0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views4 pagesOverview of the Human Respiratory System
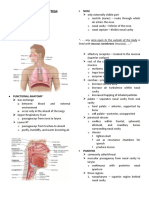
The respiratory system has three main functions: breathing, gas exchange, and cellular respiration. Breathing involves inhaling and exhaling through the respiratory tract, which filters, warms, and moistens air before it reaches the lungs. In the lungs, gas exchange occurs as oxygen passes into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide passes out. This oxygen is then used and carbon dioxide is released during cellular respiration in the body's cells. The respiratory tract includes the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs. Breathing is facilitated by the contraction and relaxation of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles.
Uploaded by
gamalie.r.violettaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views4 pagesOverview of the Human Respiratory System
The respiratory system has three main functions: breathing, gas exchange, and cellular respiration. Breathing involves inhaling and exhaling through the respiratory tract, which filters, warms, and moistens air before it reaches the lungs. In the lungs, gas exchange occurs as oxygen passes into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide passes out. This oxygen is then used and carbon dioxide is released during cellular respiration in the body's cells. The respiratory tract includes the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs. Breathing is facilitated by the contraction and relaxation of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles.
Uploaded by
gamalie.r.violettaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd