Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Demographics
Uploaded by
cbellsnlCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Demographics
Uploaded by
cbellsnlCopyright:
Available Formats
Niger
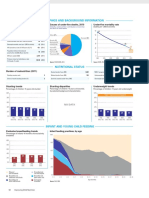
DEMOGRAPHICS MATERNAL AND NEWBORN HEALTH
Total population (000) 13,737 (2006) Under-five mortality rate Causes of under-five deaths Causes of maternal deaths Coverage along the continuum of care
Deaths per 1000 live births Globally more than one third of child deaths are attributable to Regional estimates for Africa, 1997-2002
Total under-five population (000) 2,713 (2006) undernutrition
320 Causes of neonatal
Unmet need for family planning (%) 16 (2006)
Births (000) 683 (2006) Obstructed labor Contraceptive
300 deaths Abortion 11 Pre-pregnancy
Birth registration (%) 32 (2006) 253 Diarrhoea Diarrhoea 3% Antenatal visits for woman (4 or more visits, %) 15 (2006) Anaemia 4% 4% prevalence rate
Pneumonia 20% Congenital 5% 4% Antenatal visit
Under-five mortality rate (per 1000 live births) 253 (2006) 240 25% Other 7% (1 or more) 46 Pregnancy
Tetanus 10%
Intermittent preventive treatment for malaria (%) 0 (2006)
Hypertensive Skilled attendant
Infant mortality rate (per 1000 live births) 148 (2006) disorders Haemorrhage 33 Birth
180 Preterm 17% C-section rate (total, urban, rural; %) 34%
at birth
43 (2000) 9%
Neonatal mortality rate (per 1000 live births) HIV/AIDS Neonatal (Minimum target is 5% and maximum target is 15%) 1, 5, 0 (2006)
107 1% 17% *Postnatal care Neonatal period
Total under-five deaths (000) 173 (2006) 120 Asphyxia 23% Sepsis/Infections,
Injuries Early initiation of breastfeeding (within 1 hr of birth, %) 48 (2006) including AIDS Exclusive
MDG Target 1% breastfeeding 14 Infancy
Maternal mortality ratio (per 100,000 live births) 1,800 (2005) 60 16%
7 (2005) Postnatal visit for baby (within 2 days for home births, %) --- Measles
Lifetime risk of maternal death (1 in N) Measles Other Infection 36%
Other causes
47
0 7% Malaria 15%
Total maternal deaths 14,000 (2005) 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 14% 30%
Source: Lawn JE, Cousens SN
0 20 40 60 80 100
Source: UNICEF, 2006 Source: WHO, 2006 for CHERG (Nov 2006) Source: Khan, Khalid S., et al, Lancet 2006:367:1066-74 Source: DHS, MICS, Other NS
*See Annex for indicator definition
Antenatal care Skilled attendant at delivery Neonatal tetanus protection
INTERVENTION COVERAGE FOR MOTHERS, NEWBORNS AND CHILDREN Percent women aged 15-49 years attended at least once by a Percent live births attended by skilled health personnel Percent of newborns protected against tetanus
NUTRITION skilled health provider during pregnancy
Stunting prevalence (moderate and severe, %) 55 (2006) Complementary feeding rate (6-9 months, %) 62 (2006) 100 100 100
Wasting prevalence (moderate and severe, %) 12 (2006) Low birthweight incidence (%) 13 (2000) 80 80 80 71
Underweight prevalence Exclusive breastfeeding Vitamin A supplementation 60 60 60
Percent
Percent
Percent
46
Percent children < 5 years underweight for age* Percent infants < 6 months exclusively breastfed Percent children 6-59 months receiving vitamin A doses 39 41
40 30 40 33 40
At least one dose Two doses
94 15 18 16
100 100 100 92 89 95 20 20 20
100 94
92 77
80 80 80 0 0
80 88
77 1992 1998 2000 2006 1992 1998 2000 2006 1981 1986 1991 1996 2001 2006
68
60 60 60 DHS DHS MICS DHS DHS DHS MICS DHS
Percent
Percent
Percent
Source: WHO/UNICEF
41 44
40
40 40 40
20 20 14 20 0
WATER AND SANITATION EQUITY
3 1 1
0 0 0
1992 2000 2006 1992 1998 2000 2006 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 Water Sanitation Coverage gap by wealth quintile
DHS MICS DHS DHS DHS MICS DHS Source: UNICEF
Percent population using improved drinking water sources Percent population using improved sanitation facilities
*Based on 2006 WHO reference population Rural Urban Total Rural Urban Total
100 100 100
CHILD HEALTH 80
80 80 80
62
Immunization Malaria prevention Prevention of mother to child 60
46
60 60
Percent
Percent
Percent
Percent of children immunised against measles 43
Percent of children immunised with 3 doses DPT
Percent children < 5 years sleeping under ITNs transmission of HIV 35 39 36 35
Percent HIV+ pregnant women receiving ARVs for PMTCT
40 40 40
Percent of children immunised with 3 doses Hib
13
20 20 20
7 4
100 100 10 2
0 0 0
80 80 8 1990 2004 1990 2004 Poorest 2nd 3rd 4th Wealthiest
7
Source: WHO/UNICEF JMP, 2006 Source: WHO/UNICEF JMP, 2006
60 60 6 1998 2000 2006
Percent
Percent
Percent
47
DHS MICS MICS
40
39
40 4 POLICIES SYSTEMS
2
20 20 2
7 Coverage gap (%) 70 67 60
1 International Code of Marketing of Breastmilk Financial Flows and Human Resources
0 0 0 Substitutes Partial Ratio
1990 1995 2000 2005 2006 2000 2006 2005 2006 Per capita total expenditure on health (US$) 26 (2007) poorest/wealthiest 2.0 1.8 1.8
Source: WHO/UNICEF MICS DHS Other NS Other NS
New ORS formula and zinc for management of Difference
General government expenditure on health as
diarrhoea Yes poorest-wealthiest (%) 40 34 29
% of total government expenditure (%) 10 (2007)
Diarrhoeal disease treatment Malaria treatment Pneumonia treatment
Percent children < 5 years with diarrhoea receiving oral rehydration Percent febrile children < 5 years using antimalarials Percent children < 5 years with suspected pneumonia taken to Community treatment of pneumonia with antibiotics Yes Out-of-pocket expenditure as % of total
therapy or increased fluids, with continued feeding appropriate health provider
Percent children < 5 years with suspected pneumonia receiving expenditure on health (%) 40 (2007)
IMCI adapted to cover newborns 0-1 week of age Yes
antibiotics
Density of health workers (per 1000 population) 0.3 (2004)
100 100 100 Costed implementation plan(s) for maternal,
newborn and child health available Yes Official Development Assistance to child health
80 80 80 per child (US$) 5 (2005)
Midwives be authorised to administer a core set of
60 60 60 life saving interventions Yes Official Development Assistance to maternal and
Niger
Percent
Percent
Percent
43 48 neonatal health per live birth (US$) 5 (2005)
40 40 40 Maternity protection in accordance with ILO
27 33 27 National availability of Emergency Obstetric Care
26 Convention 183 Partial
20 20 20 14 services (% of recommended minimum) 68 (2000)
12 9 Specific notification of maternal deaths No
0 0 0
1992
DHS
1998
DHS
2000
MICS
2000
MICS
2006
DHS
1992
DHS
1998
DHS
2000
MICS
Countdown to 2015
2008 Report
You might also like
- Epidemiological Aspects of Maternal and Child HealthDocument30 pagesEpidemiological Aspects of Maternal and Child HealthNitin Sharma100% (1)
- On Epidemological Aspects of Maternal and Child HealthDocument30 pagesOn Epidemological Aspects of Maternal and Child HealthBisma Maqbool67% (3)
- AKI Provinsi Bali 2018 3Document29 pagesAKI Provinsi Bali 2018 3witaNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- Guinea BissauDocument1 pageGuinea BissaucbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- Burkina FasoDocument1 pageBurkina FasocbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- An Go LaDocument1 pageAn Go LacbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- Country Health Profile: Maternal, Newborn & Child Survival in FijiDocument4 pagesCountry Health Profile: Maternal, Newborn & Child Survival in Fijipaperpin27No ratings yet
- Ye MenDocument1 pageYe MencbellsnlNo ratings yet
- Liberia: Country ProfileDocument4 pagesLiberia: Country Profilegeorgeloto12No ratings yet
- Nutrition IDN PDFDocument2 pagesNutrition IDN PDFdini mutia KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition LCADocument2 pagesNutrition LCAShernia EliboxNo ratings yet
- Maternal CZEDocument4 pagesMaternal CZEYajie LuoNo ratings yet
- Pakistan 2015Document2 pagesPakistan 2015shujahkianiNo ratings yet
- Nutrition PHL PDFDocument2 pagesNutrition PHL PDFJaiy HingcoNo ratings yet
- Jamaica Country Profile Highlights Maternal and Child Health StatisticsDocument4 pagesJamaica Country Profile Highlights Maternal and Child Health StatisticsZineil BlackwoodNo ratings yet
- Tracking Progress for Maternal and Child HealthDocument2 pagesTracking Progress for Maternal and Child Healthmichael8spree8michaeNo ratings yet
- KMC To Reduce Neonatal Mortality Hadi P Unair 29 Sept 2016Document63 pagesKMC To Reduce Neonatal Mortality Hadi P Unair 29 Sept 2016mimimomopipiNo ratings yet
- G Minaccia Parto PretDocument64 pagesG Minaccia Parto PretEleonora Francesco Consalvo DonzelliNo ratings yet
- Essential Newborn Care: From Evidence To Practice: Maria Asuncion Silvestre, MD, FPSNBM, FaapDocument84 pagesEssential Newborn Care: From Evidence To Practice: Maria Asuncion Silvestre, MD, FPSNBM, FaapShane Lim GarciaNo ratings yet
- INDICATORS of HealthDocument3 pagesINDICATORS of Healthrajforever17No ratings yet
- Child Health Programme: 4.2.2 Causes of Child Mortality in IndiaDocument24 pagesChild Health Programme: 4.2.2 Causes of Child Mortality in IndiaSolomon JosephNo ratings yet
- Mort Afro Tza TanzaniaDocument2 pagesMort Afro Tza TanzaniaJan TanzaniaNo ratings yet
- Major causes of death in children under five globally in 2008Document1 pageMajor causes of death in children under five globally in 2008raissa leeNo ratings yet
- Country Health System Fact Sheet 2006 Guinea-BissauDocument8 pagesCountry Health System Fact Sheet 2006 Guinea-BissauJonas WillmerNo ratings yet
- Maternal Mortality in OmanDocument2 pagesMaternal Mortality in OmanmRta03100% (1)
- Prenatal and Postnatal CareDocument5 pagesPrenatal and Postnatal Caresarguss14100% (7)
- 1malnutrition As Health ProblemDocument37 pages1malnutrition As Health ProblemIntan Sahara BachsinNo ratings yet
- Essential Newborn CareDocument54 pagesEssential Newborn CareBrigitte CovarrubiasNo ratings yet
- The Open Ophthalmology JournalDocument5 pagesThe Open Ophthalmology JournalFenny Duma SariNo ratings yet
- Modul Pelatihan KotaDocument7 pagesModul Pelatihan KotaladyanjaniNo ratings yet
- A Practical Approach To Preventing Child Deaths: What The Pediatrician Can DoDocument44 pagesA Practical Approach To Preventing Child Deaths: What The Pediatrician Can DoSophia Loraine Dorone JesuraNo ratings yet
- Stakeholder Meeting - Revitalizing IudDocument52 pagesStakeholder Meeting - Revitalizing Iudkarun009640No ratings yet
- 496 Mongolia Fact SheetsDocument2 pages496 Mongolia Fact SheetsShotokan Karate MongoliaNo ratings yet
- Materi Sesi 1 - Pembicara 1 - Dr. Asri C. Adisasmita, MPH, PH.D (Seminar Kesehatan Nasional Universitas Indonesia Tahun 2017 FKM)Document33 pagesMateri Sesi 1 - Pembicara 1 - Dr. Asri C. Adisasmita, MPH, PH.D (Seminar Kesehatan Nasional Universitas Indonesia Tahun 2017 FKM)Niluh Putu DikaNo ratings yet
- 1 The High Risk MotherDocument161 pages1 The High Risk MotherRaquel M. MendozaNo ratings yet
- South Sudan CD2030 2020Document2 pagesSouth Sudan CD2030 2020anjelopaul2017No ratings yet
- 2022 March of Dimes Report Card-ArkansasDocument2 pages2022 March of Dimes Report Card-ArkansasCurtisNo ratings yet
- Par To GraphDocument15 pagesPar To GraphcarNo ratings yet
- A Strategy For Reducing Maternal and Newborn Deaths by 2015 and BeyondDocument15 pagesA Strategy For Reducing Maternal and Newborn Deaths by 2015 and BeyondRifdaKhairunnisa NisaNo ratings yet
- WHO CancerReport 2020 MEXDocument2 pagesWHO CancerReport 2020 MEXAldo Leonardo De Jesus GarduzaNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- Tanzania, United Republic ofDocument1 pageTanzania, United Republic ofcbellsnlNo ratings yet
- Ye MenDocument1 pageYe MencbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- Ye MenDocument1 pageYe MencbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- The GambiaDocument1 pageThe GambiacbellsnlNo ratings yet
- Ben inDocument1 pageBen incbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- Burkina FasoDocument1 pageBurkina FasocbellsnlNo ratings yet
- Sierra LeoneDocument1 pageSierra LeonecbellsnlNo ratings yet
- Ben inDocument1 pageBen incbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- Ben inDocument1 pageBen incbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- Ben inDocument1 pageBen incbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- Ben inDocument1 pageBen incbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet