Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Indian Railways
Uploaded by
Norma0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
422 views14 pagesIR carries on an average, 13 million people across the country everyday. 1 in every ten Indians depended on IR for his livelihood. IR relied on 3 sources of financing - budget support - market borrowing - Internal resources.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIR carries on an average, 13 million people across the country everyday. 1 in every ten Indians depended on IR for his livelihood. IR relied on 3 sources of financing - budget support - market borrowing - Internal resources.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
422 views14 pagesIndian Railways
Uploaded by
NormaIR carries on an average, 13 million people across the country everyday. 1 in every ten Indians depended on IR for his livelihood. IR relied on 3 sources of financing - budget support - market borrowing - Internal resources.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
INDIAN RAILWAYS
INDIAN RAILWAYS AT THE
CROSSROADS
• Largest network under a single management.
• Often called the “lifeline of India”
• Largest employer in the world, employing about 1.6 million (2003).
• Survey revealed that 1 in every ten Indians depended on IR for his
livelihood
• IR carries on an average, 13 million people across the country everyday.
• IR operated as a department under the central government of India.
ORIGIN AND DEVELOPMENT OF IR
• Roots are in 1800’s and was started by the
British East India Company
• Initially used only to transfer goods and
later moved to passenger trains
• First passenger train between Bombay and
Thane in 1853
• To promote construction of Railway lines,
the British parliament introduced guarantee
system.
• By 1870 the total coverage was 4000 miles
ORIGIN AND DEVELOPMENT OF IR
• Darjeeling Himalayan railway was considered the
greatest engineering feat in the history of IR
• In 1950, Janata express trains were introduced
• More affordable to ordinary people
• In 1970’s and 80’s, IR introduced super fast trains
like Rajdhani and Shatabdhi
• Mid 1980’s – Computerised ticketing and reservation
at new Delhi
OPERATIONS OF IR
• A department of government where Railway
minister is the highest authority
• 16 General Managers took care of 16 Zonal
offices
• IR relied on 3 sources of financing
– Budget support
– Market borrowing
– Internal resources
• IR presented a separate budget from the general
budget
• Three types of gauges – narrow, broad and
meter.
SOCIAL ROLE vs. ECONOMIC
ROLE
• Provide subsidized fares to passengers
• Obligation to carry essential goods at a subsidized rate
• IR needed Rs.40 Billion for social obligation but got only
Rs.8 Billion
• They started to subsidise for the losses by charging
exorbitant rates for private freight
• Borrowing at a very high rate of interest from open
market
PROBLEMS FACED BY IR
• Social responsibility vs. Profitability
• Safety
– Old tracks, Bridges and Facilities
– Bad working conditions for train drivers
• Competition from Roadways and Airlines
PRIVATISATION ??
• A good option
• It will stream line operations
• More accountability and responsibility
• A corporate structure
• Implementation nightmare
GAP ANALYSIS
KNOWLEDGE GAP
• Customers seek
– Ease of ticketing, Refundable, on time arrival and
departure, hygiene and good food, cheaper fares,
safety
– Except for the timing, the zone of tolerance for all
other services are met
STANDARD GAP
• Bathroom facilities are not up to the standards
• Loose Berths (seats)
• Waiting rooms not properly maintained
• Inadequate fans and electrical
DELIVERY GAP
• Timings – Delays of trains
• Unclean linen
• Food
• No water in Bathrooms
• No hygiene
COMMUNICATION GAP
• Helpline numbers do not get through
• Improper information on train delays
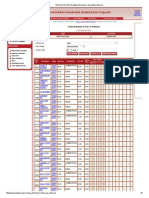
BLUE PRINT
Vehicle Station Platform Arrival/Departure Cart or Train Food TT
Exit
parking ticket display board Coolie Have
Locat tickets
and entry Buy Counter Order Exit
Arrive Give bags e the checked
tickets at Check food with the after
at to Coolie seat as
counter or concerne departu
Statio book
for train or carry it or per d TT on re
n and timings by self to birth the
online in his
enter the train no. menu arrival
advance
Deliver
Greet and Provide food as Provide
provide informati per the Confirmatio
the ticket on n on ticket
order
Check for Take
tickets
availabilit food
y orders
Ticket
registrati Prepare or
on pack food
database
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Ielts Listening Test Part 4 Practice Indian RailwaysDocument2 pagesIelts Listening Test Part 4 Practice Indian RailwaysGhulam qadir100% (1)
- Notes On Railway Signaling-1Document104 pagesNotes On Railway Signaling-1Jay JayNo ratings yet
- Signal PDFDocument56 pagesSignal PDFChinmoy BiswasNo ratings yet
- Delhi To Jammu TrainsDocument3 pagesDelhi To Jammu TrainsPrashant SharmaNo ratings yet
- RailwayDocument39 pagesRailwaysanjeewNo ratings yet
- Indian Railways Stations Re-Development ProjectDocument37 pagesIndian Railways Stations Re-Development ProjectshivNo ratings yet
- RR Toolkit EN New 2017 12 27 CASE6 INDIADocument18 pagesRR Toolkit EN New 2017 12 27 CASE6 INDIANAINA GOYALNo ratings yet
- Railway MCQ Capsule 4Document14 pagesRailway MCQ Capsule 4Vinay ReddyNo ratings yet
- GARIB RATH-Saharsa AmritsarDocument1 pageGARIB RATH-Saharsa AmritsarGaurav SinghNo ratings yet
- Jhajha Railway StationDocument1 pageJhajha Railway StationatewarigrNo ratings yet
- Railways in India - UPSCDocument10 pagesRailways in India - UPSCalokNo ratings yet
- Indian Railways: This Article Is About The Organisation. For General Information On Railways in India, SeeDocument21 pagesIndian Railways: This Article Is About The Organisation. For General Information On Railways in India, SeeAnupam0103No ratings yet
- EMD-SD InstructionsDocument42 pagesEMD-SD Instructionsamitkbharti6784No ratings yet
- Equirus Railways - Initiating Coverage PDFDocument56 pagesEquirus Railways - Initiating Coverage PDFAhmed MadhaNo ratings yet
- Transformation of Indian RailwaysDocument7 pagesTransformation of Indian RailwaysSHAIK ADIL ISLAMNo ratings yet
- Assignment RailwayDocument6 pagesAssignment RailwayAhmed MastanNo ratings yet
- June 2014Document72 pagesJune 2014rohitNo ratings yet
- Indian Railways 1234Document15 pagesIndian Railways 1234abhi0006100% (1)
- Bankruptcy To BillionsDocument14 pagesBankruptcy To BillionsRoshin P.SNo ratings yet
- Supriya's ppt-1Document9 pagesSupriya's ppt-1ABHISHEK SINGHNo ratings yet
- Development of Transport and CommunicationDocument20 pagesDevelopment of Transport and CommunicationPOORNIMA NNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety in IR For SCESDocument12 pagesElectrical Safety in IR For SCESBrijendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Basic Guide On Train OperationDocument281 pagesBasic Guide On Train Operationatliboy50% (2)
- Project Report "Transport System in India" Transport System: Ransport: Modes of TransportDocument9 pagesProject Report "Transport System in India" Transport System: Ransport: Modes of TransportAvishekNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Vi Summary of Findings, Suggestions and ConclusionDocument37 pagesChapter - Vi Summary of Findings, Suggestions and ConclusionShouvik palNo ratings yet
- Anjana - ProjectDocument112 pagesAnjana - Projectdishagohel4211No ratings yet
- HISTORY-OF-INDIAN-RAILWAY - DFCCIL-2023-02-10-10-43-32 - RemovedDocument73 pagesHISTORY-OF-INDIAN-RAILWAY - DFCCIL-2023-02-10-10-43-32 - RemovedDharnidhar kumarNo ratings yet
- BR Block 08Document16 pagesBR Block 08mailbkraoNo ratings yet
- Rolling Corridor Block Program of SC Division-1Document2 pagesRolling Corridor Block Program of SC Division-1rajini mulukuntlaNo ratings yet
- Train Time Table To MumbaiDocument3 pagesTrain Time Table To MumbaiPrashant SarojNo ratings yet