Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CI 05 Solid Remote
Uploaded by
Alagappan ArunachalamCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CI 05 Solid Remote
Uploaded by
Alagappan ArunachalamCopyright:
Available Formats
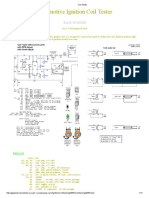
CIRCUIT IDEAS
SOLIDSTATE REMOTE CONTROL SWITCH SAN
I TH
EO
SEEMANT SINGH from the transmitter, the
output of the IR receiver
H
ere is a solidstate remote control module is high (approx.
switch which uses readily available 5V).
electronic components. The control When the transmitter
circuit comprises the transmitter and re- is pointed at the receiver
ceiver sections. The range of the transmit- and switch S1 is momen-
ter is around seven metres. tarily pressed, the trans-
The transmitter circuit (shown in Fig. mitted IR rays are sensed
1) is built around a timer IC (555) wired by the receiver module
as an astable multivibrator. It works off a and its output pulses low
9V battery. When remote control switch to trigger the monostable
S1 is pressed, the astable multivibrator (IC2). The output of IC2
built around IC1 starts oscillating at a fre- goes high for about five
quency of about 38 kHz. The signal fre- seconds. Thus, even if
quency at output pin 3 of IC1 is transmit- Fig. 1: Transmitter circuit you press the remote
Fig. 2: Receiver circuit
ted through two infrared diodes (IR LED1 consists of regulator IC 7806 (IC4), IR re- switch more than one time by mistake,
and IR LED2). A green LED (LED1) con- ceiver module (TSOP1738), timer 555 there won’t be any change in the output
nected to pin 3 glows whenever S1 is (IC2) and decade counter CD4017 (IC3). of the receiver within this period and hence
pressed, indicating the presence of a sig- Timer 555 (IC2) is wired as a monostable no undesired switching of the appliance.
nal for transmission at the output of the multivibrator. The signal reception is indicated by glow-
multivibrator. The 9V DC power supply for the re- ing of the green LED (LED3).
The output frequency F at pin 3 of IC1 ceiver circuit is regulated by regulator IC The output of IC2 is given to the clock
depends on the timing components, viz, 7806. The presence of power in the circuit is input (pin 14) of IC3. Here, IC3 is wired as
resistors R1 and R2 and capacitor C2. It is indicated by glowing of the red LED (LED2). a bistable circuit. For every clock input,
given by the following relationship: The IR receiver module (TSOP1738), pins 2 and 3 of IC3 alternately go high.
F = 1.443/(R1+2R2)C2 which gets 5.1V power supply through ze- Initially, when the power to the re-
This frequency is fed to npn transis- ner diode ZD1, receives the transmitted ceiver circuit is switched on, pin 3 of IC3
tors T1 and T2 (each BC547) through re- signal of about 38 kHz. The signal is am- is high and therefore the yellow LED
sistor R4 (470-ohm) to drive the IR LEDs. plified by transistor BC558 (T3) and given (LED4) connected to it glows. The glow-
Resistor R5 limits the current flowing to triggering pin 2 of IC2 through cou- ing of LED4 indicates that the appliance is
through the IR LEDs. pling capacitor C6. in ‘off’ condition.
The receiver circuit (shown in Fig. 2) Initially, when no signal is received When a clock pulse is received at pin 14
SEPTEMBER 2004 ELECTRONICS FOR YOU
CIRCUIT IDEAS
of IC3, pin 3 goes low to turn off LED4, while turn, controls the appliance. AC mains. Also, make sure that the neutral
pin 2 becomes high. The high output at pin Precautions. Don’t touch the leads of point of mains is connected to the ground
2 triggers the gate of triac BT136, which, in the triac as it is connected across the 230V line of the circuit and not vice versa.
ELECTRONICS FOR YOU SEPTEMBER 2004
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- SmarT VibraTion SenSorcl2april08Document1 pageSmarT VibraTion SenSorcl2april08Alagappan Arunachalam100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- 3 Phase Appliance ProtectorDocument3 pages3 Phase Appliance ProtectorchakralabsNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Fastest Finger First IndicatorDocument1 pageFastest Finger First IndicatorAlagappan Arunachalam100% (1)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Remote Control For Home ApplianceDocument1 pageRemote Control For Home ApplianceAkash MehtaNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Programmable Appliance TimerDocument2 pagesProgrammable Appliance TimerRev. MatthewNo ratings yet
- TesTer For RemoTe ConTrolCI-03 - Feb08Document1 pageTesTer For RemoTe ConTrolCI-03 - Feb08Alagappan Arunachalam100% (1)
- Traffic LightDocument1 pageTraffic LightpulkitNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- DTMF Proximity DetectorDocument1 pageDTMF Proximity DetectorAlagappan ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Heat Sensitive SwitchDocument1 pageHeat Sensitive Switchvinay reddyNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- NE555Document14 pagesNE555api-3720161100% (1)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Automatic Dipper Light Control For VehiclesDocument5 pagesAutomatic Dipper Light Control For VehiclesesatjournalsNo ratings yet
- Bike Turning Signal Indicator Circuit Using 555 TimerDocument7 pagesBike Turning Signal Indicator Circuit Using 555 Timerkaarthik KNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Police Light FinalDocument4 pagesPolice Light FinalDeepuNo ratings yet
- Important Characterstics of 555 Timer IC: Circuits Based On 5555 ICDocument6 pagesImportant Characterstics of 555 Timer IC: Circuits Based On 5555 ICManohar PotnuruNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Timers Oscillators CA 555Document6 pagesTimers Oscillators CA 555Thomas A. EDISSONNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Op Amp Dalam IC 555Document36 pagesOp Amp Dalam IC 555Dinda MayaNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Traffic Light DocumentationDocument2 pagesTraffic Light DocumentationDavid KatzNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Lab Manual Digital ElectronicsDocument47 pagesLab Manual Digital ElectronicsSenthil KumarNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Analog Electronics Project RevisedDocument19 pagesAnalog Electronics Project Revisedyug varshneyNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Lab 4Document6 pagesLab 4Carlos RodriguezNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Muscle Stimulator Project ReportDocument9 pagesMuscle Stimulator Project ReportShankarshan GautamNo ratings yet
- IC Applications Lab Manual Satish BabuDocument74 pagesIC Applications Lab Manual Satish BabuRAVIHIMAJANo ratings yet
- Water Level Indicator FinalDocument40 pagesWater Level Indicator Finalritesh chauhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 9 555 Timer: Prepared By: Asif MahfuzDocument19 pagesLecture - 9 555 Timer: Prepared By: Asif MahfuzWorld StationNo ratings yet
- Connections On Breadboard: The Diagram Shows How The Breadboard Holes Are ConnectedDocument3 pagesConnections On Breadboard: The Diagram Shows How The Breadboard Holes Are ConnectedyoungmoonNo ratings yet
- Battery Eliminator CircuitDocument5 pagesBattery Eliminator CircuitGiriNo ratings yet
- LED Running Lights CircuitsDocument17 pagesLED Running Lights CircuitsKaos Polos NakiraNo ratings yet
- Clap Switch CircuitDocument5 pagesClap Switch CircuitSabid Uddin100% (2)
- Coil Tester 2 PDFDocument11 pagesCoil Tester 2 PDFAnonymous f6yup1No ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- D14 Updated 24 Dec 2007 PDFDocument14 pagesD14 Updated 24 Dec 2007 PDFVinayak SanghaniNo ratings yet
- 555 CircuitsDocument6 pages555 CircuitscrpanelNo ratings yet
- Pe 1996 11Document116 pagesPe 1996 11franciscocampoverde8224No ratings yet
- A Reporton "4 Channel Long Range Infra Red"Document36 pagesA Reporton "4 Channel Long Range Infra Red"arudra88100% (2)
- Led Flasher Final Project PDF FreeDocument4 pagesLed Flasher Final Project PDF FreeMortal ShooterNo ratings yet
- PWM Dimmer Using NE555 and MOSFET With DIY AluminiDocument7 pagesPWM Dimmer Using NE555 and MOSFET With DIY Aluminimarius_danila8736No ratings yet
- Temperature Controlled Fan ReportDocument26 pagesTemperature Controlled Fan ReportHemant Shah43% (7)
- Mobile Phone Signal JammerDocument97 pagesMobile Phone Signal JammerAmol Bengiri100% (1)
- Basics of Electronic Components - Final Print ReadyDocument58 pagesBasics of Electronic Components - Final Print ReadyRodrigoFuenzalidaNo ratings yet
- Najmunissa NoorinDocument22 pagesNajmunissa Noorinnajmunissa noorinNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)