Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kisi - Kisi Matematika - 7.2
Uploaded by
Bambang KurniawanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Kisi - Kisi Matematika - 7.2
Uploaded by
Bambang KurniawanCopyright:
Available Formats
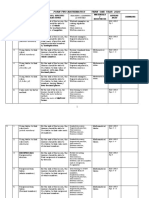
SPECIFICATION OF TEST ITEMS School Level Subject Year / Semester Question Type Number of Questions Academic Year N o.
: : : : : : Junior High School Mathematics VII / 2 Multiple Choice 40 Items 2012/2013 Basic Competence Topic Algebra 4. Using the concepts of set theory and Venn diagrams in problem solving. Set 4.1 Understanding the definition and notation of a set and its expressions. Given expressions about groups, students determine whether they are sets or not. Students determine the elements of a set. Students determine the number of the set elements. Given an expression of a set in set builder notation, students express a set by listing its elements. Students determine an empty set. Students determine a subsets of a set. Students determine the number of set that have n element. Students determine the possible universal set of a set. Given two sets which intersect each other, students determine the elements of the intersection sets. Students determine the elements of the union of two sets. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Indicator Questio n Number
Competency Standard
4.2 Understanding the concept of a subset.
4.3 Doing operations of intersection, union, difference, and complement in set.
9 10 11 7
N o.
Competency Standard
Basic Competence
Topic
Indicator Given two sets, students determine the difference of two sets. Given a set and a universal set, students determine the set complement. Students express a set in a Venn diagram. Student express two sets in a Venn diagram Students use the intersection concept in problem solving. Given a problem related to their hobbies, students use a Venn diagram to solve the problem
Questio n Number 12
4.4 Expressing a set in a Venn diagram.
13 14 15 16
4.5 Using the concept of set theory in problem solving. Geometry 5. Understanding the relationship between line and line, line and angle, and angle and angle, and determining their measures. Lines and Angles
5.1 Determining the relationship between two lines and the measure and type an angle.
5.2. Understanding the properties of angles formed by a transversal line. 5.3 Drawing an angle.
Given a cuboid, the students determine the relationship of the lines in the cuboid. Given an angle, students determine the type of the angle. Given an angle, students determine its supplementary angle Given a pair of angles, student determine the complementary angles. Given two parallel lines intersected by a transversal line, students determine the pair of equal angles. Given two parallel lines intersected by a transversal line, students determine the unknown angle. Given some angles, students determine an
17 18 19 20 21 22
23 8
N o.
Competency Standard
Basic Competence
Topic
Indicator obtuse angle. Given an angle, students determine the steps how to bisect it. Given an angle, students estimate the measure of the angle. Given the time, students determine the smaller angle that is formed between the minute hand and the hour hand. Given a triangle with its sides, students determine the type of the triangle. Given the angle measures of a triangle in algebraic expressions, students determine the type of the triangle. Given a triangle with its angles in the form of algebraic expressions, students determine the outer angle. Given some properties of a polygon, students mention the type of the polygon. Given a rhombus with all of its angles in algebraic expressions, students determine the angle in degrees. Given a trapezoid with three angles in algebraic expressions, students determine the angles in degrees. Given a real life situation related to rectangle. Students determine the area if the length, width, and perimeter are known.
Questio n Number 24 25 26
5.4 Dividing an angle. 5.5 Estimating measure. an angle
5.6 Determining the measure of an angle to the nearest unit. 6. Understanding the concept of quadrilateral and triangle, also determining their measurement. 6.1 Identifying the properties Polygo n of a triangle based on its sides, angles, or both.
27 28 29 30 31 32
6.2 Identifying the properties of a rectangle, square, trapezium, parallelogram, rhombus, and kite.
6.3 Determining the perimeter and the area of a triangle and a quadrilateral, and
33
N o.
Competency Standard
Basic Competence using them solving. in problem
Topic
Indicator Given perimeter a kite and the ratio of two sides, students find its perimeter. Given two triangles, students find the area of the two triangles. Given a shaded-figure, students find its perimeter. Given the perimeter of a square, students determine its area. Given a problem related to the area of a quadrilateral, students solve it. Given a parallelogram with the lengths of each side and height, students find the other height of the parallelogram. Given a triangle with a line inside it, students determine one altitude, bisector, median or perpendicular bisector.
Questio n Number 34 35 36 37 38 39
6.4 Drawing a triangle and its altitude, bisector, median, and perpendicular bisector.
40
10
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- 10, 3 Marks: Questions 1 EachDocument2 pages10, 3 Marks: Questions 1 EachBambang KurniawanNo ratings yet
- 2002IDDocument3 pages2002IDBambang KurniawanNo ratings yet
- 1997 Cayle y SolutionDocument8 pages1997 Cayle y SolutionBambang KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Test MTK Mid Semester 2 Class 7 2011Document6 pagesTest MTK Mid Semester 2 Class 7 2011Bambang KurniawanNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Mensuration 2D & 3DDocument45 pagesMensuration 2D & 3DHitisha agrawalNo ratings yet
- 4th Class Part A Review QuestionsDocument325 pages4th Class Part A Review QuestionsCalvin Jude Goveia86% (7)
- GENERAL-EDUCATION MATH 100-Items 2017Document303 pagesGENERAL-EDUCATION MATH 100-Items 2017Peterson R Manuel100% (1)
- 3rd Quarter Summative TestDocument4 pages3rd Quarter Summative TestLeandro BambeNo ratings yet
- Area of A Trapezium: Name: - ClassDocument2 pagesArea of A Trapezium: Name: - ClassMaryamNo ratings yet
- Topic: Grade 5 MathematicsDocument13 pagesTopic: Grade 5 MathematicssheanetienneNo ratings yet
- Properties of Trapezoid - Google SearchDocument1 pageProperties of Trapezoid - Google SearchJulia DianneNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Solutions of TrianglesDocument1 pageModule 4 - Solutions of TrianglesHayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- 2019 Math Challenge Grade 9 Division PDFDocument2 pages2019 Math Challenge Grade 9 Division PDFFe Charie DalumbarNo ratings yet
- 6-Venus Math Quarter 4 TestDocument2 pages6-Venus Math Quarter 4 TestEldon KingNo ratings yet
- Part 66 MathsDocument62 pagesPart 66 MathsmikeNo ratings yet
- G3 - M4 - C20 Quiz SolutionsDocument17 pagesG3 - M4 - C20 Quiz SolutionsewwNo ratings yet
- Jackson's GRE Math Course at Udemy Formula SheetDocument16 pagesJackson's GRE Math Course at Udemy Formula SheetShashank SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- 3c. Prove Theorems About Parallelograms Lesson PlanDocument2 pages3c. Prove Theorems About Parallelograms Lesson PlanDhingcoi Czc Allado AducalNo ratings yet
- Toughest CSAT PaperDocument38 pagesToughest CSAT Papercartoon kidsNo ratings yet
- Math (Mod 4)Document6 pagesMath (Mod 4)Erica SantosNo ratings yet
- Engg DrawingDocument38 pagesEngg DrawingKarthik CruiseNo ratings yet
- AP DSC SGT Syllabus 2024 Download PDFDocument55 pagesAP DSC SGT Syllabus 2024 Download PDFkarishma banuNo ratings yet
- Tracing Shapes BookletDocument9 pagesTracing Shapes Bookletnorshahidah5348No ratings yet
- Describing QuadrilateralsDocument1 pageDescribing QuadrilateralsbrunerteachNo ratings yet
- Math9 DLL Qtr3-Wk7 SY-22-23 Day13-16Document3 pagesMath9 DLL Qtr3-Wk7 SY-22-23 Day13-16Janice DesepidaNo ratings yet
- PARALLELOGRAM English Meaning - Cambridge DictionaryDocument1 pagePARALLELOGRAM English Meaning - Cambridge Dictionarynamlh.tgNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 TRANSFORMATIONS FINAL PLANDocument27 pagesUnit 6 TRANSFORMATIONS FINAL PLANerdawati nurdinNo ratings yet
- Geometric Reasoning Notes For Year 7Document5 pagesGeometric Reasoning Notes For Year 7api-291565828100% (1)
- Ch8 Quadrilaterals Chapter NotesDocument5 pagesCh8 Quadrilaterals Chapter NotesMohanNayakNo ratings yet
- Addition and Subtraction of PolynomialsDocument17 pagesAddition and Subtraction of PolynomialsPauline Mercado100% (1)
- Math 8th Class WorksheetDocument38 pagesMath 8th Class WorksheetAnuradha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Form 2 2020 Schemes of WorkDocument30 pagesMathematics Form 2 2020 Schemes of Worktinomuda100% (1)
- Module 1 QuadrilateralsDocument13 pagesModule 1 QuadrilateralsMaris StellahNo ratings yet
- WRM Sparx Y8Document8 pagesWRM Sparx Y8Sarah Rose MuldoonNo ratings yet