocument11 pagesDPC MCQElated TarantulaNo ratings yet
- 36 - A (P)Document16 pages36 - A (P)Mohan NuthalapatiNo ratings yet
- Stamp Act OdishaDocument19 pagesStamp Act OdishaRamesan CkNo ratings yet
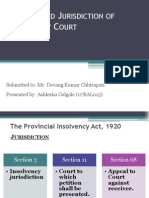
- Insolvency PetitionDocument7 pagesInsolvency PetitionAshlesha GalgaleNo ratings yet
- CLCG ReportDocument5 pagesCLCG ReportHARSHIT KUMAR GUPTA 1923334No ratings yet
- Employee's Pension Scheme .Document52 pagesEmployee's Pension Scheme .Sundara VeerrajuNo ratings yet
- CCD IssuingDocument4 pagesCCD Issuingvandana guptaNo ratings yet
- The Chairman, SEBI v. Shriram Mutual Fund & Anr. (2006) 5 SCC 361Document18 pagesThe Chairman, SEBI v. Shriram Mutual Fund & Anr. (2006) 5 SCC 361DEV PORUS SURNo ratings yet
- INDTEL CaseDocument4 pagesINDTEL CaseManisha SinghNo ratings yet
- DPC Q&aDocument45 pagesDPC Q&aMolika AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Indian Business LawDocument335 pagesIndian Business Lawmanishkul-No ratings yet
- Winding UpDocument16 pagesWinding Uputkarsh garg100% (1)
- Plaint Before The Senior Civil Judge or District Judge at TrivandrumDocument3 pagesPlaint Before The Senior Civil Judge or District Judge at TrivandrumMukesh TomarNo ratings yet
- Notice To CompanyDocument4 pagesNotice To CompanySanjay Jha100% (1)
- IBPS Law Officer Study Material Company Law MCQDocument31 pagesIBPS Law Officer Study Material Company Law MCQRohanPuthalathNo ratings yet
- Critical Analysis of Prakash Vs PhulvatiDocument8 pagesCritical Analysis of Prakash Vs PhulvatiSharthak MishraNo ratings yet
- Tax Law AssignmentDocument4 pagesTax Law AssignmentPtelearningworld Clayton0% (1)
- Salem Advocate Bar Association, ... Vs Union of India On 25 October, 2002Document6 pagesSalem Advocate Bar Association, ... Vs Union of India On 25 October, 2002Karthikeya KNo ratings yet
- Voluntary Disclosure Scheme of 1997Document11 pagesVoluntary Disclosure Scheme of 1997Shivam GuptaNo ratings yet
- Notes On MVAT Act For StudentsDocument23 pagesNotes On MVAT Act For StudentsDeepali SolankiNo ratings yet
- 34 Application For Setting Aside Arbitral AwardDocument4 pages34 Application For Setting Aside Arbitral AwardSwati KritiNo ratings yet
- Company Law CasesDocument6 pagesCompany Law CasesimranNo ratings yet
- 012 Kerala Stamp (Undervaluation) Rules 1968Document15 pages012 Kerala Stamp (Undervaluation) Rules 1968shiyas.vkNo ratings yet
- Piramal Healthcare Limited vs. Diasorin S.P.A.: FactsDocument5 pagesPiramal Healthcare Limited vs. Diasorin S.P.A.: FactsRameshwari RaoNo ratings yet
- Jugalkishore Saraf Vs Raw Cotton Co - LTD On 7 March, 1955Document31 pagesJugalkishore Saraf Vs Raw Cotton Co - LTD On 7 March, 1955Vivveck NayuduNo ratings yet
- Individual Insolvency in The Insolvency & Bankruptcy Code - An OverviewDocument4 pagesIndividual Insolvency in The Insolvency & Bankruptcy Code - An OverviewManvesh VatsNo ratings yet
- Life Insurance Corporation of Vs SMT - Asha Goel & Anr On 13 December, 2000 PDFDocument6 pagesLife Insurance Corporation of Vs SMT - Asha Goel & Anr On 13 December, 2000 PDFs2151986No ratings yet
- Draft Arbitration AgreementDocument4 pagesDraft Arbitration AgreementSamakshi PandeyNo ratings yet
- Case CommentaryDocument7 pagesCase CommentaryHritik KashyapNo ratings yet
- Applied Direct Taxation Objective Questions and AnswersDocument11 pagesApplied Direct Taxation Objective Questions and AnswersAbhijit HoroNo ratings yet
- Session Paper - 6 (Questions & Answers), For Overall Discussion On Principles of Taxation of CLDocument3 pagesSession Paper - 6 (Questions & Answers), For Overall Discussion On Principles of Taxation of CLProgga MehnazNo ratings yet
- List of Dubious Answers by Rajneesh SinghDocument15 pagesList of Dubious Answers by Rajneesh SinghlegallyindiaNo ratings yet
- Clat Writ AnnexuresDocument17 pagesClat Writ AnnexureslegallyindiaNo ratings yet
- Clat Merged Merit List 2015Document748 pagesClat Merged Merit List 2015legallyindia33% (3)
- Our Brand Story - Shardul Amarchand Mangaldas CoDocument2 pagesOur Brand Story - Shardul Amarchand Mangaldas ColegallyindiaNo ratings yet
- Salman Khan's Trial Court JudgmentDocument240 pagesSalman Khan's Trial Court Judgmentgulshankolte100% (2)
- Bar Council of India (BCI) Minutes On The All India Bar Exam in 2012Document38 pagesBar Council of India (BCI) Minutes On The All India Bar Exam in 2012legallyindiaNo ratings yet
- BCI Letter To Legally IndiaDocument6 pagesBCI Letter To Legally IndialegallyindiaNo ratings yet
- CLAT PetitionDocument56 pagesCLAT PetitionlegallyindiaNo ratings yet
- Jayalalitha - HC JudgementDocument919 pagesJayalalitha - HC JudgementJasmine TurnerNo ratings yet
- The Section 66A JudgmentDocument122 pagesThe Section 66A JudgmentThe Indian Express100% (1)
- Jay Sayta Writ Petition GamingDocument23 pagesJay Sayta Writ Petition Gaminglegallyindia100% (2)
- Cannabis PILDocument84 pagesCannabis PILlegallyindiaNo ratings yet
- Justice Manjunath Speech, Via The HinduDocument32 pagesJustice Manjunath Speech, Via The HindulegallyindiaNo ratings yet
- WP No. 69 of 2015 - Deepak Khosla vs. Khaitan & Co - Debar From PracticeDocument308 pagesWP No. 69 of 2015 - Deepak Khosla vs. Khaitan & Co - Debar From Practicelegallyindia100% (1)
- Teesta Setalvad SLPDocument14 pagesTeesta Setalvad SLPlegallyindiaNo ratings yet
- Gov't Counter Greenpeace / Priya PillaiDocument25 pagesGov't Counter Greenpeace / Priya Pillailegallyindia100% (1)
- Final Written Submissions in Priya Pillai (Greenpeace)Document9 pagesFinal Written Submissions in Priya Pillai (Greenpeace)legallyindiaNo ratings yet
- Khaitan Letter To Calcutta CJ Vs Deepak KhoslaDocument9 pagesKhaitan Letter To Calcutta CJ Vs Deepak KhoslalegallyindiaNo ratings yet
- Amended Bar Council of India (BCI) Certificate and Place of Practice Verification Rules 2015Document15 pagesAmended Bar Council of India (BCI) Certificate and Place of Practice Verification Rules 2015legallyindiaNo ratings yet
- Teesta Setalvad Affidavit in RejoinderDocument5 pagesTeesta Setalvad Affidavit in RejoinderlegallyindiaNo ratings yet
- BCCI Supreme Court JudgmentDocument138 pagesBCCI Supreme Court JudgmentlegallyindiaNo ratings yet
- Bombay High Court Anticipatory Bail OrderDocument7 pagesBombay High Court Anticipatory Bail OrderlegallyindiaNo ratings yet
- Deepak Khosla - Sanjeev Sachdeva OrderDocument118 pagesDeepak Khosla - Sanjeev Sachdeva OrderlegallyindiaNo ratings yet
- Anti AIB Draft PILDocument11 pagesAnti AIB Draft PILlegallyindia100% (1)
- Advanced Taxation: Certified Finance and Accounting Professional Stage ExaminationDocument5 pagesAdvanced Taxation: Certified Finance and Accounting Professional Stage ExaminationRoshan ZamirNo ratings yet
- Principles of Economics A Streamlined Approach 3rd Edition Frank Solutions ManualDocument5 pagesPrinciples of Economics A Streamlined Approach 3rd Edition Frank Solutions Manualkimviolet7ydu100% (25)
- Taxation 01Document17 pagesTaxation 01Julius Lester Abiera0% (1)
- Accounting For Income TaxationDocument8 pagesAccounting For Income Taxationangelian bagadiongNo ratings yet
- TaxDocument18 pagesTaxPatrickBeronaNo ratings yet
- Finals Barlis TaxDocument46 pagesFinals Barlis TaxRG BNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 IntaxDocument5 pagesQuiz 1 IntaxTOMAS, JACKY LOU C.No ratings yet
- Basic Terms MCQDocument40 pagesBasic Terms MCQSarvar PathanNo ratings yet
- 1702 Ghai2011Document5 pages1702 Ghai2011Janice CarridoNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis of Crown CementDocument26 pagesRatio Analysis of Crown CementMohammed Akhtab Ul Huda100% (1)
- Items of Gross Income Subject To RegularDocument2 pagesItems of Gross Income Subject To Regularace zeroNo ratings yet
- (Course Outline) ACT423 TaxationDocument2 pages(Course Outline) ACT423 TaxationSaiyan IslamNo ratings yet
- Wealth Tax Authorities NotesDocument3 pagesWealth Tax Authorities NotesSanjana PSNo ratings yet
- Taxation Direct and Indirect NMIMS AssignmentDocument6 pagesTaxation Direct and Indirect NMIMS AssignmentN. Karthik UdupaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 (AutoRecovered)Document58 pagesCHAPTER 8 (AutoRecovered)Isabel MalicdanNo ratings yet
- UP Tax ReviewerDocument467 pagesUP Tax ReviewerDeness Caoili-MarceloNo ratings yet
- Tools4free Merged PDFDocument12 pagesTools4free Merged PDFLokesh GiraseNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity 3.2Document2 pagesLearning Activity 3.2Mhekylha's AñepoNo ratings yet
- Accounting Past Paper 2Document2 pagesAccounting Past Paper 2Noshair AliNo ratings yet
- ProblemsDocument12 pagesProblemsJohn Carlo J. DominoNo ratings yet
- KPMG - Fiji COVID-19 Response Budget Newsletter1859921916929410238Document2 pagesKPMG - Fiji COVID-19 Response Budget Newsletter1859921916929410238Louchrisha HussainNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Discussion Questions (3 Points Each)Document9 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Discussion Questions (3 Points Each)cykenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Income Taxation Tabag 2019 Sol ManDocument21 pagesChapter 3 Income Taxation Tabag 2019 Sol ManFMM50% (2)
- Incotax Quiz 1Document7 pagesIncotax Quiz 1Claire RecioNo ratings yet
- Train Law Updates-Part 5Document23 pagesTrain Law Updates-Part 5Nikki Estores GonzalesNo ratings yet
- TAX - 001 - MC Questions - For PostingDocument5 pagesTAX - 001 - MC Questions - For PostingAnonymous YtNo ratings yet
- Personal Income Tax in Poland 2010Document21 pagesPersonal Income Tax in Poland 2010Agnieszka GryskaNo ratings yet
- Dhiraj ProjectDocument41 pagesDhiraj Projectdhiru4591No ratings yet
- Types of AssessmentDocument3 pagesTypes of Assessments.kowshik0018No ratings yet
- Income Tax On CorporationDocument54 pagesIncome Tax On CorporationJamielene Tan100% (1)