Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Control
Uploaded by
venkatsubbu0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views42 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views42 pagesBasic Control
Uploaded by
venkatsubbuCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 42
Basic Process Control
Basic Control Principles
Level
(Controlled Variable)
Overflow
Pump
Inflow
Supply
l
l
l
l
l
l
Open vs Closed Loop
! Closed loop
! Automatic control
! Open Loop
! Manual control
! Person takes the place of the controller
Feedback Control
Comparator Amplifier Process (Tank)
Error
(SP - M)
Manipulated Output
(Controlled
Variable - Level)
Disturbances
Variable
Process
Sensor
Signal
Measurement
Set Point
Controller
Feedback vs. Feedforward
! Feedback
! Control action after an error exists
! Feedforward
! Reacting to the disturbance before the
error occurs
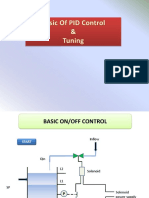
Typical ON/OFF Control System
P1
L1
L2
V
Qin
SP
Qout
1
P1 closes @ L1
P1 opens @ L2
Power Supply
Solenoid
Solenoid valve
Electrically Operated
Inflow
l
l
l
l
l
l
Typical ON/OFF Response
L2
Periodic Time
L1
SP
time
Proportional Control
Level Control of Open Tank
Qout
LT
SP
Qin
V
1
20 - 100 kPa
A/C
l
l
l
l
l
l
Simple Proportional System
Pivot
Outflow
Float
Valve
Inflow
l
l
l
l
l
l
Open Tank Control
Qin
Qout
SP
LT
20 - 100 kPa
A/O
LIC
Controller Action
Qin
Qout
SP
LT
20 - 100 kPa
A/C
LIC
l
l
l
l
l
l
Qin
Qout
SP
LT
20 - 100 kPa
A/O
LIC
l
l
l
l
l
l
Direct
Reverse
Proportional Control
+
-
ke
Setpoint
Measurement
Error
Bias
+
+
Output
m= k(SP-M) + bias
Proportional Band and Gain
Proportional Band
the input change required to
change the output 100%
PB
gain
% 100
!
input
output
gain
"
"
!
Narrow, Wide, High & Low
Wide PB Low Gain
Narrow PB High Gain
Out In
Proportional Control Response
Curve
Offset
Outflow
Loss in Volume
New mass balance
occurs here
New level
below setpoint
time
t
1
1
t
0
t
0
t
time
at setpoint
Level originally
Input/Output
Level
t
Inflow
Proportional Response with
Narrower PB
Level originally
Offset
t
t
0
time
1 Level
at setpoint
below setpoint
New level
New mass balance
occurs here
Loss in Volume
Inflow
Input/Output
0
t
1
t
t
Outflow
time
Response Versus PB, Proportional
Control Only
time
Step Disturbance
L
o
a
d
C
h
a
n
g
e
Offset
Offset
time
S
y
s
t
e
m
R
e
s
p
o
n
s
e
SP
SP
SP
"Wide" PB
"Moderate" PB
"Narrow" PB
Decay Response Curve
A
A/4
A/16
S
y
s
t
e
m
R
e
s
p
o
n
s
e
time
For You To Do
! Read pp. 89-105
! Answer Questions pp. 121-122, #1-19
Reset or Integral
Response Curve: Proportional
Control Only
S
y
s
t
e
m
R
e
s
p
o
n
s
e
SP
Step Disturbance
time
Offset
Additional Control Signal Restores
Process to Setpoint
Setpoint
Initial mass balance
Inflow
Outflow
Final mass balance
Reset Action
time
Offset
Removed
Integral Action
bias edt
TR
ke m #
$
%
&
'
(
)
# !
*
1
+
-
ke
Setpoint
Measurement
Error
Bias
+
+
Output
*
edt
TR
1
Units
! Minutes per repeat
! MPR
! The length of time that it will take the
integrator to add an amount equal to the
proportional response
! Repeats per minute
! RPM
! The number of times the proportional
response is repeated in one minute
Proportional Plus Reset, Open Loop
Response
time
e
F
a
s
t
R
e
s
e
t
N
o
r
m
a
l
R
e
s
e
t
S
low
R
e
se
t
error
ke
Proportional
Response
}
C
o
n
t
r
o
l
S
i
g
n
a
l
A problem
Output initially 50%, Gain = 2, reset = 2 minutes per repeat
A direct acting controller control is subjected to a sustained
error of 5%
What is the output after 4 minutes?
Proportional Response = ke = 2x5=10%
Integral Action- in 4 minutes the control will go through 2 repeats.
Integral action = 2 x 10 = 20%
Total output change is proportional + integral = 30%
A Couple More Things
! Reset Windup
! Instability because of lag
For You to Do
! Read over text pp. 89 110
! Answer questions pp. 121-122, 1-24
Rate or Derivative
Proportional and Derivative Open
Loop Pressure
time
I
n
p
u
t
O
u
t
p
u
t
Derivative
Derivative ceases as
error stops changing
Proportional
Action
Derivative Control
+
-
ke
Setpoint
Measurement
Error
Bias
+
+
Output
*
edt
TR
1
dt
de
TD
+
+
+
bias
dt
de
kT edt
T
ke m
D
R
# #
$
$
%
&
'
'
(
)
# !
*
1
Simple Flow Control System
l
l l
FT
FC
A/C
+
,
The open Loop Response of Proportional Plus
Derivative (PD) Action to Rapidly Changing
Error Signals
0
t
1
t
2
t
0
t
1
t
2
t
time
time
A
B
C
Rate action due to cessation of increase in e
Rate action
B -C
Rate
action
A - B
Proportional action
A - B
Proportional
action B - C
Rate action due to cessation of increase in e
Control signal at end of excursion
Control
Signal
%
P
r
o
c
e
s
s
Large System Under Proportional and
Proportional Plus Derivative Control
time
Control Signal
Setpoint
Level
Load
Disturbance
Applied
Prop. + Derivative
Prop. Only
Multiple Control Modes
! Virtually all controls have a proportional
response
! Integral and derivative are added to
improve performance
! Majority have proportional and integral
! Some, typically heat exchangers have
derivative added
Open Tank Level Control With
Valve In Inflow
Qi
A/O
l
l
l
l
l
l
Qo
SP
LIC LT
Typical Flow Control Loop
l l
FT
FIC
A/O
+
,
SP
Pressure Control Constant
Bleed
PIC PT
A/C
Feed
SP
Pressure Vessel
Pressure
Bleed
Split Ranged Feed and Bleed
Pressure Control
PIC PT
A/C
Feed
SP
Pressure Vessel Bleed
A/O
Representative Hot Bleed/Cold Service
Water Heat Exchanger
TT TC
A/C
SP
Cooled Bleed
Hot Bleed
Cold
For You To Do
! Read pp. 106-120
! Answer Questions pp. 122-123, #20-38
You might also like
- Basic Concepts of Process ControlDocument34 pagesBasic Concepts of Process ControlDozdi100% (5)
- 01 - Introduction To Process ControlDocument59 pages01 - Introduction To Process Controlafoead100% (1)
- Control and Protection of Power Plant EquipmentDocument81 pagesControl and Protection of Power Plant EquipmentFebry AryantoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note Chapter 11 PID Controller Design Tuning and Troubleshooting 2016Document61 pagesLecture Note Chapter 11 PID Controller Design Tuning and Troubleshooting 2016Rama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Process Control PDFDocument131 pagesProcess Control PDFBo Cu BinNo ratings yet
- Industrial Process Control For OperatorsDocument294 pagesIndustrial Process Control For Operatorskaezzar10100% (8)
- Introduction To Process ControlDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Process ControlaliNo ratings yet
- Process Control LoopsDocument40 pagesProcess Control LoopsjohnNo ratings yet
- BASICS of Process ControlDocument31 pagesBASICS of Process ControlMallikarjun ManjunathNo ratings yet
- Advanced Process Control SyllabusDocument52 pagesAdvanced Process Control SyllabusHaniif Prasetiawan67% (3)
- Process Control B.SDocument437 pagesProcess Control B.Sram uo100% (1)
- Introduction to Process Control Feedback and Feedforward ControlDocument30 pagesIntroduction to Process Control Feedback and Feedforward ControlRyle ArbonNo ratings yet
- Process Control Concepts: Understanding Feedback Loops, Variables, and TerminologyDocument39 pagesProcess Control Concepts: Understanding Feedback Loops, Variables, and Terminologykaezzar10100% (1)
- Each Company Has Its Own Procedure and Common Practices: Types of Loop TestDocument3 pagesEach Company Has Its Own Procedure and Common Practices: Types of Loop TestGuthayaBowsalNo ratings yet
- Rule of Thumb: Distillation and Gas AdsorptionDocument2 pagesRule of Thumb: Distillation and Gas AdsorptionChristina Joana GuzmanNo ratings yet
- PT326Document12 pagesPT326Asok Suthakar50% (2)
- Overview of Reliability Engineering: Eric MarsdenDocument34 pagesOverview of Reliability Engineering: Eric MarsdenLuis Gonzalo100% (1)
- Process Control InstrumentationDocument200 pagesProcess Control InstrumentationJaneesh VayalilakathNo ratings yet
- Auto Loops TVNLDocument144 pagesAuto Loops TVNLRajeevAgrawalNo ratings yet
- Coal to electricity process diagram and instrumentationDocument36 pagesCoal to electricity process diagram and instrumentationAshwani Dogra100% (1)
- Process Measurement Control in Practice First Edition SamplerDocument62 pagesProcess Measurement Control in Practice First Edition Samplerajrojas1359100% (1)
- Instrumentation and Control Valves 1Document31 pagesInstrumentation and Control Valves 1Ahmed ElShoraNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation For StudentsDocument157 pagesInstrumentation For StudentsBalasubramanyaNo ratings yet
- MitroDocument53 pagesMitroMiftakhul KhoirudinNo ratings yet
- MMC PPT 3.2Document21 pagesMMC PPT 3.2arbaz khanNo ratings yet
- Intro To Process ControlDocument19 pagesIntro To Process Controlenigmaticmind23No ratings yet
- Process Control Fundamentals: Revision Date: January 2020Document202 pagesProcess Control Fundamentals: Revision Date: January 2020DidiNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Process Control FundamentalsDocument111 pagesIntroduction to Process Control FundamentalsNazif Jaafar86% (7)
- Unisim Explained 2015-06-08Document196 pagesUnisim Explained 2015-06-08Yudha ArtikaNo ratings yet
- Basic Instrumentation and Process ControlDocument2 pagesBasic Instrumentation and Process ControlathariqubalNo ratings yet
- Control System Analysis & Design by Frequency ResponseDocument38 pagesControl System Analysis & Design by Frequency ResponseDozdiNo ratings yet
- The ECOSSE Control HyperCourseDocument234 pagesThe ECOSSE Control HyperCoursefri_13thNo ratings yet
- PLC Fundamentals Terminology PLC TutorialDocument23 pagesPLC Fundamentals Terminology PLC Tutorialrlnandha_2006No ratings yet
- Working Principle of Force-Balance Pneumatic PositionersDocument4 pagesWorking Principle of Force-Balance Pneumatic PositionerssandystaysNo ratings yet
- Essential Process Control For Chemical Engineers PDFDocument208 pagesEssential Process Control For Chemical Engineers PDFcgoveia9No ratings yet
- Practical Process Control Textbook 20060612Document296 pagesPractical Process Control Textbook 20060612karopa904082No ratings yet
- Process Instrumentation and Control SystemDocument78 pagesProcess Instrumentation and Control SystemMorgen Mukamwi100% (1)
- Process Control and InstrumentationDocument27 pagesProcess Control and InstrumentationchandakberaNo ratings yet
- Control (Compatibility Mode)Document59 pagesControl (Compatibility Mode)Robby KurniawanNo ratings yet
- 140358649-CCST Part10Document1 page140358649-CCST Part10CH1253No ratings yet
- PID Instr Sec 01 Introduction To Process ControlDocument38 pagesPID Instr Sec 01 Introduction To Process ControlJamal SafdarNo ratings yet
- Cascade Control PDFDocument4 pagesCascade Control PDFjhuskanovicNo ratings yet
- Control Engineering For Chemical EngineersDocument11 pagesControl Engineering For Chemical EngineersYoga WiranotoNo ratings yet
- InstrumentationDocument3 pagesInstrumentationdesignselvaNo ratings yet
- Real-World-Modeling PDFDocument12 pagesReal-World-Modeling PDFGATOMICONo ratings yet
- Why Effective Process Control is Required for Safety, Quality and ProfitDocument6 pagesWhy Effective Process Control is Required for Safety, Quality and ProfitSebastien PaulNo ratings yet
- Process Control FundamentalsDocument22 pagesProcess Control FundamentalsJude HarrisonNo ratings yet
- Basic of Instrumentation EyassDocument34 pagesBasic of Instrumentation EyassLu'ay ElyaeNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Process Control CHEAT SHEET Final Exam 5 Col 4ptDocument2 pagesChemical Engineering Process Control CHEAT SHEET Final Exam 5 Col 4ptradekrybsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Process Control SystemDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Process Control Systembsme MEfreeNo ratings yet
- Process Control 128Document60 pagesProcess Control 128Gagan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Practical Process ControlDocument325 pagesPractical Process Controlpanchogancho100% (1)
- Basic Programmable Logic Control - PLCDocument6 pagesBasic Programmable Logic Control - PLCIzan SiroonNo ratings yet
- 4-20ma Junction Box Versus Fieldbus (FF) Junction BoxDocument4 pages4-20ma Junction Box Versus Fieldbus (FF) Junction BoxsuhailfarhaanNo ratings yet
- Process Control Fundamentals for Continuous OperationsDocument21 pagesProcess Control Fundamentals for Continuous Operationsحاتم غيدان خلفNo ratings yet
- Instrument Alarm & Trip List Checklist TemplateDocument1 pageInstrument Alarm & Trip List Checklist TemplateAdivaraghan Chittambakkam0% (1)
- Pid Oil&gasDocument26 pagesPid Oil&gasRicardo ZambranaNo ratings yet
- M1 Figure 1: L LL L LLDocument23 pagesM1 Figure 1: L LL L LLthevendNo ratings yet
- BASIC ON/OFF CONTROL PID TUNINGDocument26 pagesBASIC ON/OFF CONTROL PID TUNINGNair67udayNo ratings yet
- Presentation On 3-Element Control and Surge Control SystemDocument11 pagesPresentation On 3-Element Control and Surge Control SystemriteshrishabhNo ratings yet
- RF CMOS Power Amplifier - Theory Design and Implementation (Document111 pagesRF CMOS Power Amplifier - Theory Design and Implementation (ghass81593% (14)
- Basic Instrumentation Measuring Devices and Basic Pid ControlDocument125 pagesBasic Instrumentation Measuring Devices and Basic Pid ControlCuong Nguyen ChiNo ratings yet
- الحب في زمن الكوليراDocument152 pagesالحب في زمن الكوليراghass81575% (4)
- Programming in C & C++Document121 pagesProgramming in C & C++shailesh_khandelwalNo ratings yet
- Electrical Catodic ProtectionDocument60 pagesElectrical Catodic Protectionghass815No ratings yet
- Basic Control TheoryDocument20 pagesBasic Control Theoryghass815No ratings yet
- Cathodic ProtectionDocument5 pagesCathodic ProtectionrotsinroNo ratings yet
- 7300 CV Quick Start Programming GuideDocument10 pages7300 CV Quick Start Programming Guidenitin hadkeNo ratings yet
- PRS Neoweb Load Support Technical Overview v013.01Document21 pagesPRS Neoweb Load Support Technical Overview v013.01Chowdhury PriodeepNo ratings yet
- Ficha Tecnica Batería RITAR 12V 7ah RT 1704414 PDFDocument2 pagesFicha Tecnica Batería RITAR 12V 7ah RT 1704414 PDFAzter MagolloNo ratings yet
- Printers' Marketplace 11/3/2009Document40 pagesPrinters' Marketplace 11/3/2009Christopher AllenNo ratings yet
- Continuous Regenerative (Moving Bed) CCR PlatformingDocument4 pagesContinuous Regenerative (Moving Bed) CCR PlatformingAnnissa Nur HidayatiNo ratings yet
- O MM 8060 Series Iveco MotorsDocument79 pagesO MM 8060 Series Iveco Motorsfishhunter18100% (3)
- Installation Instructions Rubber Bellows: Engineering AppliancesDocument2 pagesInstallation Instructions Rubber Bellows: Engineering Appliancessateesh chand100% (1)
- Dl8000 Preset ControllerDocument74 pagesDl8000 Preset ControllerFIRMANSYAHNo ratings yet
- Group - 6 MobileyeDocument14 pagesGroup - 6 MobileyevNo ratings yet
- Magnasoft HSSD MB - InddDocument4 pagesMagnasoft HSSD MB - InddCao TuanNo ratings yet
- Contoh Resume Terbaik 2Document2 pagesContoh Resume Terbaik 2Amin IqmalNo ratings yet
- Drilling and Mining - Unit1Document73 pagesDrilling and Mining - Unit1umesh deshmukh0% (1)
- Energy ConversionDocument16 pagesEnergy ConversionPinjala AnoopNo ratings yet
- Concrete Slump TestDocument5 pagesConcrete Slump TestVel Dhanish100% (1)
- Megane Diesel Diagrama Bosch EDC16C3 F9Q 730 2Document1 pageMegane Diesel Diagrama Bosch EDC16C3 F9Q 730 2Diego Filice100% (2)
- Hackingstem Hotwheels InstructionsDocument19 pagesHackingstem Hotwheels Instructionsapi-275968397No ratings yet
- Owner Manual 4stroke 2007 Eng st1Document80 pagesOwner Manual 4stroke 2007 Eng st1Brian ConacherNo ratings yet
- SH1 Dhi P1PCB M M01 Pid 5325Document1 pageSH1 Dhi P1PCB M M01 Pid 5325Thanh SonNo ratings yet
- Aalco Aluminium PDFDocument33 pagesAalco Aluminium PDFMihai NedeaNo ratings yet
- Mos GRPDocument53 pagesMos GRPslxanto100% (3)
- Visual Design CompositionDocument42 pagesVisual Design CompositionRey100% (1)
- 1135 PDF TocDocument4 pages1135 PDF TocAlex DicuNo ratings yet
- Features:: Advanced Protection TechnologiesDocument2 pagesFeatures:: Advanced Protection Technologiesdnps2011No ratings yet
- Himsan Catalog PDFDocument16 pagesHimsan Catalog PDFSreesanth SaruvilNo ratings yet
- Sample Project Completion ReportDocument1 pageSample Project Completion ReportAndroNo ratings yet
- NTB R9800 enGB-USDocument22 pagesNTB R9800 enGB-USEnzo Miguel Sarabia Montes100% (1)
- Oi/N Malaysia Final Examination: SessionDocument10 pagesOi/N Malaysia Final Examination: Sessionsharif100% (1)
- Jibon Kumar GhoshDocument2 pagesJibon Kumar GhoshArshad SadatNo ratings yet
- Select the Right Industrial Gearbox in 15 StepsDocument4 pagesSelect the Right Industrial Gearbox in 15 StepssanjushaNo ratings yet
- Galvanized Steel As Part of Earthing, Lightning Protection SystemDocument8 pagesGalvanized Steel As Part of Earthing, Lightning Protection SystemJanuargo100% (2)