Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4 Ethics Social Responsibility
Uploaded by
santasantitaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
4 Ethics Social Responsibility
Uploaded by
santasantitaCopyright:
Available Formats
23/1/2007
1
ETHICS & SOCIAL
RESPONSIBILITY
23/1/2007
2
TODAYS PLAN
TOPIC: Ethics & Social Responsibility
Social Responsibility & the Corporation
Cultural relativism & ethical imperialism?
CORRUPTION
Caselets
Discussion
23/1/2007
3
WHEN IS DIFFERENT JUST
DIFFERENT, & WHEN IS DIFFERENT
WRONG?
23/1/2007
4
GUIDELINES THAT HAVE BEEN
USED
Cultural relativism
No cultures ethics are better than any others (no
international rights & wrongs)
Ethical imperialism
Do everywhere exactly as they do at home
Theory behind cultural imperialism: absolutism
Single list of truths
Can only be expressed with one set of concepts
Call for the same behavior around the world.
23/1/2007
5
BALANCING THE EXTREMES:
THREE GUIDING PRINCIPLES
Respect for core human values, which
determine the absolute moral threshold for
all business activities
Respect for local traditions
The belief that context matters when
deciding what is right & what is wrong
23/1/2007
6
GUIDELINES FOR ETHICAL
LEADERSHIP
Treat corporate values & formal standards of
conduct as absolutes
Design & implement conditions of engagement
for suppliers & customers
Allow foreign business units to help formulate
ethical standards & interpret ethical issues
In host countries, support efforts to decrease
institutional corruption
Exercise moral imagination
23/1/2007
7
ADVERTISING & FREE SPEECH? THE
CASE OF NIKE & HUMAN RIGHTS
Identify the ethical issues faced by MNCs in their treatment of foreign workers that could
bring allegations of misconduct in their operations?
Would the use of third party independent contractors alleviate or insulate MNCs from being
attached, and would such use be a good defensive shield against charges of abuse of
their employees?
Are statements by companies that show good social and moral conduct in the treatment of
their workers part of the image they create therefore part of their advertising message?
Are statements by companies that show good social and moral conduct in the
treatment of their workers part of the image they create therefore part of their
advertising message? Do consumers judge companies and make their buying
decision based on their perceptions of corporate behavior and values they
exhibit? Is the historic made in question (e.g. Made in the USA) now being
replaced by the made by inquiry (e.g. Made by Company X or for Company
X by Company Y)?
Given the principles noted in the case, how can companies comment on their
positive actions to promote human rights so consumers will think well of them?
What would propose a company do (a) nothing? (b) construct a corporate code
of ethics? (c) align with some of the universal covenants or compacts prepared
by international agencies?
23/1/2007
8
CASELETS ON CORRUPTION
Divide into groups
Decide what you
should do in each
case if you were the
decision-maker
Class discussion
23/1/2007
9
BRIBERY & CORRUPTION
Corruption: abuse of public office for
private gain
Corruption is both an ethical matter & an
economic matter (large costs
Considered by many to be the key reason
for the lack of progress in economic reform
in non-Western countries.
23/1/2007
10
CORRUPTION
Causal factors
Interdependence of the economic & political spheres
Types of corruption
Petty
Grand
How do you draw the line between legitimate &
illegitimate interactions between the private sector &
politicians is more difficult to draw
23/1/2007
11
WHERE DOES CORRUPTION
OCCUR?
Most of the corrupt countries are developing
countries
Corruption also varies across sectors and
activities
Highest in the public works, construction, & defense
sectors
Lowest in banking & agriculture
In terms of government activities, most prone are: tax
departments, police departments, customs agencies,
procurement & distribution of international aid
23/1/2007
12
THE COSTS OF CORRUPTION
Corruption is associated with a range of negative
macroeconomic effects
Reduced investment & GDP growth, reductions in
the flow of foreign direct investment, income
inequality, & misallocation of government resources
For managers engaged in international business,
corruption has become a major concern
Prediction that half of the worlds GDP growth will
occur in non-OECD countries & those countries rank
high in corruption
23/1/2007
13
ECONOMIC COST OF CORRUPTION
CORRUPT ACTIVITY ECONOMIC COST
Government bureaucrat accepts
speed money to issue licenses
3% to 10% premium above licensing
fee
Organized crime, with sanction of
local officials, controls & sets prices in
the markets
Goods sell at 15% to 20% premium
Tax collectors permit under-reporting
of income in exchange for a bribe
Income tax revenues reduced by up to
50%
Government officials order expensive
capital goods, or overpay or
overinvoice for public works, in
exchange for kickbacks.
Goods & services priced 20% to 100%
higher than necessary.
23/1/2007
14
THE CANADIAN SITUATION
BUSINESS ACTIVITY: International Code of
Ethics for Canadian Business (1997)
GOVERNMENT ACTIVITIES:
OECD Guidelines for Multinational Enterprises (
Canada obliged to established a National Contact Point to
promote the guidelines
OECD Analytical Work on Corporate Codes
Corruption Convention of the OECED
Corruption of Foreign Public Officials Act passed by
Parliament in 2/1999
23/1/2007
15
EFFORTS BY INTERNATIONAL
DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS: THE
WORLD BANK
World Bank
Since 1996, Bank launched more than 600 anti-
corruption programs in nearly 100 countries
(including loans)
Institutionalized efforts: Department of Institutional
Integrity to investigate claims of fraud & corruption
& a Sanctions Committee to adjudicate cases &
assess penalties
More than 180 companies & individuals debarred
from doing business with the Bank
23/1/2007
16
EFFORTS BY INTERNATIONAL
DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS:
REGIONAL DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS
The Inter-American, European, & Asian
Development Banks followed World
Banks lead
IMF has suspended aid to some countries
because they did not combat corruption
Suggestion that anti-corruption
requirements be placed in the
conditionality agreements
23/1/2007
17
PRIVATE EFFORTS:
TRANSPARENCY INTERNATIONAL
Founded in 1994 in Berlin active in more than
70 countries
72 national chapters, source book of best
practices & started several innovative pilot
projects.
Lobby governments, inform media & bring
together people concerned with corruption
Annual corruption Perception Index (measures
perception of corruption in 85 countries)
23/1/2007
18
2006 BRIBE PAYERS INDEX
HIGHEST LEVEL LOWEST LEVEL
India Switzerland
China Sweden
Russia Australia
Turkey Austria
Taiwan Canada
Malaysia UK
South Africa Germany
23/1/2007
19
2006 CORRUPTION
PERCEPTIONS INDEX
MOST CORRUPT MOST HONEST
Haiti Finland, Iceland, New Zealand
Myanmar, Iraq, Guinea
Denmark
Sudan, Congo, Chad, Bangladesh
Singapore
Uzbekistan, Guinea, Ivory Coast,
Cambodia, Belarus
Sweden
Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Sierra
Leone, Pakistan, Nigeria,
Kyrgyzstan, Kenya, Rep. Congo,
Angola
Switzerland
23/1/2007
20
CORPORATE TRANSPARENCY
Role of codes of conduct
Large accounting firms have forensic accounting
experts
Collective action several industry groups
developed sector-specific guidelines on tackling
corruption & promoting access to information.
Whistleblowers importance of giving these
individuals protection
Importance of tightening up financial reporting &
maintaining the independence of auditors
23/1/2007
21
BRIBERY IN BUSINESS SECTORS
Public works/construction
Arms & defense
Oil & gas
Real estate/property
Power generation/transmission & telecommunications
Mining
Pharmaceuticals/medical care & transportation & storage
Heavy manufacturing
Banking & finance
Civilian aerospace
IT & forestry
Agriculture, light manufacturing, fishery
23/1/2007
22
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN GNP
& PROPENSITY FOR BRIBERY
23/1/2007
23
ASSIGNMENT FOR 25/1/2007
CASE: Conocos Green
Oil Strategy
Division of the class into
four groups:
Read both the main case &
your case
First part of class: work in
groups: Ecuadorian
government, indigenous
peoples, environmental
groups, management
Second part: negotiation (2
representatives per side)
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- DishonestyDocument2 pagesDishonestysantasantitaNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Atty. Sixto Rodriguez JRDocument1 pageAtty. Sixto Rodriguez JRsantasantitaNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- PolcaseDocument243 pagesPolcasesantasantitaNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- PolcaseDocument243 pagesPolcasesantasantitaNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- 1ST SetDocument53 pages1ST SetMyra De Guzman PalattaoNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- ARD's QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesARD's QuestionnairesantasantitaNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- School HymnDocument1 pageSchool Hymnsantasantita100% (1)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Republic of The PhilippinesDocument6 pagesRepublic of The PhilippinessantasantitaNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Case 1Document65 pagesCase 1santasantitaNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Punctuation: This Is Mine. Come and Get MeDocument12 pagesPunctuation: This Is Mine. Come and Get MesantasantitaNo ratings yet
- Health EducationDocument7 pagesHealth EducationsantasantitaNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Edward Kenneth Ngo TeDocument41 pagesEdward Kenneth Ngo TesantasantitaNo ratings yet
- Transparency and Accountability: Managing' To Reduce Corruption Involving The StaffDocument24 pagesTransparency and Accountability: Managing' To Reduce Corruption Involving The StaffsantasantitaNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Classification of DiabetesDocument2 pagesClassification of DiabetessantasantitaNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Ecg MachineDocument8 pagesEcg MachinesantasantitaNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- WomanDocument1 pageWomansantasantitaNo ratings yet
- Types of Communication in The WorkplaceDocument32 pagesTypes of Communication in The Workplacesantasantita100% (2)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- WomanDocument1 pageWomansantasantitaNo ratings yet
- Health EducationDocument7 pagesHealth EducationsantasantitaNo ratings yet
- 10 Laws For The CommunityDocument2 pages10 Laws For The CommunitysantasantitaNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Civil Law CasesDocument222 pagesCivil Law CasessantasantitaNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- CambodiaDocument11 pagesCambodiasantasantitaNo ratings yet
- People of CambodiaDocument3 pagesPeople of CambodiasantasantitaNo ratings yet
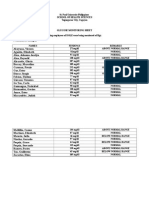
- St. Paul University Philippines School of Health Sciences Tuguegarao City, CagayanDocument2 pagesSt. Paul University Philippines School of Health Sciences Tuguegarao City, CagayansantasantitaNo ratings yet
- Balance Sheet StatementDocument8 pagesBalance Sheet StatementsantasantitaNo ratings yet
- Tax 2 CasesDocument48 pagesTax 2 CasessantasantitaNo ratings yet
- Classification of DiabetesDocument2 pagesClassification of DiabetessantasantitaNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- GlucoseDocument2 pagesGlucosesantasantitaNo ratings yet
- Belongings and Underpayment of Wages Against Petitioner. Petitioner Offered To Amicably Settle The Money Claims ofDocument20 pagesBelongings and Underpayment of Wages Against Petitioner. Petitioner Offered To Amicably Settle The Money Claims ofsantasantitaNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)