Professional Documents
Culture Documents
By Andrhiani, Chandra Puspita,: Dila Annisa Dan Virgia Maulida Xii Ipa 2
Uploaded by
rinandityo2508Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
By Andrhiani, Chandra Puspita,: Dila Annisa Dan Virgia Maulida Xii Ipa 2
Uploaded by
rinandityo2508Copyright:
Available Formats
By Andrhiani, Chandra Puspita, Dila Annisa dan Virgia Maulida XII IPA 2
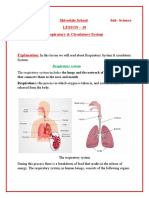
Respiration is the act of breathing: inhaling (inspiration) - taking in oxygen. exhaling (expiration) - giving off carbon dioxide.
Internal or cellular respiration is the process by which glucose or other small molecules are oxidised to produce energy: this requires oxygen and generates carbon dioxide. The body tissues need the oxygen and have to get rid of the carbon dioxide, so the blood carried throughout the body exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide with the body's tissues. Internal respirtaion is basically the exchange of gasses between the blood in the capillaries and the body's cells.
Which is the processes by which external air is drawn into the body in order to supply the lungs with oxygen, and (used) air is expelled from the lungs in order to remove carbon dioxide from to body. (The processes of internal respiration concern the exchange of gases in the lungs with those in the tissues and is described on the next page).
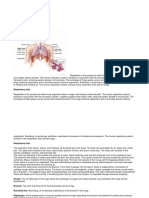
The respiratory system is made up of the organs involved in the interchanges of gases, and consists of the: nose pharynx larynx trachea bronchi lungs
our lungs contain almost 1500 miles of airways and over 300 million alveoli. Every minute you breathe in 13 pints of air. Plants are our partners in breathing. We breathe in air, use the oxygen in it, and release carbon dioxide. Plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen. People tend to get more colds in the winter because we're indoors more often and in close proximity to other people. When people sneeze, cough and even breathe -- germs go flying!
Thank you!
You might also like
- Lec 17 Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesLec 17 Circulatory SystemEnmuskNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System PDFDocument25 pagesThe Respiratory System PDFbilly sauraNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Anatomy of Respiratory Organs and Their FunctionsDocument6 pagesRespiratory System: Anatomy of Respiratory Organs and Their FunctionsRishabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Class 7 RespirationDocument5 pagesClass 7 RespirationGopi SNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: (A Written Report)Document16 pagesRespiratory System: (A Written Report)hellofrom theothersideNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17Document10 pagesChapter 17Yash Singh 11th BNo ratings yet
- Respiration NotesDocument7 pagesRespiration NotesKrishna SharmaNo ratings yet
- WWW Studyrankers Com 2017 07 Notes of CH 6 Life Process Part II Class 10th HTMLDocument15 pagesWWW Studyrankers Com 2017 07 Notes of CH 6 Life Process Part II Class 10th HTMLbaapmatsikha5No ratings yet
- Respiratory System in Human BeingsDocument11 pagesRespiratory System in Human BeingsSarada KasyapNo ratings yet
- Chapter II - Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesChapter II - Respiratory SystemIndranil SinhaNo ratings yet
- Respiration Is A Chemical Reaction That Happens in All Living CellsDocument3 pagesRespiration Is A Chemical Reaction That Happens in All Living CellsKani KurmanbekovaNo ratings yet
- RespiratorychempowerpointDocument10 pagesRespiratorychempowerpointapi-252255196No ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument10 pagesBreathing and Exchange of GasesAnonymous 9uu04elNo ratings yet
- A New BookDocument8 pagesA New Bookapi-327183872No ratings yet
- Human Respiratory SystemDocument15 pagesHuman Respiratory Systempraneeth satishNo ratings yet
- B. Inggris Kel 1Document9 pagesB. Inggris Kel 1davina mandaNo ratings yet
- Respiration & BreathingDocument18 pagesRespiration & BreathingKristal CampbellNo ratings yet
- Gr. 9 Science LM (AG)Document33 pagesGr. 9 Science LM (AG)Aizalonica GalangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 BioDocument18 pagesChapter 11 BioRylee LNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 NotesDocument12 pagesChapter 1 NotesLim Zhi EnNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheets Grade 9 Science (Biology) First QuarterDocument18 pagesLearning Activity Sheets Grade 9 Science (Biology) First QuarterAngel88% (8)
- Chapter 1 Part B - Respiration, Breathing and Circulation NotesDocument15 pagesChapter 1 Part B - Respiration, Breathing and Circulation NotesHailey CaruanaNo ratings yet
- 1r3ntvbfve - Ipa Kelas 8 Bab 9Document19 pages1r3ntvbfve - Ipa Kelas 8 Bab 9aulyamaltha.2008No ratings yet
- Adenosine Triphosphate (Document2 pagesAdenosine Triphosphate (Anime Player ccNo ratings yet
- CH 6 E - Notes RespirationDocument5 pagesCH 6 E - Notes RespirationRajvir tradaNo ratings yet
- Group No. 4Document7 pagesGroup No. 4Prince Jezzeille BonaoNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument28 pagesThe Respiratory SystemRoland Jacques AlconisNo ratings yet
- Sistem RespirasiDocument26 pagesSistem RespirasiAnnida LegiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesRespiratory SystemjoimaciascorreaNo ratings yet
- Science Week 1 (Bil)Document6 pagesScience Week 1 (Bil)shashaNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument1 pageDocumentHannah CastroNo ratings yet
- Respiratory & Circulatory SystemDocument12 pagesRespiratory & Circulatory SystemYaSHVaRDHaN DaGaNo ratings yet
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Respiratory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Respiratory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesThe Respiratory SystemChikuta ShingaliliNo ratings yet
- Chapter10. Class 10th (Page7)Document7 pagesChapter10. Class 10th (Page7)Abdus samiNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Inspiration (Inhalation)Document2 pagesRespiration: Inspiration (Inhalation)Zunaira NoreenNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologymalindaNo ratings yet
- Life Process RespirationDocument51 pagesLife Process RespirationJatin Kalra 10 DNo ratings yet
- MLP HLP Class VII Respiration in OrganismsDocument4 pagesMLP HLP Class VII Respiration in OrganismsDivyanshi BansalNo ratings yet
- Breathing and RespirationDocument30 pagesBreathing and Respirationhamzahazard527No ratings yet
- Circulatory and Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesCirculatory and Respiratory Systemclarisse100% (1)
- CH 11 Gas Exchange in HumansDocument4 pagesCH 11 Gas Exchange in HumansPranitha RaviNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System of Frog: External RespirationDocument3 pagesRespiratory System of Frog: External RespirationShaira CogollodoNo ratings yet
- Health Respiratory System - PPT Group1Document19 pagesHealth Respiratory System - PPT Group1NinaRicci RetritaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Respiratory System1Document2 pagesLesson 1 Respiratory System1Glaisa CudiaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument31 pagesRespiratory SystemMark Jhosua Austria GalinatoNo ratings yet
- The Human Respiratory System LeasonDocument1 pageThe Human Respiratory System Leasonjk6019006No ratings yet
- ScienceDocument3 pagesScienceVaughn Siegfried FuertezNo ratings yet
- The Human Breathing SystemDocument5 pagesThe Human Breathing SystemHarry Cianne Luther Sayon100% (1)
- Resprn in Humns-KDBDocument52 pagesResprn in Humns-KDBKiranNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory System Aniket DasDocument11 pagesHuman Respiratory System Aniket DasChep KepNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesRespiratory Systemgamalie.r.violettaNo ratings yet
- Gaseous Exchange in The Mammalian Lungs: by Vytautas KontrimasDocument10 pagesGaseous Exchange in The Mammalian Lungs: by Vytautas KontrimascluendoNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument15 pagesNutrition in PlantspranayaNo ratings yet
- Why Do You Need To Breathe? - To LiveDocument5 pagesWhy Do You Need To Breathe? - To LiveJuan DavisNo ratings yet
- Notes On The Respiratory SystemDocument1 pageNotes On The Respiratory SystemNessa GNo ratings yet
- Notes RespirationDocument6 pagesNotes Respirationakheel7353No ratings yet
- HSB Week 9Document18 pagesHSB Week 9EmilyNo ratings yet
- Respiration in AnimalsDocument2 pagesRespiration in AnimalsroopamsNo ratings yet
- Animal Physiology and Physiological Chemistry Paper Mzo503 Paper Mzo503Document19 pagesAnimal Physiology and Physiological Chemistry Paper Mzo503 Paper Mzo503Abhishek Singh ChandelNo ratings yet