Introduction
MKK1123 ADVANCED PROCESS CONTROL
Semester II 2011/2012
�LECTURER
Introduction
Name Faculty Room Tel E-mail : DR. RAMESH KANTHASAMY : FKKSA, UMP : A3-04 : 09-5492855 : ramesh@ump.edu.my
�SYLLABUS
Review of feedback controlled processes
Introduction
Feedback control of systems with large dead-time
or Inverse response
Control systems with multiple loops Feed forward and ratio Control Adaptive and inferential control systems
Multivariable Processes
Analysis of Multivariable Systems Design of Controllers For Multivariable Processes
3
�SYLLABUS (Cont)
Sampled-Data Control Systems
Introduction
Stability Analysis of Sampled-Data Systems
Design of Digital Compensators Model Predictive control
�Importance of Process Control
safety and reliability of a process
Introduction
Quality of the products produced by a process
Operating a process efficiently (Operational constraints) Environmental regulations Bottom Line: PC has a major impact on the profitability of a company
�Safety and Reliability
Introduction
The control system must provide safe operation
Alarms, safety constraint control, start-up and shutdown.
A control system must be able to absorb a variety of disturbances and keep the process in a good operating region:
Thunderstorms, feed composition upsets, temporary loss of utilities (e.g., steam supply), day to night variation in the ambient conditions
�Why Safety important?
Introduction
Bhopal Disaster (December 1984)
- Union Carbide factory (US based company) - 40 tons of Methyl Isocyanate (MIC) leaked - MIC boiling point 39.50C
- Water leaked into MIC storage tank
- 22000 people died and 500,000 injured in 72 hours - The refrigeration unit shut off due to coolant drained off - The gas scrubber designed to neutralize escaping MIC vapors
shut off for maintenance 3 weeks prior
- Lack of effective warning system (Alarm failed)
�Bhopal Disaster
Introduction
�Better Control Means Products with Reduced Variability
Introduction
For many cases, reduced variability products
are in high demand and have high value added Product certification procedures (e.g., ISO 9000) are used to guarantee product quality and place a large emphasis on process
control
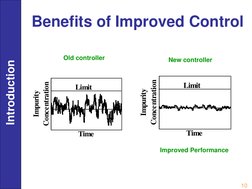
�Benefits of Improved Control
Introduction
Old controller
New controller
Impurity Concentration
Impurity Concentration
Limit
Limit
Time
Time
Improved Performance
10
�Constraint Control Example
Consider a reactor temperature control
Introduction
example for which at excessively high
temperatures the reactor will experience a temperature runaway and explode.
But the higher the temperature the greater
the product yield Therefore, better reactor temperature
control allows safe operation at a higher
reactor temperature and thus more profit
11
�Environmental Regulations
Various federal and state laws may specify
Introduction
that temperatures, concentrations of
chemicals and flow rates of the effluents from a plant be within certain limits.
PC is necessary to maintain those variables
within the limit For example the quality of the waste water
returned to a river or lake should follow
certain norms
12
�Maximizing the Profit of a Plant
Introduction
Many times involves controlling against constraints.
The closer that you are able to operate to these constraints, the more profit you can make. For example, maximizing the product production rate usually involving controlling the process against one or more process constraints.
13
�Importance of Process Control for the Chemical &Bio-Process Industries
Introduction
Improved product quality Faster and less expensive process validation Increased production rates.
14
�LEARNING RESOURCES
Reference Books: 1. Donald Coughnowr and Steven LeBlanc, Process Systems Analysis and Control, Mc Graw Hill 2010. 2. Seborg, D.E., Edgar, T.F. and Mellichamp., Process Dynamic and Control, John Wiley 2004. 3. Marlin, T.E., Process Control: Designing Processes and Control Systems for Dynamic Performance, Mc Graw Hill 2000. 4. Smith, C.A., Corripio, A.B., Principles and Practice of Automatic Process Control, John Wiley 1997. 5. Stephanopoulos, G., Chemical Process Control: An Introduction to Theory and Practice, Prentice-Hall 1984.
15
Introduction
�Elements of control system
Process Equipment together with physical or
Introduction
chemical operations that occur there Measuring instruments or sensors Thermocouples, flow meters, Gas chromatography
Transducers Temp, flow rate etc. to electric voltage
or current Controller Receives information from measuring
devices and decides what action to be taken
Final control element Implement the decision taken by the controller
16
�Control Terminology
Introduction
Controlled variable (Output variable) The process variable that we want to maintain at a particular value (set point) Manipulated variable (Input variable) Process variable that is adjusted to bring the controlled variable back to the set-point Disturbance variable (Input variable) Any process variables that can cause the controlled variable to deviate from its set point. Also called as "load" variable
�Flow Diagram for a Feedback Control Loop
Introduction
Disturbance
Setpoint
+-
Controller
c
Actuator
Process
CV
Sensor
18
�Temperature Control for a Heat Exchanger
Introduction
Steam Setpoint Product Stream TT TC
Feed
Condensate
19
�Heat Exchanger Control
Controlled variable- Outlet temperature of product stream Manipulated variable- Steam flow Actuator- Control valve on steam line Sensor- Thermocouple on product stream Disturbance- Changes in the inlet feed temperature
Introduction
20
�Control Diagram of a Typical Control Loop (Blending Process)
Introduction
Actuator System
F1 T1
F2 T2
Sensor System
Controller
TC TT
T F
�Components and Signals of a Typical Control Loop
Introduction
Actuator System
F1 T1
3-15 psig
F2 T2
Thermowell
T F
Air I/P 4-20 mA D/A Thermocouple millivolt signal
Operator Console
Tsp
DCS Control Computer Controller
A/D
4-20 mA
Transmitter
Sensor System
�Types of Control Problems
Servo Problem
Introduction
Set point changes and load remains constant. The ability to move process from one set point to a new set point (This is termed as Set Point Tracking)
Regulator Problem Load changes and set point remains constant. The ability to maintain the process variable at its desired value (set point) in spite of disturbances that might be experienced (This is termed as Disturbance Rejection)
�DIGITAL COMPUTER CONTROL
Introduction
�MULTIPLEXER
It quite often happens, in the design of large-scale digital systems, that a single line is required to carry two or more different digital
Introduction
signals. Of course, only one signal at a time can be placed on the one
line. What is required is a device that will allow us to select, at different instants, the signal we wish to place on this common line. Such a circuit is referred to as a Multiplexer. A multiplexer performs the function of selecting the input on any one of 'n' input lines and feeding this input to one output line.
�MULTIPLEXER
Multiplexers are used as one method of reducing the number of integrated circuit
Introduction
packages required by a particular circuit design. This in turn reduces the cost of the system. Assume that we have four lines, C0, C1, C2 and C3, which are to be multiplexed on a single line, Output (f). The four input lines are also known as the Data Inputs. Since there are four inputs, we will need two additional inputs to the multiplexer, known as the Select Inputs, to select which of the C inputs is to appear at the output. Lines A and B are called Select Inputs
�Sampler
Introduction
Green Line Continuous Signal
Blue Dots Discrete Signal
27
�Sampler
Sampler is a switch, which closes every T seconds and
Introduction
remains closed for an infinitesimally short period of time.
As the sampling period tends zero, the sampled representation comes closer to the continuous signal but requires an explosively large number of sampled values.
On the other hand, as the sampling period increases,
fewer sampled values are required, but the sampled representation of a continuous signal deteriorates, and the reconstruction of the original signal becomes poor or
sample.
�Introduction
Sampler
�Sampler
Introduction
t 0 ___ 0 0.632 0.865 0.950 0.982 0.993
2 3 4 5
Response of first-order system to a step of magnitude, M
�Sampling of oscillating signal
Introduction
Sampling an oscillating signal more than 2 times per cycle of oscillation; otherwise its impossible to reconstruct the original signals from its sampled values.
�Hold Element
Introduction
�First-order Hold Element
Introduction
�Comparison of Zero and First-order Hold Elements
Introduction
Slowly varying Signals
�Comparison of Zero and First-order Hold Elements
Introduction
Rapidly Changing Signals
�Analog-to-Digital Converter
Introduction
03 07 10 14 09 02 00 04
�Analog-to-Digital Converter
Resolution:
Introduction
Suppose a binary number with N bits is to represent an analog value ranging from 0 to A There are 2N possible numbers (including zero).
Resolution = A / (2N 1)
For example, consider a voltage range of 0 to 10V and 12 bit converter. The 12 bits define 4096 integer numbers, which in turn defines 4095 voltage intervals between 0 and 10. ADC used for process control allow 20,000 to 100,000 conversions per second
�Digital-to-analog converter
Digital-to-analog converter (DAC) function in the reverse manner to ADC. The 12 bits define 4096 integer numbers, which in turn defines 4095 voltage intervals between 0 and 10. Then the integer number 516 causes an analog output of (516/4095) X 10 = 1.26V
Introduction
�Time Delay or Dead-time
Let, u fluid property (e.g., temperature or composition) at point 1 fluid property at point 2
Introduction
Fluid In
Fluid Out
Point 1
Point 2
Assume that the velocity profile is flat, that is, the velocity is uniform over the cross-sectional area.
�Time Delay or Dead-time
Introduction
�Feedback control of systems with large dead-time
Introduction
�Feedforward Control
Introduction
In some cases, the major disturbance to a process is measured and utilized to adjust the manipulated variable The advantage feedforward control is that corrective action is taken for a change in a disturbance input before it affects the control parameter Feedforward control is used in conjunction with feedback control to provide multipleinput single output (MISO) control
�Feedforward Temperature Control
Introduction
�Feedforward and Feedback Temperature Control
Introduction
�Analysis of Feedforward and Feedback Temperature Control
Feedback - only must absorb the
Introduction
variations in exit temperature by feedback
action Feedforward - only handle variation in exit
temperature by measuring the warm liquid
flow into the tank Combined feedforward and feedback has best features of both controllers
�Ratio Control
Ratio control is a special type of feedforward
Introduction
control where both manipulated variable and
disturbance (load) are measured and held in a constant ratio to each other Useful when the manipulated variable scales directly with the feed rate to the process Both flow rates are measured but only one can be controlled The stream whose flow rate is under control is known as wild stream
�Ratio Control for Wastewater Neutralization
Introduction
FT
RSP
FC FT
Acid Wastewater
pHC pHT
NaOH Solution
Effluent
�Analysis of Ratio Control Example
The flow rate of base scales directly with the
Introduction
flow rate of the acidic wastewater The output of the pH controller is the ratio of NaOH flow rate to acid wastewater flow rate Here, the product of the controller output and the measured acid wastewater flow rate become the setpoint for the flow controller on the NaOH addition.
�ADAPTIVE CONTROL
Adaptive control is the one in which the controller parameters are
Introduction
adjusted automatically to compensate for changing process
conditions. control method used by a controller which must adapt to a controlled system with parameters which vary, or are initially
uncertain.
Examples: - Changes in equipment characteristics (eg. Heat exchanger fouling) - Large frequent disturbances (feed composition, fuel quality etc.) - Unusual operational status such as failure, start up, and shut down)
�ADAPTIVE CONTROL
Introduction
�Inferential Control
Inferential control is the one where the primary variables are difficult to measure or slow sampling then the fast
Introduction
sampling secondary variables are measured and using a
mathematical model (soft sensor) to infer the value of the controlled variable.
�Inferential Control
Introduction