Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pregnancy Rates After Tubal Reversal by Fallopian Tube Lengths
Uploaded by
Gary S Berger MDCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pregnancy Rates After Tubal Reversal by Fallopian Tube Lengths
Uploaded by
Gary S Berger MDCopyright:
Available Formats
Tubal Reversal Pregnancy Study 2009
Pregnancy Rates By Fallopian Tube Lengths
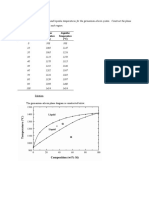
The fallopian tube lengths remaining after a tubal ligation procedure are important
determinants of the chances of getting pregnant after tubal reversal surgery. (Normal
fallopian tube length before a tubal ligation is approximately 10 cm or 4 inches.)
Tubal segment lengths are measured routinely during surgery at Chapel Hill Tubal
Reversal Center. The average length of the two fallopian tubes after repair was correlated
with the likelihood of pregnancy after tubal reversal (Table 6). Women with longer tubal
lengths had higher pregnancy rates than women with shorter lengths following tubal
reversal. Women with tubal lengths of 7.5 cm or longer had a pregnancy rate of 77%. The
pregnancy rate declined as tubal length decreased, but even women with the shortest
tubes (less than 2.5 cm) became pregnant (38%). Although previously unreported in the
medical literature, it became apparent during this study that a repaired fallopian tube of
any length can result in pregnancy. Based on reports by women with only 1 fallopian
tube, we now know that tubal lengths as short as 1 cm can result in a normal pregnancy.
Table 6. Pregnancy Rates by Tubal Length (cm)
Length Total Women Pregnant (No.) Pregnant (%)
7.5+ 469 362 77%
5.0-7.4 2826 1966 70%
2.5-4.9 1602 920 57%
<2.5 112 42 38%
Tubal Ligation Method And Tubal Length
When tubal ligation method and average tubal lengths are taken into account
simultaneously, it becomes clear that the amount of fallopian tube remaining after a
sterilization procedure is the more important factor predicting the chances of getting
pregnant after tubal reversal surgery (Table 7). This makes sense, since the less damage
that occurs to the fallopian tube during a sterilization procedure, the more remains to be
able to function normally once the tube has been surgically repaired.
Table 7. Pregnancy Rates by Tubal Ligation Method and Tubal Length (cm)
Method 7.5+ 5.0-7.4 2.5-4.9 <2.5
Clip 137/168 (82%) 155/222 (70%) 7/11 (64%) -
Ring 86/118 (73%) 493/672 (73%) 35/62 (57%) -
Coagulation 49/62 (79%) 516/774 (69%) 448/706 (64%) 27/76 (36%)
Ligation/Resection 72/92 (78%) 723/1060 (68%) 395/736 (54%) 12/26 (46%)
Tubal Reversal Pregnancy Study 2009
Table Of Contents:
• Overview
• Study Method
• Patient Population – US States
• Patient Population – Age and Tubal Ligation Procedures
• Pregnancy Rates by Age and Method
• Tubal Reversal Pregnancy Rates by Tubal Lengths (this page)
• Pregnancy Outcomes
• Tubal Reversal vs. IVF
• About Pregnancy Statistics
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Tubal Ligation Reversal Editorial Published in TrianglePhysician April 2010Document2 pagesTubal Ligation Reversal Editorial Published in TrianglePhysician April 2010Gary S Berger MD100% (1)
- Pregnancy Outcomes After Tubal ReversalDocument2 pagesPregnancy Outcomes After Tubal ReversalGary S Berger MD100% (1)
- Pregancy Rates by Age and Tubal Ligation MethodDocument3 pagesPregancy Rates by Age and Tubal Ligation MethodGary S Berger MDNo ratings yet
- Scholarly Research and PublicationsDocument3 pagesScholarly Research and PublicationsGary S Berger MD100% (1)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Well (Version 2.4)Document3 pagesThe Well (Version 2.4)Thaís EspinosaNo ratings yet
- PASSMEDICINE MCQs-PHARMACOLOGYDocument107 pagesPASSMEDICINE MCQs-PHARMACOLOGYMohammad Saleh100% (1)
- Highest Efficiencies For Various Industrial Applications: PumpsDocument8 pagesHighest Efficiencies For Various Industrial Applications: Pumpsahmed MareiNo ratings yet
- MSDS Industrial MargarineDocument3 pagesMSDS Industrial MargarineAeropaulo14No ratings yet
- CPHQ Text BookDocument20 pagesCPHQ Text BookCphq Cphq Ali100% (2)
- Plant Based Plan White PaperDocument24 pagesPlant Based Plan White PaperSara AdemovicNo ratings yet
- Big BazaarDocument6 pagesBig BazaaraniketsangodcarNo ratings yet
- 6 Instrumentation PDFDocument144 pages6 Instrumentation PDFWanderley MandruzatoNo ratings yet
- Glycerin As A Renewable Feedstock For EpichlorohydDocument6 pagesGlycerin As A Renewable Feedstock For EpichlorohydMuhammad RidhauddinNo ratings yet
- Method Setting Out of Drainage 2Document9 pagesMethod Setting Out of Drainage 2amin100% (1)
- VW Golf 8 Variant WD EngDocument664 pagesVW Golf 8 Variant WD EngLakhdar BouchenakNo ratings yet
- Put The Verbs in Brackets Into The - Ing Form or The InfinitiveDocument10 pagesPut The Verbs in Brackets Into The - Ing Form or The InfinitiveThao DaoNo ratings yet
- Composition Solidus Temperature Liquidus Temperature: (WT% Si) (°C) (°C)Document7 pagesComposition Solidus Temperature Liquidus Temperature: (WT% Si) (°C) (°C)Muhammad Ibkar YusranNo ratings yet
- CTS Flexible Benefit PlanDocument53 pagesCTS Flexible Benefit Plannivasshaan100% (2)
- Hookah Bar Business PlanDocument34 pagesHookah Bar Business PlanAbdelkebir LabyadNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Boiler Efficiency - CaseDocument89 pagesAnalysis of Boiler Efficiency - CaseSaritha Yadav100% (5)
- MPCA Response 5.29.20Document2 pagesMPCA Response 5.29.20Duluth News TribuneNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5: Prejudice and StereotypesDocument31 pagesLesson 5: Prejudice and StereotypesZeynep SulaimankulovaNo ratings yet
- Reishi MushroomDocument5 pagesReishi Mushroomjunver100% (4)
- Chapter 4 - Medical Aspects of Food SafetyDocument17 pagesChapter 4 - Medical Aspects of Food SafetyasushkNo ratings yet
- Challenges in The Functional Diagnosis of Thyroid Nodules Before Surgery For TSH-producing Pituitary AdenomaDocument5 pagesChallenges in The Functional Diagnosis of Thyroid Nodules Before Surgery For TSH-producing Pituitary AdenomaAthul IgnatiusNo ratings yet
- Complications of Diabetes MellitusDocument46 pagesComplications of Diabetes MellitusAbhijith MenonNo ratings yet
- Michigan Clinic 2008 NotesDocument10 pagesMichigan Clinic 2008 NotesCoach Brown100% (3)
- LaserDocument12 pagesLasercabe79No ratings yet
- Enzymes in Grain ProcessingDocument1 pageEnzymes in Grain ProcessingAttila-Levente FogarasiNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Consumption and Related Crime Incident in John Paul CollegeDocument17 pagesAlcohol Consumption and Related Crime Incident in John Paul Collegejoy mesanaNo ratings yet
- Leoline Installation and MaintenanceDocument8 pagesLeoline Installation and MaintenanceFloorkitNo ratings yet
- Sebuguero V NLRC Case Digest PDFDocument2 pagesSebuguero V NLRC Case Digest PDFYodh Jamin Ong0% (1)
- Cocktails For A CrowdDocument117 pagesCocktails For A CrowdΓιώργης Δημητρίου100% (2)
- Lecture 38Document10 pagesLecture 38Deepak GuptaNo ratings yet