Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Atenolol Tenor Min)
Uploaded by
E100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
1K views2 pagesCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
XLS, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as XLS, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
1K views2 pagesAtenolol Tenor Min)
Uploaded by
ECopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as XLS, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
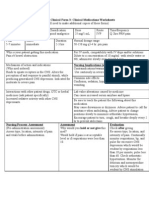
INDEX NURS 2236 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications Worksheet
(You will need to made additional copies of these forms)
Generic Trade Classification Dose Route Time/Frequency
Name Name antianginals 50mg PO Once/daily - antianginal
antihypertensives 25-50mg PO once/daily - antihypertensive
atenolol Tenormin 50mg PO given 10 min after last IV dose, then 50mg 12 hr later,
then 100/mg/day as a single dose - MI
Peak Onset Duration For IV meds, compatability with IV drips and/or solutions
2-4 hr 1 hr 24 hr
Why is your patient taking this medication?
Mechanism of action and indications Nursing Implications (what to focus on)
Management of hypertension; management of angina Contraindications/warnings/interactions Uncompensated CHF; pulmonary
pectoris; prevention of MI. edema; cardiogenic shock; bradycardia or heart block. Use cautiously in:
Renal impairment; geriatric patients; pulmonary disease; diabetes mellitus;
Decreased BP and HR. thyrotoxicosis; severe allergic reactions; pregnancy; lactation; children
Decreased frequency of attacks of angina pectoris.
Prevention of MI Common side effects fatigue; weakness; anxiety; depression; dizziness;
brady cardia; CHF; pulmonary edema; hypotension; peripheral vasoconstriction;
constipation; diarrhea; nausea; vomiting; impotence; urinary frequency; rash;
hyperglycemia; hypoglycemia; arthralgia; back pain; joint pain; blurred vision;
nervousness; bronchospasm; wheezing.
Interactions with other patient drugs, OTC, or herbal Lab value alterations caused by medicine
medicines (ask patient specifically)
General anesthesia; IV phenytoin; verapamil; digoxin;
antihypertensives; alcohol; nitrates; amphetamine; cocaine;
ephedrine; epinephrine; norepinephrine; phenylephrine; Be sure to teach the patient the following about this medication
pseudoephedrine; thyroid; insulins; oral hypoglycemic Take at same time each day; check pulse and BP; change position slowly;
agents; theophylline; dopamine; dobutamine; may increase sensitivity to cold; consult doctor before taking OTC meds;
MAO inhibitor. diabetic patients should montior blood glucose levels; notifiy doctor of slow
pulse, dizziness, light-headedness, unusual bleeding, bruising; additional
therapy of weight loss; Na+ restriction; stress reduction; exercise, no smoking or alcohol
Nursing Process - Assessment Assessment Evaluation
(Pre-administration assessment Why would you hold or not give Check after giving
Vital Signs this med? Decrease in BP
Monitor intake and output ratios and daily Bradycardia (<60) Reduction in frequency of angina
weights. Assess routinely for CHF. Assess for Increase in activity tolerance
frequency of angina. Prevention of MI
or alcohol
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Pyelonephritis 1 Running Head: PYELONEPHRITISDocument4 pagesPyelonephritis 1 Running Head: PYELONEPHRITISENo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Left-Side CHF PathoDocument5 pagesLeft-Side CHF PathoENo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument4 pagesCongestive Heart FailureENo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Chemical Burns PathoDocument2 pagesChemical Burns PathoENo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hyponatremic Dehydration PathoDocument4 pagesHyponatremic Dehydration PathoENo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Autonomic DysreflexiaDocument2 pagesAutonomic DysreflexiaENo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Hyperparathyroidism PathoDocument2 pagesHyperparathyroidism PathoENo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Iron Deficiency Anemia PathoDocument6 pagesIron Deficiency Anemia PathoENo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Influenza B PathoDocument4 pagesInfluenza B PathoENo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- Congestive Heart Failure-ABDocument3 pagesCongestive Heart Failure-ABENo ratings yet
- Acute Pancreatitis PathoDocument5 pagesAcute Pancreatitis PathoENo ratings yet
- Bowel Resection PathoDocument7 pagesBowel Resection PathoENo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Subluxation c6c7 Short PathoDocument1 pageSubluxation c6c7 Short PathoENo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Pneumonia Short PathoDocument2 pagesPneumonia Short PathoENo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Campral (Acamprosate Calcium)Document1 pageCampral (Acamprosate Calcium)E100% (1)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Clinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsDocument1 pageClinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsENo ratings yet
- Buspar (Buspirone)Document1 pageBuspar (Buspirone)ENo ratings yet
- Pancreatitis Short PathoDocument2 pagesPancreatitis Short PathoENo ratings yet
- Geodon (Ziprasidone)Document2 pagesGeodon (Ziprasidone)ENo ratings yet
- Prozac (Fluoxetine) 40mgDocument1 pageProzac (Fluoxetine) 40mgENo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Lexapro (Escitalopram Oxalate)Document2 pagesLexapro (Escitalopram Oxalate)ENo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Zosyn (Piperacillin/tazobactram)Document2 pagesZosyn (Piperacillin/tazobactram)E67% (3)
- ZofranDocument1 pageZofranKatie McPeek0% (1)
- Silvadene (Silver Sulfadiazine)Document1 pageSilvadene (Silver Sulfadiazine)ENo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- FiberCon (Polycarbophil)Document1 pageFiberCon (Polycarbophil)ENo ratings yet
- Reglan (Metoclopramide)Document3 pagesReglan (Metoclopramide)E100% (1)
- Darvocet (Propoxyphene Napsylate/Acetaminophen)Document1 pageDarvocet (Propoxyphene Napsylate/Acetaminophen)ENo ratings yet
- Theragran (Multiple Vitamins)Document3 pagesTheragran (Multiple Vitamins)ENo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Florinef (Fludrocortisone)Document3 pagesFlorinef (Fludrocortisone)E100% (1)
- Keppra (Levetiracetam)Document2 pagesKeppra (Levetiracetam)E100% (1)
- Daftar Obat Aman Dan Berbahaya Untuk Ibu Hamil DanDocument4 pagesDaftar Obat Aman Dan Berbahaya Untuk Ibu Hamil Daninne_fNo ratings yet
- Minutes Prac Meeting 26 29 October 2020 - enDocument80 pagesMinutes Prac Meeting 26 29 October 2020 - enAmany HagageNo ratings yet
- DemerolDocument1 pageDemerolCassie100% (1)
- SacubitrilValsartan (Entresto) For Heart FailureDocument2 pagesSacubitrilValsartan (Entresto) For Heart FailureWatchara TansiriNo ratings yet
- IV iron safe, effective for anemia in HDDocument5 pagesIV iron safe, effective for anemia in HDSri Siti KhadijahElfNo ratings yet
- Acr ArtrozaDocument14 pagesAcr Artrozacodruta soareNo ratings yet
- MCQ AntiepilepticDocument4 pagesMCQ AntiepilepticMickey Brown91% (33)
- Insulin Chart: Insulin Type Onset of Action Peak Duration of ActionDocument1 pageInsulin Chart: Insulin Type Onset of Action Peak Duration of ActionGeorge ZachariahNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Adi Azfar Bin Rosli Muhammad Nazirul Fikri Bin Ahmad Rijaludin Nurshakila Binti SanisDocument23 pagesMuhammad Adi Azfar Bin Rosli Muhammad Nazirul Fikri Bin Ahmad Rijaludin Nurshakila Binti Sanisnazki farNo ratings yet
- Analgesic Policy (2009)Document84 pagesAnalgesic Policy (2009)Ramon MagsaysayNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Troglitazone Withdrawal Due to Liver InjuryDocument12 pagesTroglitazone Withdrawal Due to Liver Injuryheyyo ggNo ratings yet
- Gpat 2023Document11 pagesGpat 2023Bobi JiNo ratings yet
- Final RD - Nove 2020Document282 pagesFinal RD - Nove 2020Janaka KodagodaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name 123Document14 pagesGeneric Name 123Laiba RehmanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 5 Medicine LabelDocument35 pagesLesson Plan 5 Medicine Labelnta tiekaNo ratings yet
- USFDA - Pre-Approval InspectionDocument53 pagesUSFDA - Pre-Approval Inspectionvg_vvg100% (1)
- Neuromuscular Blocking AgentsDocument18 pagesNeuromuscular Blocking AgentsLalibah AntartikaNo ratings yet
- History of PharmacyDocument8 pagesHistory of PharmacyHello50% (2)
- Percutaneous Endoscopic GastrostomyDocument27 pagesPercutaneous Endoscopic GastrostomyDoha EbedNo ratings yet
- Sample Pharmacist Manager ResumeDocument7 pagesSample Pharmacist Manager Resumemarko2606No ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy Functions of PharmacistsDocument42 pagesPharmacotherapy Functions of Pharmacistskhalid a.qazi100% (1)
- Stock TSJ 020823Document17 pagesStock TSJ 020823APOTEK K24 JAKALNo ratings yet
- Akut DistoniaDocument5 pagesAkut DistoniaawendikaNo ratings yet
- RV Ollero MD's Guide to Advanced Trauma Life SupportDocument18 pagesRV Ollero MD's Guide to Advanced Trauma Life SupportPrincess Cate MercadoNo ratings yet
- Tricyclic antidepressants overviewDocument2 pagesTricyclic antidepressants overviewAaLona RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Abu Dhabi Plan Drug ListDocument45 pagesAbu Dhabi Plan Drug ListicebreakNo ratings yet
- Colchicine drug information and nursing implicationsDocument3 pagesColchicine drug information and nursing implicationsTri Purma SariNo ratings yet
- Review: Theodore M. Sievers, Bernard M. Kubak and Annie Wong-BeringerDocument15 pagesReview: Theodore M. Sievers, Bernard M. Kubak and Annie Wong-BeringerRazzak CoolNo ratings yet
- Medication Errors: BY DR - Divya Ashok Kulkarni. Pharm DDocument68 pagesMedication Errors: BY DR - Divya Ashok Kulkarni. Pharm DShrenil LagadNo ratings yet
- 4 - Approved Regulatory Bodies and AgenciesDocument16 pages4 - Approved Regulatory Bodies and AgenciesSparsh SharmaNo ratings yet