Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Oracle Ebs: Multiorg Concept: Organization"
Uploaded by
kumar_amit_99Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Oracle Ebs: Multiorg Concept: Organization"
Uploaded by
kumar_amit_99Copyright:
Available Formats
Oracle EBS: MultiOrg Concept
Since Oracle EBS or E-Business Suite is a complete automated application and caters
the need of variety of industries. It has an architecture called MultiOrg or Multiple
Organization.
Whenever we talk about an organization irrespective of its multiple structure, we will
find certain common things or feature or let me call it departments. It is not necessary
that every organization has every department. But some departments and/or processes
are more or less the same.
What is an Organization? In EBS it is a vague term, infact, varied term. In
Oracle EBS an organization can be a Legal Entity, or an Inventory, or a department.
Anything can be treated as organization in Oracle. When we go through the
Oracle EBS documentation we will find the excessive use word Organization. But it not
the organization we refer it to here in daily routine.
In our daily routine if we say the word organization, we will certainly be referring to
some company, for example, Inbox Business Technologies, IBM, Acer, HP, these are the
example of organization selling hardware. But in Oracle Multi Org structure they are
referred to as Legal Entities.
The Multi Org structure in Oracle consists of following organizations
1. Business Group or HR Business Group
2. Ledger
3. Legal Entity or GRE
4. Operating Unit
5. Inventory Organization
BUSINESS GROUP (BG)
A business group is the top level in multi org structure. Oracle view human
resource as the basis for the business. A human resource is selling the products that
organization is manufacturing, a human resource is purchasing raw materials required
to make a product, a human resource is making accounting and financials statement. In
short a legal entity transacts because of Human Resources.
In Oracle EBS, Business Group holds the employee information. If there is a Group
of Companies and they all are using a single instance of Oracle Apps then every
employee in each company will be defined at BG level. Each employee will then be
assigned aresponsibility. That responsibility determines which company that
employee belongs to and what type of transaction can be carried out. When a fresh EBS
instance is installed it has a Default Business Group namely Setup Business Group.
We usually rename it as per our requirement.
A BG can have multiple ledger attached to it and there can beMultiple Business
Groups in one instance.
Oracle HR resides at this level of MultiOrg structure.
LEDGER
Formerly called Set of Book in R11i. Ledger is an accounting book.
Take an example of a utility shop with an old man sitting with a big register. In
that register he notes every transaction related to money or finances. Lets say he
sells some bottles of mineral water to a person. He notes the Date on the transaction
took place, theAmount involved in that transaction, Persons name, particulars of
goods sold to that person.
This is similar to what we do in a ledger. There are 4Cs concepts in Ledger.
1. Chart of Account (Particulars of Goods)
2. Currency (Amount)
3. Calendar (Date)
4. Subledger Accounting Convention (Cash / Accrual)
Oracle General Ledger resides at this level.
LEGAL ENTITY
Legal Entity definition by book is any company which is reporting to Government, an
entity which exists. In Oracle EBS a company is also referred to as GRE Government
Reporting Entity. A legal entity has a disclosure requirement of their annual revenue.
An organization which prepares its Balance Sheet and Income Statement.
Oracle says anything can be your legal entity. Yourmanufacturing plant can be your
legal entity, your departmentscan be your legal entity. Your inventory can be your
legal entity. A legal entity is the one for which you want a Balance Sheet and Income
statement. How can a balance sheet be generated for a department is another topic
OPERATING UNIT
Operating Unit (OU) comes under a ledger with a legal context.Legal Context is
referred to as the Legal entity to which it is attached. The purpose of an operating unit
is to segregate or separate subledger transactions. A legal entity having different
branches in Pakistan can treat each branch an operating unit.
Oracle Payables, Purchasing, Receivables, Order Management resides at this level
of MultiOrg.
In general an operating unit is the one dealing with paper work. How?
Take an example of P2P (Procure to Pay) cycle. It involvesPurchasing and Payables.
From Purchasing you generated an RFQ(Request for Quotation) and send it to
vendor, against the RFQyou receive a Quotation. Against that quotation you send
the PO (Purchase Order), Against that PO you receive Goods and GRN(Goods
Received Note), against that GRN you receive payablesInvoice, against that invoice
you make Payment. Each of these documents are from Oracle Purchasing
and Payables.
Similarly there is a O2C (Order to Cash) cycle.
INVENTORY ORGANIZATION
Inventory Organization is last or the lowest level of MultiOrgstructure. Inventory
organization refers to any kind storage of item, finished goods and raw materials, etc.
This storage can be Warehouse, Floors, Cabinets, Drawers, or a logical store
whichdont exists physically.
Inventory in general refers to storage and movement of goods from
one Inventory organization to another. Inventory has two types of inventory: Master
Item Inventory Org, Inventory Organizationand Sub-Inventory Org.
Master item inventory stores the every information of item or the definition of item.
It does not store the information of locationthat item is placed or the quantity of
item available. InventoryOrganization is same as the Master but it has the costing
definition, locator information, and types of item it can store. Each Inventory
organization should have at least one Sub Inventory Organization. There can
be multiple sub inventories under one Inventory Organization. Costing method can
also be defined at subinventory level.
Oracle Inventory, Manufacturing, Warehouse Management, Enterprise Asset
Management resides at this level.
ORACLE PURCHASING
There are two types of Hierarchies used for approval routing.
a. Position Hierarchies
b. Supervisor Hierarchies
Position Hierarchies
========================
Position Hierarchies are hierarchies that have a JOB/POSITION relationship.
For example, you could have a JOB called BUYER and within BUYER you could have various
grades or POSITIONS of BUYER Junior, Senior and Chief
Each POSITION has an approval limit, so when a purchase order exceeds the limits of the
POSITION, the purchase order is forwarded onto the next POSITION in the Hierarchy.
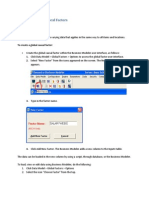
The hierarchy for this JOB/POSITION type of hierarchy is defined on the Position Hierarchy
form. When this is complete or is changed, the Fill Employee Hierarchy concurrent process must
be run for the new hierarchy to come into effect.
The Position Hierarchy form can be found at PO Navigator Setup Personnel Position
Hierarchy
Supervisor Hierarchies
==========================
Supervisor Hierarchies are hierarchies that have an Employee/Supervisor relationship
The supervisor of an employee is defined on the Assignment zone of the Employee form
This type of hierarchy does not use the Position Hierarchy form, but is defined by the employee /
supervisor relationship
If the purchase order raised by the employee exceeds the approval limits, the purchase order is
forwarded onto the employees supervisor, as defined on the Employee form
You might also like
- Oracle Advanced Planning and Scheduling: Implementation and User's Guide, Volumes 1 & 2Document908 pagesOracle Advanced Planning and Scheduling: Implementation and User's Guide, Volumes 1 & 2priyaNo ratings yet
- Sample Use CaseDocument2 pagesSample Use CaseKunal AgarwalNo ratings yet
- DemantraDocument4 pagesDemantraPrikrishnanNo ratings yet
- ASCP - 101: A Beginners Guide To Implementing ASCP Sandeep Gandhi Independent ConsultantDocument21 pagesASCP - 101: A Beginners Guide To Implementing ASCP Sandeep Gandhi Independent ConsultantNavin SidanaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Planning Command Center Installation and Setup For 12.2.5Document28 pagesAdvanced Planning Command Center Installation and Setup For 12.2.5bommakanti.shivaNo ratings yet
- Oracle Advanced Supply Chain PlaningDocument14 pagesOracle Advanced Supply Chain PlaningAmine GallahNo ratings yet
- This Document Was Authored by An Oracle Customer and Has Not Been Subject To An Independent Technical ReviewDocument15 pagesThis Document Was Authored by An Oracle Customer and Has Not Been Subject To An Independent Technical ReviewshankarNo ratings yet
- Global Forecasting: ASCP FundamentalsDocument18 pagesGlobal Forecasting: ASCP FundamentalspavanNo ratings yet
- Ascp Collection ProfilesDocument78 pagesAscp Collection Profilesmkasi2k9No ratings yet
- Demantra Performance Solutions - Real World Problems and Solutions (ID 1081962.1)Document11 pagesDemantra Performance Solutions - Real World Problems and Solutions (ID 1081962.1)gentoo68No ratings yet
- How To Improve ASCP Data Collections PerformanceDocument6 pagesHow To Improve ASCP Data Collections PerformancePramodNo ratings yet
- Oracle Demantra Demand ManagementDocument29 pagesOracle Demantra Demand Managementeuge_prime2001No ratings yet
- Oracle Advanced Planning and SchedulingDocument768 pagesOracle Advanced Planning and SchedulingJaya SuriyaNo ratings yet
- SCP DemandPlanningScalability R13Document20 pagesSCP DemandPlanningScalability R13javierNo ratings yet
- ASCP Collection MethodsDocument2 pagesASCP Collection MethodsSenthamarai Selvan BNo ratings yet
- ASCP Profile Option DesciptionsDocument35 pagesASCP Profile Option DesciptionsNaveed MohammadNo ratings yet
- Global & Local Causal Factors in DemantraDocument9 pagesGlobal & Local Causal Factors in DemantraGaurav SinghNo ratings yet
- ASCP and Safety Stock PeggingDocument2 pagesASCP and Safety Stock PeggingRamakrishna Reddy GorantlaNo ratings yet
- Demantra Performance TuningDocument4 pagesDemantra Performance TuningchandanjeeNo ratings yet
- In Memory Management OPMDocument35 pagesIn Memory Management OPMKarthikeya BandaruNo ratings yet
- Forecast ConsumptionDocument11 pagesForecast Consumptionshital9099No ratings yet
- IT in Supply Chain Management Session IIIDocument56 pagesIT in Supply Chain Management Session IIIPankhoori VidyaNo ratings yet
- MRP To ASCP InsightDocument29 pagesMRP To ASCP InsightSarah BakerNo ratings yet
- AtpDocument17 pagesAtpramana341100% (1)
- Global Order Promising - 1Document418 pagesGlobal Order Promising - 1shankarNo ratings yet
- Difference Between CTO & PTODocument4 pagesDifference Between CTO & PTOpulluri1234No ratings yet
- Cycle CountDocument40 pagesCycle Countmadhappan100% (1)
- Apscheck 092614Document571 pagesApscheck 092614sivap253256No ratings yet
- Production SchedulingDocument22 pagesProduction Schedulingammini kaosNo ratings yet
- Oracle Quality: Manufacturing Functional FoundationDocument23 pagesOracle Quality: Manufacturing Functional FoundationJose DuqueNo ratings yet
- ASCP Pegging Information LogicDocument3 pagesASCP Pegging Information LogicSai YakkalaNo ratings yet
- Demand Management Cloud An In-Depth LookDocument32 pagesDemand Management Cloud An In-Depth Lookamrit_75No ratings yet
- Ascp IgDocument1,616 pagesAscp IgParag BhayaniNo ratings yet
- ASCP Implementation Steps For One OrganizationDocument16 pagesASCP Implementation Steps For One OrganizationSanthosh SantyNo ratings yet
- Safety Stock Planning-2 PDFDocument30 pagesSafety Stock Planning-2 PDFlearnoracle19No ratings yet
- SM7 - Oracle Production SchedullingDocument4 pagesSM7 - Oracle Production SchedullingRakha Setyoadi Dwi LeksonoNo ratings yet
- Types of Plan: Constraint Plan Unconstraint Plan Optimized Plan Output of PlansDocument30 pagesTypes of Plan: Constraint Plan Unconstraint Plan Optimized Plan Output of PlansRamesh GarikapatiNo ratings yet
- Concurrent ProcessingDocument52 pagesConcurrent Processingmoosa.dba9332100% (1)
- Implementing Demantra As A Replacement To A Legacy Forecasting Tool: A TI Success StoryDocument73 pagesImplementing Demantra As A Replacement To A Legacy Forecasting Tool: A TI Success StoryRai Prashant Kumar RaiNo ratings yet
- Oracle Shop Floor Management/Advanced Supply Chain Planning Oracle Advanced Planning Command CenterDocument81 pagesOracle Shop Floor Management/Advanced Supply Chain Planning Oracle Advanced Planning Command CenterNagaraj GuntiNo ratings yet
- Demantra Engine On LinuxDocument43 pagesDemantra Engine On LinuxBirendra PadhiNo ratings yet
- Kanban Way in Oracle ApplicationsDocument12 pagesKanban Way in Oracle Applicationsvinodkumar_sivaNo ratings yet
- Atp Api 11510Document16 pagesAtp Api 11510Sid KendNo ratings yet
- Br100 SCM - OmDocument83 pagesBr100 SCM - OmFranciscoRBNo ratings yet
- MRP Setup PDFDocument2 pagesMRP Setup PDFKhurram HussainNo ratings yet
- Oracle WMS Meta Link ID - 1426936Document2 pagesOracle WMS Meta Link ID - 1426936lingesh6b100% (1)
- Oracle Order Management - Sales Order Overview: An Oracle White Paper October 2000Document43 pagesOracle Order Management - Sales Order Overview: An Oracle White Paper October 2000floatingbrain100% (7)
- Back To Back Promising - Fusion Gop Supply Planning PDFDocument11 pagesBack To Back Promising - Fusion Gop Supply Planning PDFJorge DeaThrider VazquezNo ratings yet
- OPM Planning Setup TrainingDocument17 pagesOPM Planning Setup TrainingDheeraj ThapaNo ratings yet
- MFG OPM Advisor Webcast 2016 0105Document61 pagesMFG OPM Advisor Webcast 2016 0105Steffi StevenNo ratings yet
- Reconciliation Between Inventory Valuation & Subledger Postings (R12) For OPM CostingDocument44 pagesReconciliation Between Inventory Valuation & Subledger Postings (R12) For OPM Costinghaitham ibrahem mohmed100% (1)
- Libero HRDocument48 pagesLibero HRedayNo ratings yet
- Oracle® E-Records: Implementation Guide Release 12.1Document118 pagesOracle® E-Records: Implementation Guide Release 12.1oneeb350No ratings yet
- Demantra - VikramDocument3 pagesDemantra - VikramVikram SimhaNo ratings yet
- Demantra End 2 End Sol GooDDocument16 pagesDemantra End 2 End Sol GooDRamesh PoshalaNo ratings yet
- Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition 12c A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandOracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition 12c A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- Report in BriefDocument30 pagesReport in Briefkumar_amit_99No ratings yet
- How To Audit Application TableDocument3 pagesHow To Audit Application Tablekumar_amit_99No ratings yet
- Pre MRP SetupsDocument25 pagesPre MRP Setupskumar_amit_99100% (1)
- Examples of Customer InterfaceDocument41 pagesExamples of Customer InterfaceSuneelTejNo ratings yet
- GST Functional P2P FlowDocument74 pagesGST Functional P2P FlowKommanapalli Jeeten100% (5)
- ISupplier Portal TablesDocument2 pagesISupplier Portal Tableskumar_amit_99No ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- GST Functional O2C Flow Phase1 2Document127 pagesGST Functional O2C Flow Phase1 2kumar_amit_99No ratings yet
- Step by Step Reading and Writing A Text File Using UTLDocument7 pagesStep by Step Reading and Writing A Text File Using UTLkumar_amit_99No ratings yet
- Rejection Reason Mandatory in Oracle WorkflowDocument1 pageRejection Reason Mandatory in Oracle Workflowkumar_amit_99No ratings yet
- If You Are IT Guys You Can Understood SCM As:: Supply-Chain Operations Reference-Model (SCORà à ®) Supply-Chain CouncilDocument7 pagesIf You Are IT Guys You Can Understood SCM As:: Supply-Chain Operations Reference-Model (SCORà à ®) Supply-Chain Councilkumar_amit_99No ratings yet
- SCM OverviewDocument7 pagesSCM Overviewkumar_amit_99No ratings yet
- Oracle NVL FunctionDocument1 pageOracle NVL Functionkumar_amit_99No ratings yet
- Accessing Oracle Forms From WorkflowDocument7 pagesAccessing Oracle Forms From Workflowkumar_amit_99No ratings yet
- Order Management Functional DocumentDocument31 pagesOrder Management Functional Documentkumar_amit_99No ratings yet
- Order Management Basic Setup Steps During ImplementationDocument1 pageOrder Management Basic Setup Steps During Implementationkumar_amit_99No ratings yet
- Chapter 06Document56 pagesChapter 06kumar_amit_99No ratings yet
- Move Order Process Move Order Tables: Oracle InventoryDocument4 pagesMove Order Process Move Order Tables: Oracle Inventorykumar_amit_99No ratings yet
- Adf Tutorial 1 134167Document172 pagesAdf Tutorial 1 134167Vishaal MallickNo ratings yet
- Oracle Release 12+ Forms PersonalizationDocument18 pagesOracle Release 12+ Forms PersonalizationamoussaaNo ratings yet
- MRP CancelDocument1 pageMRP Cancelkumar_amit_99No ratings yet
- Best Practices PL SQLDocument22 pagesBest Practices PL SQLkumar_amit_99No ratings yet
- Oaf Personalization SDocument99 pagesOaf Personalization Sumar7318No ratings yet
- MRP Rank AnalysisDocument1 pageMRP Rank Analysiskumar_amit_99No ratings yet
- PurchasingDocument89 pagesPurchasingkumar_amit_99No ratings yet
- Form PersonalizationDocument25 pagesForm Personalizationkumar_amit_99No ratings yet
- Registration of A Custom Form in Oracle ApplicationsDocument15 pagesRegistration of A Custom Form in Oracle Applicationskumar_amit_99No ratings yet
- PurchasingDocument89 pagesPurchasingkumar_amit_99No ratings yet
- Workflow AwarenessDocument52 pagesWorkflow Awarenesskumar_amit_99No ratings yet
- Order To Cash Cycle - Tables Get Affected at Each StepDocument3 pagesOrder To Cash Cycle - Tables Get Affected at Each Stepkumar_amit_99No ratings yet