Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP For Bronchitis
Uploaded by
Jefherrson Nericua Jemilo50%(2)50% found this document useful (2 votes)
4K views2 pagesOriginal Title
Ncp for Bronchitis
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
50%(2)50% found this document useful (2 votes)
4K views2 pagesNCP For Bronchitis
Uploaded by
Jefherrson Nericua JemiloCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
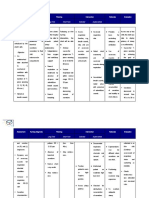
CUES AND NURSING DIAGNOSIS DISERED OUTCOME NURSING RATIONALE EVALUATION
EVIDENCES CRETERIA INTERVENTION
subjective: ineffective airway short term: Patient display
1. Assess 1.Useful in
“maglisod ko ug clearance related to improved
ginhawa excessive, thickened respiratory.rate, evaluating ventilation and
as mucous secretions After 8 hours of adequate
verbalized by the depth. Note use the degree or
nursing interventions oxygenation of
patient. of accessory respiratory distress tissues and
Objective: the patient will: Arterial blood
• Presence of muscles, and chronicity of the
gases (ABGs)
rhonchi. pursed lip breathing, disease process.
• Demonstrate within normal
• Ineffective
improved Inability to speak. range and free
cough.
• V/S taken as ventilation and from symptoms
adequate oxygen. 2.Oxygen delivery of respiratory
follows:
• Arterial blood 2. Elevate head of distress.
may be improved by
gases (ABGs) the
within normal bed, assist patient upright position and
T: 37.2 assume position to
range.
ease work of breathing exercises
P: 79 • No signs of
respiratory breathing. Encourage to decrease airway
R: 24 deep slow or pursed
distress.
lip breathing as collapse, dyspnea
Long term:
BP: 110/80 individually tolerated and work of
or indicated.
After months of 3. Routinely monitor breathing.
skin
nursing and mucous
3.Cyanosis may be
membrane color.
interventions, peripheral in nail
4. Encourage
beds or central in
the patient: expectoration of
lips or earlobes.
sputum; suction
Duskiness and
when
• Ventilation or central cyanosis
indicated
oxygenation is indicate advanced
5.evaluate level of
adequate to meet hypoxemia.
activity tolerance.
self care needs 4.Thick, tenacious,
Provide calm and
copious secretions
quiet environment.
are major source if
ineffective airways.
Deep suctioning
6.Evaluate sleep may be required
patterns, note report when cough is
ineffective for
of difficulties and expectoration of
whether patient feels secretions.
5.during severe or
well rested. acute respiratory
distress, patient may
7. Monitor vital signs be totally unable to
and perform basic self
cardiac rhythm. care activities
Collaborative: because of
8.Administer hypoxemia and
supplemental oxygen dyspnea.
as indicated by ABG 6.Multiple external
results and patients stimuli and presence
tolerance. of dyspnea may
prevent relaxation
and inhibit sleep.
7.Tachycardia,
dysrhythmias, and
changes in blood
pressure can reflect
effect of systemic
hypoxemia on
cardiac function.
8.May correct or
prevent worsening
of hypoxia.
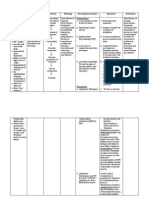
CUES AND EVIDENCES NURSING DIAGNOSIS OBJECTIVE NURSING INTERVENTION RATIONALE
Subjective: Activity After 10 hours of Evalua te the Provide cooperative
bug.at akong intolerance nursing interventions pt.’s baseline
pamati as vervalize by r/t to generalized the pt. will current activity tolera nce
the pt. body weakness participate willingly in Adjust To prevent
as manifested necessary activity and overexertion
Objective: by: activIty reduce intensity of
Received Body Will be task that may cause
malaise noted able to undesired
Difficulty move her physiological
awake lying moving left arm noted left arm changes
Facial with ease Increase exercise
on bed with Enhance
grimace noted Learn how to and activity levels
activity
an ongoing Pallor noted conserve gradu ally
tolerance
Complains of energy Teach
IVF of PLRS Helps mini mize
fatigue Verbalize methods to
waste of
1 L at 340 relief from fatigue conserve energy
energy
such as sitting than
cc level standing while dressing
Assist the pt.
regulated Prevent the pt. from
while doing
injury
at 10 gtts, ADLs
Give the pt.
infusing To sustain
info. That provides
the pt.’s motivation
well at right evidence of progress
arm.
Conscious/c
oherent
Body
malaise
noted
Difficulty
moving left
arm noted
Facial
grimace
noted
Pallor noted
Complains
of fatigue
Jefherrson jemilo
You might also like
- Student NurseDocument2 pagesStudent NurseTAYABAN, KENNETH JAKE, Q.No ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance - PTBDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance - PTBIrish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet
- BPN NCPDocument6 pagesBPN NCPJoart EspinozaNo ratings yet
- ANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationEdrianne Tui100% (2)
- Nursing ManagementDocument16 pagesNursing ManagementNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance: Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance: Nursing Care PlanJose Mari F. Esguerra0% (1)
- NCP Acitivity IntoleranceDocument3 pagesNCP Acitivity IntolerancegizelleNo ratings yet
- CP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesCP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanShiella Heart MalanaNo ratings yet
- Medication ThalassemiaDocument3 pagesMedication ThalassemiaDivya ToppoNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Document1 pageChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Bheru LalNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective DataDocument6 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective DataDeinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanKath RubioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Peptic UlcerDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Peptic UlcerJefferson Baluyot PalmaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (Bronchitis) Nursing Care PlansDocument10 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (Bronchitis) Nursing Care PlansjamieboyRN100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan: IndependentDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: IndependentAdhaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceCaroline ChaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument13 pagesNursing Care PlanCris Solis33% (3)
- NCP PSHDocument17 pagesNCP PSHMargareth OrtizNo ratings yet
- NCP PneumoniaDocument28 pagesNCP PneumoniaW'ton Borbe83% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan FinalDocument16 pagesNursing Care Plan FinalErickson OcialNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Managing Risk of AspirationDocument6 pagesAssessing and Managing Risk of AspirationaianrNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermErika Danalle ArceoNo ratings yet
- NCP Copd4Document15 pagesNCP Copd4Alessa Marie Crisostomo Salazar100% (1)
- FAELDONEA, PJ - Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesFAELDONEA, PJ - Nursing Care PlanPatricia Jean Faeldonea100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlansDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plansapi-19762967No ratings yet
- Hyperthermia Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageHyperthermia Pneumonia Nursing Care Planjustin_saneNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesNursing Care PlanAnthea ValinoNo ratings yet
- St. Anthony's College Nursing Department Patient Care Plan for S.LDocument2 pagesSt. Anthony's College Nursing Department Patient Care Plan for S.LAirme Raz AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlanElijah S GomezNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesFluid Volume DeficitpeternohibiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (NCP)Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan (NCP)Sha PinedaNo ratings yet
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pages6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansShaina Fe RabaneraNo ratings yet
- Pleural EffusionDocument5 pagesPleural EffusionTerizla MobileNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing ActualDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing ActualArian May Marcos100% (1)
- PHASE 2 NCP (Injury, Risk For Bleeding)Document3 pagesPHASE 2 NCP (Injury, Risk For Bleeding)NE TdrNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care Planrois romaNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Treating Pneumonia Through Respiratory Monitoring and InterventionsDocument3 pagesAssessing and Treating Pneumonia Through Respiratory Monitoring and InterventionsDyanne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care Planapi-309251523No ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument13 pagesNursing Care PlanRen DolosaNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBKath TalubanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanAnnahNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENT HEALTH NURSING INTERVENTION EVALUATIONDocument3 pagesASSESSMENT HEALTH NURSING INTERVENTION EVALUATIONtflorenzNo ratings yet
- Wk2 NCP Edited2012Document6 pagesWk2 NCP Edited2012Jessely Caling SalasNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Billy Admitted with Ear and Throat InfectionsDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan for Billy Admitted with Ear and Throat InfectionsNatukunda Dianah100% (1)
- Managing Respiratory Infection with Nursing InterventionsDocument4 pagesManaging Respiratory Infection with Nursing InterventionsJessa Borre100% (1)
- NCP Measles Case PresDocument1 pageNCP Measles Case PresFranz RolfNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPMarius Clifford BilledoNo ratings yet
- Gastrectomy NCP IBPDocument3 pagesGastrectomy NCP IBPKevin T. Katada100% (1)
- NCP - AnxietyDocument1 pageNCP - AnxietyNovie Carla100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For A Person With Croup Nursing DiagnosisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For A Person With Croup Nursing DiagnosisMonica Rivera100% (1)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Short Term IndependentDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Short Term IndependentMoi Valdoz100% (1)
- Assessment Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation: Mechanism of ActionDocument2 pagesAssessment Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation: Mechanism of ActionNicole CalpoturaNo ratings yet
- Renal Failure NCPDocument3 pagesRenal Failure NCPJet Ray-Ann GaringanNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - BronchitisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan - Bronchitisderic94% (36)
- Bronchitis N C P BY BHERU LALDocument1 pageBronchitis N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternEna Katherine CanonoNo ratings yet
- CopdDocument6 pagesCopdapi-3717941100% (2)
- Broncho DilatorsDocument53 pagesBroncho DilatorsDocRNNo ratings yet
- Minimally Invasive Spine SurgeryDocument510 pagesMinimally Invasive Spine SurgeryLuis RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Benazepril Hydrochloride (Drug Study)Document3 pagesBenazepril Hydrochloride (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (1)
- Hernia Repair Surgery ExplainedDocument13 pagesHernia Repair Surgery Explainedbugoy_bugoyNo ratings yet
- Attending Osteomyelitis ModuleDocument9 pagesAttending Osteomyelitis ModuleMrLarry DolorNo ratings yet
- E383 Full PDFDocument11 pagesE383 Full PDFBarryNo ratings yet
- EmekaDocument17 pagesEmekamutiyasNo ratings yet
- Hematology - Oncology - PREP 2021Document46 pagesHematology - Oncology - PREP 2021drthanalla100% (1)
- الهيئة 3Document10 pagesالهيئة 3mohsenNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN On Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN On Impaired Skin IntegrityAngelika VeluzNo ratings yet
- Sodium Chromate Anhydrous PDFDocument6 pagesSodium Chromate Anhydrous PDFErika WidiariniNo ratings yet
- Vet Histology Lecture Notes on Digestive System IDocument62 pagesVet Histology Lecture Notes on Digestive System IDEV3LLS100% (3)
- Primary Chest Wall Hydatid Cyst - A Rare Case Report: - PresenterDocument8 pagesPrimary Chest Wall Hydatid Cyst - A Rare Case Report: - PresenterEdison Varghese VadakkencheryNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Replacement Therapy Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesHormonal Replacement Therapy Lesson PlanBaljinder kaurNo ratings yet
- Rotator Cuff TendonitisDocument1 pageRotator Cuff TendonitisenadNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Set 8Document5 pagesOphthalmology Set 8ajay khadeNo ratings yet
- MSN I 20.4.2020 FN TyphoidDocument20 pagesMSN I 20.4.2020 FN TyphoidDr. DhaneshNo ratings yet
- IMCI - For PakistanDocument35 pagesIMCI - For Pakistanerajkhan100% (1)
- Attesta™ DR Mri Surescan™ Atdr01: Dual Chamber Rate Responsive Pacemaker (DDDR)Document42 pagesAttesta™ DR Mri Surescan™ Atdr01: Dual Chamber Rate Responsive Pacemaker (DDDR)mytake100No ratings yet
- Manage Preterm Labor with Bed Rest and TocolysisDocument4 pagesManage Preterm Labor with Bed Rest and TocolysisYeni PuspitaNo ratings yet
- Dialysis Inspection Tool 2014Document11 pagesDialysis Inspection Tool 2014Maek100% (1)
- Eclampsia Guidelines FINAL Ratified MCYP SG Sept20 15Document20 pagesEclampsia Guidelines FINAL Ratified MCYP SG Sept20 15Grigore PopaNo ratings yet
- Rebekah Wilson PT ResumeDocument3 pagesRebekah Wilson PT Resumeapi-487211279No ratings yet
- Scopolamine Intoxication As A Model of Transient Global AmnesiaDocument10 pagesScopolamine Intoxication As A Model of Transient Global AmnesiaDakotaJimNo ratings yet
- A Prospective Study On Acute Limb Ischemia - Presentation, Management, Outcome - Our Institutional ExperienceDocument6 pagesA Prospective Study On Acute Limb Ischemia - Presentation, Management, Outcome - Our Institutional ExperienceIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- The Pelvic Floor and Core ExercisesDocument4 pagesThe Pelvic Floor and Core ExercisesJeffrey PeekoNo ratings yet
- Anterior Open Bite Correction Using Bite Block - Case ReportDocument6 pagesAnterior Open Bite Correction Using Bite Block - Case ReportNovita BerlianaNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Nursing: An OverviewDocument64 pagesCritical Care Nursing: An OverviewProf. Ramsharan Mehta100% (2)
- Studies On The Stability of Chicken IgY in Different Sugars Complex Carbohydrates and Food MaterialsDocument12 pagesStudies On The Stability of Chicken IgY in Different Sugars Complex Carbohydrates and Food MaterialsJohnrel SecretariaNo ratings yet
- Asthma Inhale and ExhaleDocument14 pagesAsthma Inhale and ExhaleNguyen Nhu VinhNo ratings yet