Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Product Development: PRODUCT INTRODUCTION or Product Launch
Uploaded by
Cheenee Mariekeith Comin Vehemente0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views4 pagespaper for masteral class
Original Title
ProDUCTION MANAGEMENT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentpaper for masteral class
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views4 pagesProduct Development: PRODUCT INTRODUCTION or Product Launch
Uploaded by
Cheenee Mariekeith Comin Vehementepaper for masteral class
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Product development takes place, works or functions as under:
1. Creation of an entirely new product or upgrading an existing product by
exploring all possibilities and outcomes.
2. Innovation of a new or an existing product to deliver better and enanced
services to end!users.
". Continuous improvement of a new product or enancing an existing
product by giving preference to satisfy te demand of end!users.
#. $nancing te utility of a new product or upgrading features of an existing
product, for te personal and%or commercial use, to expand te defined goal
&ob'ective(.
Product development involves risk of investing precious time, money &capital(
and intellectual resources. )erefore, it is necessary tat it is well!planned.
* good product development elps to:
1. Create new business opportunities and bring growt.
2. +oost productivity and profitability of te entrepreneurs.
". $nance te satisfaction levels of te consumers.
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION or product launch
Product introduction is a business process through which a new product is launched,
debuted or published in the market for general users and or businesses.
For example, a software development company may introduce a new product
through a beta version before launching the complete solution. This allows the
company to gain valuable user feedback, and to fix bugs and errors before the
complete launch.
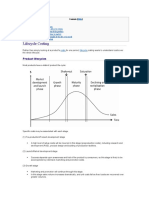
The growth stage is the period during which the product eventually and
increasingly gains acceptance among consumers, the industry, and the wider
general public. During this stage, the product or the innovation becomes accepted
in the market, and as a result sales and revenues start to increase Figure 1. Profits
begin to be generated, though the break even point is likely to remain unbreached
for a significant time--even until the next stage, depending on the cost and revenue
structures.
Features of the growth stage:
Costs reduced due to economies of scale: as production and distribution
are ramped up, economies of scale kick in and reduce the per unit costs.
Sales volume increases significantly: as the product increases in
popularity, sales volumes increase.
Profitability begins to rise: revenues begin to exceed costs, creating
profit for the company
Public awareness increases: through increased promotion, visibility
and word of mouth, public awareness grows.
Competition begins to increase with a few new players in establishing
market
ncreased competition leads to price decreases: price wars may erupt,
technology may get cheaper, or other factors can ultimately lead to falling
prices.
!"#$%#&
As the company will attempt to prolong the maturity phase as long as possible, it
will likely introduce alterations and innovations to the product to keep customers
interested and stay a step ahead of the competition.
Advances in technology and changes in consumer taste and demand may also add
to the slowing down of sales growth of the product during this phase.
Prices tend to drop in this phase due to lower costs as well as a high level of
competition, and so industrial profits will fall as well.
#he stage that lasts the longest in the product life cycle is the !aturity stage. t is at
this time that repeat business and purchases take the place of new customer buying.
he decline stage of the product life cycle is the one where the product ultimately
!dies! due to the low or negative growth rate in sales "see Figure #$.
Profitability will fall, eventually to the point where it is no longer profitable to
produce, and production will stop. %s a number of companies start to dominate the
market, it becomes increasingly difficult for the company in &uestion to maintain
its level of sales. 'onsumer tastes also change, as do new technologies which may
make the product become ultimately obsolete "as in the case of 'Ds and D(Ds,
and now )lu-*ay$.
#he PC was state'of'the'art technology in ())*. +nly technologically'advanced
individuals would buy one at the very steep price of ,(-.. /and bear in mind, ,(-.. in
())* was worth a lot more than it is today0. " large number of companies were
competing in the field. "s the market grew, businesses learned to be more efficient in
producing the PC and prices came down. #he drop in prices and improvements in
technology made PCs more attractive to other consumers. 1owever, the market
became saturated after *... and went into decline. PCs started to become obsolete as
laptops, net books, tablets, and smart phones started to enter the market, shifting the
emphasis from power to portability. #he PC is still used all over the world, but its
popularity has declined dramatically.
Line extension
A line extension is a product that incorporates a slight twist on an established brand. It utilizes the
older brands na!e and i!ager"# and is usuall" in the sa!e general product categor". $ore than
%& percent o' all new product launches each "ear are 'or line extensions that si!pl" ha(e a new
'la(or# size or nutritional content# according to Iowa )tate Uni(ersit". In the 'ood and be(erage
industr"# 'or exa!ple# !an" line extensions are si!pl" diet# organic# whole grain or gluten*'ree
(ersions o' the original brand or are si!pl" new 'la(ors.
Brand Extension
Like line extensions, brand extensions also utilize an existing brands name and imagery. What makes
them different is that they sit in a completely different product category. Companies ith ell!established
brands that ha"e solid consumer loyalty often use brand extension tactics, such as #tarbucks ith its
$%%& launch of a premium ice cream line and 'odaks foray into batteries. (n order for a brand extension
to be successful, it must be distinctly different from the parent brand, but related enough so that
consumers are not confused. Brand extensions that ere confusing for the consumer, and ultimately
failed, include B(Cs perfume and pantyhose, Colgates frozen foods and )rito!Lays lemonade drink.
*hese extensions might ha"e had a better chance of success if they had been launched under a ne
brand name, although it ould ha"e cost the manufacturer significantly more money.
benefits
While a ne brand ould re+uire a great deal of aareness ad"ertising and marketing to
de"elop recognition and consumer perception, a brand extension has aareness and
recognition built in. (n other ords, a familiar brand name instantly communicates messages to
consumers based on the existing brand promise.
, ell!planned and ell!executed brand extension can benefit from hats knon as the halo
effect herein the established brand promise and brand image of the parent brand carries o"er
to the brand extension automatically. *his positions the brand extension for greater and faster
success than an entirely ne brand.
Brand extensions can also benefit the parent brand by creating a greater sense of loyalty,
reaffirming the brand promise and consumer perceptions of the brand, and sustaining the parent
brands rele"ance in its existing category. Extensions can also help to establish a brands
position in ne categories.
-isks
a poorly executed brand extension can tarnish the parent brands image, and a brand extension
into a category that doesnt fit appropriately ith the original brand promise can confuse e"en
the most loyal consumers causing them to sitch to brands that do meet their expectations
You might also like
- Product Life CycleDocument11 pagesProduct Life CycleASHWINI SINHANo ratings yet
- Product Life CycleDocument7 pagesProduct Life CycleSujeewa LakmalNo ratings yet
- Stages of Product Life CycleDocument16 pagesStages of Product Life Cycleanon_952No ratings yet
- New Product Development: Objectives and Overview of The TopicDocument5 pagesNew Product Development: Objectives and Overview of The TopicJohn CarpenterNo ratings yet
- Caca&Caillo - Developing Products For The Foreign Market Entry StrategiesDocument18 pagesCaca&Caillo - Developing Products For The Foreign Market Entry StrategiesDulce Amor Margallo ValdescoNo ratings yet
- Stages of The Life CycleDocument6 pagesStages of The Life CycleanusuyambaNo ratings yet
- Product Life CycleDocument9 pagesProduct Life CycleShah JeetNo ratings yet
- Marketing MixDocument27 pagesMarketing MixArjunsingh HajeriNo ratings yet
- Unit3 Ce (AS)Document29 pagesUnit3 Ce (AS)punte77No ratings yet
- Brand ExtensionsDocument8 pagesBrand ExtensionsSiddheshDanaitNo ratings yet
- Product Category LifecyclesDocument13 pagesProduct Category LifecyclesAdam Andrew OngNo ratings yet
- EssayDocument14 pagesEssaypersephoniseNo ratings yet
- Basic Marketing A Strategic Marketing Planning Approach 19Th Edition Perreault Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument32 pagesBasic Marketing A Strategic Marketing Planning Approach 19Th Edition Perreault Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFJoshuaJohnsonwxog100% (12)
- Product Line 2020Document7 pagesProduct Line 2020Da GwapingsNo ratings yet
- Embarrassment of Product Choices 1: How to Consume DifferentlyFrom EverandEmbarrassment of Product Choices 1: How to Consume DifferentlyNo ratings yet
- Lean Solutions: How Companies and Customers Can Create Value and Wealth TogetherFrom EverandLean Solutions: How Companies and Customers Can Create Value and Wealth TogetherRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (16)
- Product An IntroductionDocument9 pagesProduct An IntroductionSonia JoseNo ratings yet
- Int MK - Unit 5Document30 pagesInt MK - Unit 5Pol PalesNo ratings yet
- Week 7.2 Product Life CycleDocument8 pagesWeek 7.2 Product Life CycleAmos JacobNo ratings yet
- Challenges in New Product DevelopmentDocument16 pagesChallenges in New Product DevelopmentFazal Mahmood100% (2)
- Product Life Cycle Stages ExplainedDocument4 pagesProduct Life Cycle Stages ExplainedAyushi ChopraNo ratings yet
- The Product Life CycleDocument6 pagesThe Product Life CycleDuc Dam Hoang CongNo ratings yet
- Understand the Product Life Cycle Stages with ExamplesDocument5 pagesUnderstand the Product Life Cycle Stages with ExamplesVishal SoniNo ratings yet
- Notes - P & BDocument18 pagesNotes - P & BJiten BendleNo ratings yet
- Que. 1. Explain Product Life Cycle. ? AnsDocument9 pagesQue. 1. Explain Product Life Cycle. ? Ansviga1880No ratings yet
- Introduction To Product Life CycleDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Product Life CyclepranvirkaurNo ratings yet
- 【产品生命周期+定价策略】) product life cycleDocument5 pages【产品生命周期+定价策略】) product life cycleanakinNo ratings yet
- How to Outsmart Your Competitor Without a Price War: A Book Which You Do NOT Want Your Competitors to Get It First.From EverandHow to Outsmart Your Competitor Without a Price War: A Book Which You Do NOT Want Your Competitors to Get It First.No ratings yet
- ProductDocument6 pagesProduct11shikha44No ratings yet
- Industry Life CycleDocument3 pagesIndustry Life CycleJesus RedeemerNo ratings yet
- Product Launch 123: Launch a New Product or Service in 3 Proven StepsFrom EverandProduct Launch 123: Launch a New Product or Service in 3 Proven StepsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Product Modification Apple I4Document82 pagesProduct Modification Apple I4Gaurav Ssuvarna100% (2)
- New Product Development Essentials: Hands-on Help for Small Manufacturers and Smart Technical People: No Nonsence Manuals, #2From EverandNew Product Development Essentials: Hands-on Help for Small Manufacturers and Smart Technical People: No Nonsence Manuals, #2Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Brand ExtensionDocument28 pagesBrand ExtensionsureshkachhawaNo ratings yet
- Using Firms Familiar WithDocument3 pagesUsing Firms Familiar WithAbhiNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle CostingDocument3 pagesProduct Life Cycle CostingCarbon Nano TubeNo ratings yet
- Project 2Document6 pagesProject 2Tanmay ChhikaraNo ratings yet
- Dissertation On Product Life CycleDocument5 pagesDissertation On Product Life CycleCustomThesisPapersOmaha100% (1)
- The Stages of The Product Life CycleDocument7 pagesThe Stages of The Product Life CycleJorge Yeshayahu Gonzales-LaraNo ratings yet
- Why Do Firms Delete BrandsDocument4 pagesWhy Do Firms Delete BrandsDipanjan DashNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle StagesDocument4 pagesProduct Life Cycle StagesShruti TopraniNo ratings yet
- Building Brand Equity: The Importance, Examples & How to Measure ItFrom EverandBuilding Brand Equity: The Importance, Examples & How to Measure ItNo ratings yet
- Leveraging Strong Brands for New Product SuccessDocument7 pagesLeveraging Strong Brands for New Product SuccessFawax HassanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document17 pagesAssignment 1twinklegodhwaniNo ratings yet
- Apple Brand ElementsDocument10 pagesApple Brand ElementsMohit ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle of Tata ComDocument11 pagesProduct Life Cycle of Tata ComRahul Kamble0% (1)
- The Product Life Cycle Products Are Born, They Prosper and Die PDFDocument2 pagesThe Product Life Cycle Products Are Born, They Prosper and Die PDFYeshambel EwunetuNo ratings yet
- PLC Stages of Amul Butter and Gold Spot DrinkDocument15 pagesPLC Stages of Amul Butter and Gold Spot DrinkSonali ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Batch - 1 EemDocument17 pagesBatch - 1 EemTummeti SujithNo ratings yet
- Product & Brand ManagementDocument105 pagesProduct & Brand ManagementvipinNo ratings yet
- Product and Process InnovationDocument14 pagesProduct and Process InnovationVinay VinnuNo ratings yet
- Product management essentialsDocument30 pagesProduct management essentialstanvirNo ratings yet
- Four Types of Innovation: Breakthrough, Sustaining, New Market, DisruptiveDocument6 pagesFour Types of Innovation: Breakthrough, Sustaining, New Market, DisruptiveChai AmandaNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle:: Group MembersDocument18 pagesProduct Life Cycle:: Group MembersimykoNo ratings yet
- Changeship - Workbook: Building and scaling next generation businesses in the digital polypol: Purpose driven - Customer dedicated - Sustainability enabledFrom EverandChangeship - Workbook: Building and scaling next generation businesses in the digital polypol: Purpose driven - Customer dedicated - Sustainability enabledNo ratings yet
- Pricing StrategyDocument9 pagesPricing StrategyMark Xavier SalazarNo ratings yet
- Operations MGT FinalsDocument16 pagesOperations MGT FinalsHannah Francesca Sarajan EstrellaNo ratings yet
- OBLICON ReviewerDocument54 pagesOBLICON ReviewerMaria Diory Rabajante93% (300)
- MC 2017-03 13th CBMS National ConferenceDocument8 pagesMC 2017-03 13th CBMS National ConferenceCheenee Mariekeith Comin VehementeNo ratings yet
- The Human Resource Management Officer: Besides Being A Joy To Work WithDocument1 pageThe Human Resource Management Officer: Besides Being A Joy To Work WithCheenee Mariekeith Comin VehementeNo ratings yet
- DILG MC 2017-01 National General Assembly and Forum On Revenue Generation and Budget Authorization of (FOUR-L)Document2 pagesDILG MC 2017-01 National General Assembly and Forum On Revenue Generation and Budget Authorization of (FOUR-L)Cheenee Mariekeith Comin VehementeNo ratings yet
- OBLICON ReviewerDocument54 pagesOBLICON ReviewerMaria Diory Rabajante93% (300)
- Emb FilesDocument44 pagesEmb FilesCheenee Mariekeith Comin VehementeNo ratings yet
- Filipinos often confuse goal and instrumental valuesDocument1 pageFilipinos often confuse goal and instrumental valuesCheenee Mariekeith Comin Vehemente67% (6)
- The Visitation of The GodsDocument8 pagesThe Visitation of The Godsargus-eyed100% (11)
- Problem Areas in Legal EthicsDocument1 pageProblem Areas in Legal EthicscrazeeeemeNo ratings yet
- ConstiDocument68 pagesConstiCheenee Mariekeith Comin VehementeNo ratings yet
- Problem Areas in Legal EthicsDocument1 pageProblem Areas in Legal EthicscrazeeeemeNo ratings yet
- Knock Out BreweryDocument5 pagesKnock Out BreweryCheenee Mariekeith Comin VehementeNo ratings yet
- Adr PaperDocument9 pagesAdr PaperCheenee Mariekeith Comin VehementeNo ratings yet
- The Judicial DepartmentDocument4 pagesThe Judicial DepartmentRamil G. AustriaNo ratings yet
- CRIMINAL LAW 2: CRIMES AGAINST NATIONAL SECURITY AND PUBLIC ORDERDocument8 pagesCRIMINAL LAW 2: CRIMES AGAINST NATIONAL SECURITY AND PUBLIC ORDERCheenee Mariekeith Comin VehementeNo ratings yet
- Omnibus Election Code of The PhilippinesDocument64 pagesOmnibus Election Code of The PhilippinesElfenLiedFanGirlNo ratings yet
- Additional Cases in Persons and Family Relations DigestedDocument178 pagesAdditional Cases in Persons and Family Relations DigestedCheenee Mariekeith Comin VehementeNo ratings yet
- Lim Tanhu vs. RamoleteDocument53 pagesLim Tanhu vs. RamoleteCheenee Mariekeith Comin VehementeNo ratings yet
- Re BrillantesDocument14 pagesRe BrillantesCheenee Mariekeith Comin Vehemente100% (1)
- SACLOBDocument10 pagesSACLOBRicardo OrgeNo ratings yet
- Esprit Holdings Limited Annual Report FY 15/16 Highlights Progress and Path to RecoveryDocument140 pagesEsprit Holdings Limited Annual Report FY 15/16 Highlights Progress and Path to RecoveryMissBeautiful MindNo ratings yet
- Business Environment NotesDocument88 pagesBusiness Environment NotesShaikh NazafNo ratings yet
- Technology & Its Importance: by Dr. Vijay KR KhuranaDocument41 pagesTechnology & Its Importance: by Dr. Vijay KR KhuranaKritika JainNo ratings yet
- BAC 3634 - Corporate Accounting IDocument20 pagesBAC 3634 - Corporate Accounting IBongDanielNo ratings yet
- BSC Framework Translates StrategyDocument6 pagesBSC Framework Translates StrategyAhmad ZydanNo ratings yet
- GBusiSBG11 PDFDocument168 pagesGBusiSBG11 PDFkemime100% (2)
- Introduction of Managerial EconomicsDocument21 pagesIntroduction of Managerial EconomicsSandesh ShettyNo ratings yet
- Fa Project Mcom IDocument54 pagesFa Project Mcom IPOOJANo ratings yet
- Corporate Social Responsibility Report Highlights NICOZDIAMOND's Community SupportDocument72 pagesCorporate Social Responsibility Report Highlights NICOZDIAMOND's Community SupportKristi DuranNo ratings yet
- Social/Ethical Decisions in Management ObjectivesDocument21 pagesSocial/Ethical Decisions in Management ObjectivesVaughn Reyes VillegasNo ratings yet
- Monte Carlo SimulationDocument5 pagesMonte Carlo SimulationIulia Roman GaroafaNo ratings yet
- Estée Lauder Expands GloballyDocument5 pagesEstée Lauder Expands GloballyMhegan ManarangNo ratings yet
- A K A: A Review of The Models Used To Measure Intellectual CapitalDocument25 pagesA K A: A Review of The Models Used To Measure Intellectual CapitalBundanya SavinaNo ratings yet
- EconomicsfinalDocument293 pagesEconomicsfinalpravinNo ratings yet
- Kristen Cookie CompanyDocument32 pagesKristen Cookie CompanyShabnam Dhaliwal100% (2)
- 2013–2014 Baldrige Criteria for Performance Excellence: Category and Item CommentaryDocument16 pages2013–2014 Baldrige Criteria for Performance Excellence: Category and Item CommentaryAl HattanNo ratings yet
- 2-The Business Mission and VisionDocument36 pages2-The Business Mission and VisiontalakayutubNo ratings yet
- MCKPST - Practice Form - Ver 1.0Document10 pagesMCKPST - Practice Form - Ver 1.0Dolampochki100% (1)
- Remote Deposit CaptureDocument60 pagesRemote Deposit Capture4701sandNo ratings yet
- Apple Inc. Performance Case Study: Jobs' Leadership & Cook's SuccessionDocument9 pagesApple Inc. Performance Case Study: Jobs' Leadership & Cook's SuccessionSalma Yassin100% (1)
- ACCA F9 Revision Kit ACCA 2.4 Old Past Paper Solved Old Professional Scheme 2002 - 2007Document237 pagesACCA F9 Revision Kit ACCA 2.4 Old Past Paper Solved Old Professional Scheme 2002 - 2007Haider Ali60% (5)
- Business EconomicsDocument23 pagesBusiness Economicsdeepeshvc83% (6)
- Fund Flow Analysis & Distilleries in Sugar IndustryDocument57 pagesFund Flow Analysis & Distilleries in Sugar IndustryYugendra Babu KNo ratings yet
- Arch 159: The Architectural Firm: Architect Perry Jan N. Remolador, UapDocument15 pagesArch 159: The Architectural Firm: Architect Perry Jan N. Remolador, UapApril GabayanNo ratings yet
- Gujarat HC Reduces Gross Profit Rate in Diamond Firm Tax CaseDocument5 pagesGujarat HC Reduces Gross Profit Rate in Diamond Firm Tax CaseExcelNo ratings yet
- .Capital Structure and Profitability of A FirmDocument26 pages.Capital Structure and Profitability of A FirmRomaan QamarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To Product Design and DevelopmentDocument4 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To Product Design and DevelopmentKadie EdwardsNo ratings yet
- US Economic Indicators: Corporate Profits in GDP: Yardeni Research, IncDocument16 pagesUS Economic Indicators: Corporate Profits in GDP: Yardeni Research, IncJames HeartfieldNo ratings yet
- Organizational Goals and Key Result AreasDocument33 pagesOrganizational Goals and Key Result AreasmnjbashNo ratings yet