Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nitric Acid
Uploaded by
David Meza Carbajal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views18 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPS, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPS, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views18 pagesNitric Acid
Uploaded by
David Meza CarbajalCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPS, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
500 TPD
Nitric Acid Plant
500 TPD
Nitric Acid Plant
Please click on our
logo or any link in
this presentation to
be redirected to our
website, email or
other
documentation.
Thank You!
17A Marlen Drive w Hamilton, NJ 08691 w USA
Tel: (609) 586-8004 w Fax: (609) 586-0002
www.ippe.com
General Overview
Capacity: 500 TPD
Shut Down: January 2006
Design: C&I Girdler
Concentration: 64%-67%
NOx Emission: 180 PPM
General Overview
This facility has been producing 65% strength nitric acid since 1971
The production of nitric acid is a continuous process and the plant produces about
170,000 tons per year
The manufactured Nitric Acid is constantly circulated in a 2,000 ton storage tank
before loading tank trucks for delivery
Nitric acid is used in a variety of applications from fertilizer to explosives, as well as a
raw material used in the manufacture of other chemical products
There are a complete set of Spare Rotors for the Compressor
New Tailgas Heaters (Never Installed)
Zirconium Tube Bundle Cooler Condenser
Key Points
The purpose of the nitric acid unit is to produce 65% strength nitric acid from raw
materials and a catalyst for use in a variety of applications.
Purpose
Materials and Products
The production of nitric acid requires only four materials: ammonia, air, platinum and
water
Anhydrous ammonia (NH
3
) and oxygen from the air (O
2
) is mixed, passed through and
reacted with a platinum catalyst gauze to form NOx, then absorbed with H
2
O to form
basic nitric acid
The ammonia is heated to a gas and the gas is then superheated and transferred to
the mixer
Air is taken in through the compressor and transferred to the mixer
This ammonia/air mixture is forced through the platinum gauze in the converter
This new gas then enters the absorber column where it is absorbed with water to form
basic nitric acid
Materials and Products
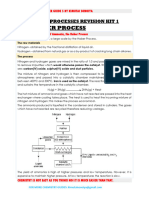
Manufacturing Process Unit Sections
Manufacturing Process Unit Diagram
Manufacturing Process Unit Sections
The Ammonia Section contains a storage tank from which the anhydrous ammonia is
transferred to the vaporizer, superheater and filters
Ammonia Section
Manufacturing Process Unit Sections
The Process Air Section contains the Steam Turbine, Vera Compressor (filter, silencer,
compressor case 1, air cooler and compressor case 2), Expander and Process Air
Filter for the required compressed air
Process Air Section
The Product Process Section contains the following:
Mixer
Where ammonia gas and compressed air mix
Converter
Where the mixed gases react with a platinum catalyst within the converter
Waste Heat Exchanger & Platinum Filter
The mixed gases continue through the waste heat exchanger, then through the platinum
filter
Tail Gas Heater, Boiler Feedwater Heaters and Cooler Condenser
Used to cool the process stream after passing through the platinum filter
Absorption Column
The process stream then enters the absorption column, where nitric acid is formed
Acid Heater
The acid is heated to make the bleaching process more efficient
Bleacher Column
The acid enters the bleacher column where it is bleached to a clear color
Product Acid Cooler
The acid is then cooled in the product acid cooler, which promotes less fumes and
decreased corrosion in the storage area.
Product Platinum Filter
Prior to the storage area, the acid passes through the product platinum filter
Storage Area
Manufacturing Process Unit Sections
Product Process Section
Manufacturing Process Unit Sections
Product Process Section Diagram
The Tailgas Treatment Section contains the components to eliminate unconverted
gases (nitric oxide) that were not absorbed in the absorption column. The components
in this section include:
The mist eliminator
Removes any liquid acid from the tailgas stream
Bleach Air Cooler
Cools air from the air compressor
Tailgas Heater
Reheats the tailgas before it enters the fume abater
Fume Abater
Destroys and eliminates nitric oxides in the tailgas
Expander
Uses the hot gases from the fume abater to drive the compressor 2
nd
stage
Economizer
Uses its heat to heat and send water to the boiler
Stack
Vents the cleaned gas to the atmosphere
Manufacturing Process Unit Sections
Tailgas Treatment Section
Manufacturing Process Unit Sections
Tailgas Treatment Section
The Process Utility Section includes hydrogen, butane, instrument air, demin water,
cooling tower water and equipment components that are used to produce their own
steam and heating/cooling from the heat made by the nitric acid process to continue
the process in a complete cycle
When running at mid to full rates, the nitric acid unit produces more thermal utility than
it uses. The components include the steam header, surface condenser, steam traps,
heat exchangers and demin water supply
The deaerator receives steam and water from the above components where it is
heated and transferred to the ammonia superheater
The heated water flows to the ammonia vaporizer, boiler feedwater heaters A&B and to
the acid heater
The vestibule jacket is a boiler around the converter
The waste heat exchanger is a boiler in line with the process stream
Water is heated to steam and transferred to the turbine; the excess is exported to plant
utilities
Manufacturing Process Unit Sections
Process Utility Section
Ammonia from the storage tanks is transferred to the ammonia vaporizer through a magnetic
filter, to the ammonia superheater through filters and into the mixer
Air is drawn through an intake filter and silencer to the first case compressor
The air is cooled by the air intercooler and enters the second case compressor then through
a process filter and into the mixer
Air and ammonia mix enter the converter where it passes through a platinum/rhodium gauze
which forms nitrogen oxide
As it passes through the waste heat exchanger, nitrogen dioxides are also formed
This process gas passes through a platinum filter for platinum recovery
The gas then passes through the tailgas heater, cooler condenser and boiler feedwater
heaters for process cooling and enters the absorption column
The nitric oxide is oxidized to form nitrogen dioxide
Water is introduced into the column where it absorbs the nitrogen dioxides to form nitric acid
The acid enters the acid heater where it is heated to make the bleaching process more
efficient
The acid enters the bleacher column where it is bleached to a clear color
The acid is then cooled in the product acid cooler. This promotes less fumes and decreased
corrosion in the storage area. Prior to the storage area the acid passes through the product
platinum filter
Process Flow
Process Flow Path
Process Flow
Process Flow Diagram
Photos
Photos
Photos
Contact Information
MICHAEL JOACHIM
DIRECTOR, PLANTS DEPT.
Tele: 609-838-5930 (direct)
Mobile: 609-516-9107
MichaelJ@ippe.com
SANJEEV REGE
VP GLOBAL PLANT SALES
Tele: 609-838-5938 (direct)
Mobile: 609-510-2616
SanjeevR@ippe.com
You might also like
- Amine Filtration: By: John Hampton & Guy WeismantelDocument20 pagesAmine Filtration: By: John Hampton & Guy WeismantelwaheedNo ratings yet
- Purification of Laboratory Chemicals: Part 2 Inorganic Chemicals, Catalysts, Biochemicals, Physiologically Active Chemicals, NanomaterialsFrom EverandPurification of Laboratory Chemicals: Part 2 Inorganic Chemicals, Catalysts, Biochemicals, Physiologically Active Chemicals, NanomaterialsNo ratings yet
- Technical Report of Formic Acid PlantDocument6 pagesTechnical Report of Formic Acid PlantMuzzamilNo ratings yet
- Eschweiler-Clarke Solventfree PDFDocument10 pagesEschweiler-Clarke Solventfree PDFRenæ NaeNo ratings yet
- Acetic AnhydrideDocument1 pageAcetic AnhydrideCarlos Vargas de MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Acetic AnhydrideDocument8 pagesAcetic AnhydrideVinayak KhairnarNo ratings yet
- Alternative Control Techniques Document - Nitric and Adipic Acid Manufacturing PlantsDocument147 pagesAlternative Control Techniques Document - Nitric and Adipic Acid Manufacturing PlantsAun AliNo ratings yet
- Ester Formation and Hydrolysis and Related ReactionsFrom EverandEster Formation and Hydrolysis and Related ReactionsNo ratings yet
- Production of Acetic Anhydride From AcetoneDocument13 pagesProduction of Acetic Anhydride From AcetoneCrispin Brewu-AsieduNo ratings yet
- Benzyl Cyanide: α-TolunitrileDocument3 pagesBenzyl Cyanide: α-TolunitrileEric M NevarezNo ratings yet
- Acetic AnhydrideDocument117 pagesAcetic AnhydrideEsquivel EmilioNo ratings yet
- Urea Tech Manual 2006Document15 pagesUrea Tech Manual 2006Khalid GamalNo ratings yet
- Nitric Acid Plant DetailsDocument21 pagesNitric Acid Plant DetailsBon BonNo ratings yet
- Summation of The Sciencemadness Phosphorous ThreadDocument29 pagesSummation of The Sciencemadness Phosphorous ThreadImranNo ratings yet
- Butenediol PDFDocument6 pagesButenediol PDFJaamac DhiilNo ratings yet
- NALCO® EC9149A: Section 1. Identification of The Substance/Mixture and of The Company/UndertakingDocument14 pagesNALCO® EC9149A: Section 1. Identification of The Substance/Mixture and of The Company/UndertakingDonatas BertasiusNo ratings yet
- Nalco Guide To Boiler Failure AnalysisDocument2 pagesNalco Guide To Boiler Failure AnalysisRizqi Priatna0% (1)
- Guideline For Technical Regulation Vol.2 - Design of Thermal Power Facilities Book 10.12 Environment FacilityDocument93 pagesGuideline For Technical Regulation Vol.2 - Design of Thermal Power Facilities Book 10.12 Environment FacilityQuang Minh TrầnNo ratings yet
- Acrylic Acid and Derivatives: Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial ChemistryDocument18 pagesAcrylic Acid and Derivatives: Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial ChemistryNoman Abu-FarhaNo ratings yet
- The Reaction of Acetaldehyde With MethanolDocument6 pagesThe Reaction of Acetaldehyde With MethanolHugo WizenbergNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument53 pagesProject ReportChunchu Anil100% (1)
- Chloride in Palm OilDocument4 pagesChloride in Palm OilFebrian IsharyadiNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Silica From Puddy HuskDocument19 pagesExtraction of Silica From Puddy HuskFauzaan KhanNo ratings yet
- Ullmann's HNO3 PDFDocument40 pagesUllmann's HNO3 PDFRegalpaz RegalpazNo ratings yet
- Nitric Acid Design Project: Shivam PandyaDocument15 pagesNitric Acid Design Project: Shivam PandyaShivam PandyaNo ratings yet
- SIMULATIONDocument85 pagesSIMULATIONcreativechand100% (18)
- Isopropyl Alcohol (IPA) - Chemical Economics Handbook (CEH) - IHS MarkitDocument5 pagesIsopropyl Alcohol (IPA) - Chemical Economics Handbook (CEH) - IHS MarkitarmanNo ratings yet
- Plug Flow ReactorDocument6 pagesPlug Flow Reactormattgrisewood100% (11)
- Butanediol and Derivatives PDFDocument4 pagesButanediol and Derivatives PDFJaamac DhiilNo ratings yet
- Ammonia CrackerDocument2 pagesAmmonia CrackerPuneet Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Kinetics of The Catalytic Oxidation of Phthalic AnhydrideDocument214 pagesKinetics of The Catalytic Oxidation of Phthalic Anhydrideannisa plNo ratings yet
- Process Description of Ammonia PlantDocument12 pagesProcess Description of Ammonia PlantSridharNo ratings yet
- Manufacture of Nitric AcidDocument2 pagesManufacture of Nitric AcidJay D PatelNo ratings yet
- Membrane Separation ProcessesDocument15 pagesMembrane Separation ProcessesJaamac DhiilNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument47 pagesPresentationAsim FarooqNo ratings yet
- GFL ReportDocument43 pagesGFL Reportmanoj singhNo ratings yet
- Alkaloids Written ReportDocument12 pagesAlkaloids Written ReportRuvie Ann Alamo BallesterNo ratings yet
- Original Lit SurveyDocument52 pagesOriginal Lit SurveyMayank KrNo ratings yet
- Phosphoric: Diammonium Phosphate Fertilizer FromDocument6 pagesPhosphoric: Diammonium Phosphate Fertilizer FromFatima KhanNo ratings yet
- APPLICATIONs OF ACETIC ACIDDocument6 pagesAPPLICATIONs OF ACETIC ACIDJohn Patric Ranjo SiaNo ratings yet
- Adsorption and Solvent ExtractionDocument5 pagesAdsorption and Solvent ExtractionWisnu WardanaNo ratings yet
- Epoxidation of LimoneneDocument92 pagesEpoxidation of Limoneneflorinmax5100% (1)
- Cost Estimation HNO3Document4 pagesCost Estimation HNO3yogeshdama100% (1)
- A01 045 PDFDocument30 pagesA01 045 PDFjaimeNo ratings yet
- Resorcinol ProductionDocument1 pageResorcinol Productionsaipa1No ratings yet
- (Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology 338) Wolfgang Pfleiderer (Auth.), Dr. June E. Ayling, M. Gopal Nair, Dr. Charles M. Baugh (Eds.)-Chemistry and Biology of Pteridines and Folates-SpringerDocument805 pages(Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology 338) Wolfgang Pfleiderer (Auth.), Dr. June E. Ayling, M. Gopal Nair, Dr. Charles M. Baugh (Eds.)-Chemistry and Biology of Pteridines and Folates-SpringerdiannanicaNo ratings yet
- Methylamine BrochureDocument4 pagesMethylamine BrochureRaven1013100% (1)
- Sodium Silicate 30mtperdayDocument5 pagesSodium Silicate 30mtperdaySubrata BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Acetic AnhydrideDocument60 pagesAcetic Anhydridecyper zoonNo ratings yet
- Product Description Acetic Acid GlacialDocument3 pagesProduct Description Acetic Acid GlacialNatko47No ratings yet
- Chapter Two Feasibility Study 2.0 Methods of Producing Ammonium Sulphate, ( (NH) SO)Document9 pagesChapter Two Feasibility Study 2.0 Methods of Producing Ammonium Sulphate, ( (NH) SO)Adeyoju RebeccaNo ratings yet
- 0809S2 - Abs Nexant Report Phosphoric AcidDocument6 pages0809S2 - Abs Nexant Report Phosphoric Acidlhphong021191No ratings yet
- Model # SS-370-E: Product SpecificationsDocument1 pageModel # SS-370-E: Product SpecificationsMagikFungusNo ratings yet
- Linear Alpha Olefins Plant CostDocument3 pagesLinear Alpha Olefins Plant CostIntratec SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Benzene: Chemical Economics HandbookDocument3 pagesBenzene: Chemical Economics HandbookMaría VásquezNo ratings yet
- Document PDFDocument2 pagesDocument PDFOki Andri Oktaviana0% (1)
- Industrial Repor1Document33 pagesIndustrial Repor1Truly SelenatorNo ratings yet
- Propylene Oxide - New MethodDocument8 pagesPropylene Oxide - New Methodvinicius_amaral_5No ratings yet
- Nitro ReviewDocument16 pagesNitro ReviewLarry PierceNo ratings yet
- IADOT Hr243 Production Eval Calcium Magnesium Acetate 1982Document11 pagesIADOT Hr243 Production Eval Calcium Magnesium Acetate 1982hamidNo ratings yet
- Ammonia - Semi Final PDFDocument108 pagesAmmonia - Semi Final PDFAmer AlkalaifhNo ratings yet
- Transcript For Search Clini Chemicals and Drugs in PubMedDocument9 pagesTranscript For Search Clini Chemicals and Drugs in PubMedangelso77No ratings yet
- Acetyl Bronners Acid ChlorosulphonationDocument3 pagesAcetyl Bronners Acid Chlorosulphonationkanji63No ratings yet
- DOC052.53.25020 - Hach Methods Quick Reference Guide PDFDocument4 pagesDOC052.53.25020 - Hach Methods Quick Reference Guide PDFLiney Gutiérrez OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Dimethylformamide (DMF) : The Applications and AlternativesDocument2 pagesDimethylformamide (DMF) : The Applications and AlternativesKazy Mohammad Iqbal HossainNo ratings yet
- Haber - Bosch ProcessDocument12 pagesHaber - Bosch Processapi-487208181No ratings yet
- 1 Chemical Engineering-An Overview 1Document5 pages1 Chemical Engineering-An Overview 1R E Vin GNo ratings yet
- 424 Manual 11Document45 pages424 Manual 11Jaamac DhiilNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practicals 2023-2024Document30 pagesChemistry Practicals 2023-2024prashant10thbNo ratings yet
- Garbage EnzymeDocument5 pagesGarbage Enzymehaw6298100% (1)
- Catalytic Oxidation of Ammonia I Ilchenko Etl J. Catal. 1975Document14 pagesCatalytic Oxidation of Ammonia I Ilchenko Etl J. Catal. 1975juan davidNo ratings yet
- Industrial Processes For ChemistryDocument12 pagesIndustrial Processes For Chemistryncaroline443No ratings yet
- Manures Fertilizers AgrochemicalsDocument188 pagesManures Fertilizers AgrochemicalsYugraj GawandeNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems: Problem-1Document35 pagesSolved Problems: Problem-1Sushma ThakurNo ratings yet
- CuO Graphene Nanocomposite For Nitrogen Reduction ReactionDocument8 pagesCuO Graphene Nanocomposite For Nitrogen Reduction ReactionAminu HassanNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Laboratory ReagentDocument15 pagesPreparation of Laboratory ReagentAbhishek RajNo ratings yet
- March 3, 1936. J. W. Hayes E Al 2,032,699: W. We Arza Wa Wag 562ufzarzDocument4 pagesMarch 3, 1936. J. W. Hayes E Al 2,032,699: W. We Arza Wa Wag 562ufzarzRuchita PoilkarNo ratings yet
- Buletinul Ipt Iasi - 2005Document308 pagesBuletinul Ipt Iasi - 2005danmertzNo ratings yet
- III.1 2 The Transannular CyclizationDocument5 pagesIII.1 2 The Transannular CyclizationRichard PortillooNo ratings yet
- IA and IIA Group ElementsDocument4 pagesIA and IIA Group ElementsGagan NdNo ratings yet
- Prepare Cuprammonium Rayon Threads From Filter PaperDocument5 pagesPrepare Cuprammonium Rayon Threads From Filter PaperChetan ChhalaniNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: CHEMISTRY 5070/03Document10 pagesCambridge O Level: CHEMISTRY 5070/03Sandra PepesNo ratings yet
- Nutrients (Nitrogen and Phosphorus) in Water and WastewaterDocument72 pagesNutrients (Nitrogen and Phosphorus) in Water and WastewaterDr. Akepati Sivarami ReddyNo ratings yet
- BOW Guru Antra Goal: Anand PrakashDocument35 pagesBOW Guru Antra Goal: Anand PrakashCube WorldNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Solution 25%Document10 pagesAmmonia Solution 25%lailahalim1994No ratings yet
- 0 B6 G3 o Mrvda NZB 3 Pa WWVWB Wty X1 EDocument142 pages0 B6 G3 o Mrvda NZB 3 Pa WWVWB Wty X1 EAishNo ratings yet
- ISEE-Understading The Volatility of Ammonium Nitrate PriceDocument23 pagesISEE-Understading The Volatility of Ammonium Nitrate PriceJorge Luis JamesNo ratings yet
- THOMSON 1965 Air PollutionDocument22 pagesTHOMSON 1965 Air PollutionbbbbbbbNo ratings yet
- Applied Catalysis B: EnvironmentalDocument13 pagesApplied Catalysis B: EnvironmentalAishwarya K NNo ratings yet
- Review QuestionsDocument40 pagesReview QuestionsHyumi DarthNo ratings yet
- Arti IndustryDocument30 pagesArti Industryविनय कुमार शर्माNo ratings yet
- Chemical Composition of Rainwater Captured in An Oil RefineryDocument6 pagesChemical Composition of Rainwater Captured in An Oil RefineryseventhsensegroupNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument16 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelRoseNo ratings yet
- CH2103 Lab Manual 2017Document30 pagesCH2103 Lab Manual 2017Anuraj LahaNo ratings yet
- Identifying Ions and Gases.Document15 pagesIdentifying Ions and Gases.phineas123No ratings yet