Professional Documents
Culture Documents
03 VESPR and Polarity
Uploaded by
Nursalfarinah BasirOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
03 VESPR and Polarity
Uploaded by
Nursalfarinah BasirCopyright:
Available Formats
VSEPR & Determining the Polarity of Molecules
VSEPR Theory: Many of the properties of molecular compounds depend on the three dimensional shape of the molecule. The shape of a molecule is predicted by using the VSEPR theory: VSEPR Theory: the electrostatic repulsion between the valence level electron pairs surrounding an atom causes these pairs to be oriented as far apart as possible. To use VSEPR theory: 1. Draw the Lewis Dot Structure for the molecule. 2. Determine the number of links on the central atom (single, double and triple bonds all count as one link.) 3. Determine the number of lone pairs on the central atom. Number of Links on Central Atom 2 3 2 2 4 3 Number of Lone Pairs on Central Atom 0 0 1 2 0 1 Shape of Molecule Linear Trigonal Planar Bent Bent Tetrahedral Trigonal Pyramidal
Polar Molecule vs Nonpolar Molecules One very important property of molecule or is whether it is polar or nonpolar. If the electrons in a molecule are not evenly distributed, the molecule or can have a negative and positive side. A polar molecule will dissolve in another polar substance (such as water) where a nonpolar substance will not. Similarly, a nonpolar molecule will dissolve in another nonpolar substance (such as carbon tetrachloride) and a polar molecule will not dissolve in a nonpolar substance. We can determine if a molecule is polar or nonpolar by looking at the Lewis Dot Structure and following the rules below: To determine if a molecule is a polar or nonpolar, look at the central atom. 1. If the central atom has no lone pairs and has all the same types of atoms attached to it, then the molecule is nonpolar. 2. If the central atom has no lone pairs but different atoms attached to it, the molecule is polar. 3. If the central atom has lone pairs, the molecule is polar, Draw the Lewis Dot structure, determine the shape and if the molecule is polar/nonpolar for each of the following 1. CH4 4. BH3
2.
NH3 5. CH3Cl
3.
CO2
6.
HCN
Lewis Structures, VSEPR, and Molecule Polarity Homework
Draw the Lewis Structure for each compound or ion listed below, give its shape, and determine if its polar or not: 1. HOCl 6. HOF
Shape: Polar or nonpolar: 2. Cl2CO
Shape: Polar or nonpolar: 7. CS2
Shape: Polar or nonpolar: 3. CHClF2
Shape: Polar or nonpolar: 8. HBF2
Shape: Polar or nonpolar: 4. NH2Cl
Shape: Polar or nonpolar: 9. SiH4
Shape: Polar or nonpolar: 5. Cl2O
Shape: Polar or nonpolar: 10. SO2
Shape: Polar or nonpolar:
Shape: Polar or nonpolar:
VSEPR Homework 1-10
Draw the Lewis Structure for each compound or ion listed below, give its shape, and determine if its polar or not: 1. FCl2+ 6. SO3
Shape: Polar or nonpolar: 2. CS2
Shape: Polar or nonpolar: 7. FO3-
Shape: Polar or nonpolar: 3. AsO3-3
Shape: Polar or nonpolar: 8. N2O (put 1 N in the middle)
Shape: Polar or nonpolar: 4. IO4-
Shape: Polar or nonpolar: 9. H2CO
Shape: Polar or nonpolar: 5. SeO2
Shape: Polar or nonpolar: 10. NO2-
Shape: Polar or nonpolar:
Shape: Polar or nonpolar:
VSEPR Homework 11-20
Draw the Lewis Structure for each compound or ion listed below, give its shape, and determine if its polar or not: 11. SbH3 16. PCl4+
Shape: Polar or nonpolar: 12. NF3
Shape: Polar or nonpolar: 17. CO3-2
Shape: Polar or nonpolar: 13. IO2-
Shape: Polar or nonpolar: 18. SiO4-4
Shape: Polar or nonpolar: 14. NO3-
Shape: Polar or nonpolar: 19. BF3
Shape: Polar or nonpolar: 15. CNBr
Shape: Polar or nonpolar: 20. CBr4
Shape: Polar or nonpolar:
Shape: Polar or nonpolar:
You might also like
- Organic ChemistryDocument60 pagesOrganic ChemistryddddddffdfdfNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: A Practical Introduction to Structure, Mechanism, and Data AnalysisFrom EverandEnzymes: A Practical Introduction to Structure, Mechanism, and Data AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
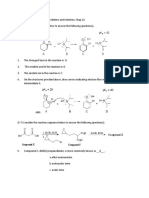
- Chap 04 Acids and BasesDocument22 pagesChap 04 Acids and BasesavNo ratings yet
- CHEM A 14B COMP Qual - Anions PDFDocument6 pagesCHEM A 14B COMP Qual - Anions PDFxerxeshakaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - An Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument29 pagesChapter 14 - An Introduction To Organic ChemistryNabindra RuwaliNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry 494 PDFDocument55 pagesElectrochemistry 494 PDFHarsh SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lecture Notes - 0Document44 pagesChapter 2 Lecture Notes - 0KirilKocevskiNo ratings yet
- Alkene Reaction GuideDocument41 pagesAlkene Reaction GuideAbhishek Isaac MathewNo ratings yet
- Lab Polymer - SlimeDocument4 pagesLab Polymer - SlimeThats Gone WrongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument102 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Organic ChemistryMELVINDO JACOBNo ratings yet
- Mgo LabDocument3 pagesMgo Labapi-336093393No ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument6 pagesChemical Bondingchong56100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry NotesDocument6 pagesOrganic Chemistry NotesAzib ZararNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Acid and BaseDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Acid and BaseKelsi Kyla PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Class10 ChemistryG12 Notes and HomeworkDocument38 pagesClass10 ChemistryG12 Notes and HomeworkAndy Rei KouNo ratings yet
- Shapes of Molecules and Ions PDFDocument9 pagesShapes of Molecules and Ions PDFMagenta SparklegemNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Coordination ChemistryDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Coordination ChemistryDnyaneshwar Shinde100% (2)
- Final Exam 40% Exams 45% Report 5% Homework 10%Document74 pagesFinal Exam 40% Exams 45% Report 5% Homework 10%kaleijaNo ratings yet
- CH 6 - Organic ReactionsDocument18 pagesCH 6 - Organic Reactionskevincai96No ratings yet
- Hard Soft Acid Base TheoryDocument41 pagesHard Soft Acid Base TheorythinhbuNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis of CationsDocument0 pagesQualitative Analysis of CationsKaran SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Review of Fundamental Concepts F12Document7 pagesReview of Fundamental Concepts F12DerrickGMcCoyNo ratings yet
- University of Santo TomasDocument5 pagesUniversity of Santo TomasJanine MontaNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy and ChromatographyDocument7 pagesSpectroscopy and ChromatographyPa GesNo ratings yet
- VSEPR Handout PDFDocument2 pagesVSEPR Handout PDFLittle One0% (1)
- Rings, Polymers and Analysis (Unit 4) - OCR Chemistry Notes - Robbie PeckDocument14 pagesRings, Polymers and Analysis (Unit 4) - OCR Chemistry Notes - Robbie Peckrobbiepeck100% (1)
- Johniya Cochran - Ionic and Covalent Bonds ActivityDocument4 pagesJohniya Cochran - Ionic and Covalent Bonds ActivityJohniya CochranNo ratings yet
- Module Acids, Bases, SaltsDocument7 pagesModule Acids, Bases, SaltsAndy TanNo ratings yet
- Preib Enrichment Quantum Numbers Edit3Document2 pagesPreib Enrichment Quantum Numbers Edit3api-270154205No ratings yet
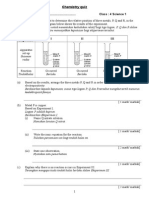
- Chemistry QuizDocument6 pagesChemistry QuizlimananthonyNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductoryDocument45 pages1 IntroductoryTuhin Sahu100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry Worksheet 6Document2 pagesOrganic Chemistry Worksheet 6Daniel WalshNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Practice Problems-Answers PDFDocument5 pagesAcid-Base Practice Problems-Answers PDFSuci PrameswariNo ratings yet
- Organometallic ChemistryDocument24 pagesOrganometallic ChemistryFatma TaherNo ratings yet
- Molecular Orbital TheoryDocument28 pagesMolecular Orbital TheoryYen Yen YapNo ratings yet
- 1 - Complete Acid Base NotesDocument45 pages1 - Complete Acid Base NotesJohn JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons: K. Atkins IB Chemistry Pensacola High SchoolDocument31 pagesHydrocarbons: K. Atkins IB Chemistry Pensacola High Schoollianchen251110No ratings yet
- Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination: Organic Chemistry, 7Document61 pagesAlkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination: Organic Chemistry, 7haha_le12100% (4)
- Organic Chemistry SummaryDocument8 pagesOrganic Chemistry SummaryZeath ElizaldeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9. Chemical BondingDocument55 pagesLecture 9. Chemical BondingDione Gale NavalNo ratings yet
- 110 Oxidation NumberDocument3 pages110 Oxidation NumberTerry100% (1)
- Group 18 ElementsDocument19 pagesGroup 18 ElementsPeki_EnglishNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry II Chapter22Document8 pagesOrganic Chemistry II Chapter22RangikaNo ratings yet
- Alkenes and AlkynesDocument2 pagesAlkenes and AlkynesLewis AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Chapter 3 - An Introduction To Organic Reactions and Their MechanismsDocument81 pagesOrganic Chemistry Chapter 3 - An Introduction To Organic Reactions and Their MechanismsGian BanaresNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidDocument21 pagesCarboxylic AcidShalsabila NHNo ratings yet
- Balancing Equations 42 PDFDocument1 pageBalancing Equations 42 PDFIgnacio Jr. Paguyo100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Atoms Molecules IonsDocument42 pagesChapter 2 Atoms Molecules IonsCarlo CortesNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Lab Technique Notes For The DATDocument3 pagesOrganic Chemistry Lab Technique Notes For The DATOscar Federico SpadaNo ratings yet
- Test BanksDocument21 pagesTest Banksalex_flutistNo ratings yet
- Alkyl Halides PDFDocument66 pagesAlkyl Halides PDFAhmed Sideeg83% (6)
- Formal Charge WorksheetDocument3 pagesFormal Charge WorksheethbjvghcgNo ratings yet
- PHA611 LAB-Group4 Lab ReportDocument2 pagesPHA611 LAB-Group4 Lab ReportAcuCJamNo ratings yet
- 14 Lewis Structures and Molecuar Models S19Document14 pages14 Lewis Structures and Molecuar Models S19victorNo ratings yet
- Ismail Yusuf: Arts, Science and Commerce College, MumbaiDocument43 pagesIsmail Yusuf: Arts, Science and Commerce College, MumbaiBapu ThoratNo ratings yet
- Limiting Reagents and Percentage Yield WorksheetDocument1 pageLimiting Reagents and Percentage Yield WorksheetFandy ArdyNo ratings yet
- PeriodicityDocument6 pagesPeriodicityHadi AlnaherNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument2 pagesLipidsKier Daniel BorromeoNo ratings yet
- 5 PDFDocument23 pages5 PDFAsif Ullah Khan FaryadiNo ratings yet
- Molecule of The Week - GlutamateDocument1 pageMolecule of The Week - GlutamateCraftychemistNo ratings yet
- P24 Answers Kweyete AlbertDocument7 pagesP24 Answers Kweyete AlbertMuhammad HashirNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 22: Properties of AlcoholsDocument17 pagesLaboratory 22: Properties of AlcoholsElvis BartingeiNo ratings yet
- Free Radicals and AntioxidantsDocument26 pagesFree Radicals and AntioxidantsNitin FaldesaiNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Theory AnswersDocument3 pagesAcid Base Theory Answersvinaybharadwajbs0% (1)
- TLC ReagentsDocument5 pagesTLC Reagentsteodoro11100% (1)
- Introduction To CarbohydratesDocument6 pagesIntroduction To CarbohydratesKhazel CasimiroNo ratings yet
- Atoms and MoleculesDocument42 pagesAtoms and MoleculesMd firoz AlamNo ratings yet
- LAB #11 Molecular Geometry: That You Will Fill in During Lab and Turn in at The End of ClassDocument4 pagesLAB #11 Molecular Geometry: That You Will Fill in During Lab and Turn in at The End of ClassbooklookingboiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 445 Lecture 10 Hydrolysis of Metal IonsDocument16 pagesChemistry 445 Lecture 10 Hydrolysis of Metal IonsMario RojasNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry Guide - BasicDocument2 pagesStoichiometry Guide - BasicViviana PlacentinoNo ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument34 pagesAcid Basehay0117No ratings yet
- In thinking HL Topic 3&13 Periodicity and transition metals (1) - 副本Document7 pagesIn thinking HL Topic 3&13 Periodicity and transition metals (1) - 副本Xueren LyuNo ratings yet
- UNIT 6 ALKYL HALIDE SolutionsDocument16 pagesUNIT 6 ALKYL HALIDE Solutionssuryansh.yt9641No ratings yet
- NamereactionorganicDocument13 pagesNamereactionorganicdeykrishna654100% (1)
- 'Acid-Base Physiology' by Kerry BrandisDocument187 pages'Acid-Base Physiology' by Kerry Brandisyoshiuda100% (1)
- Grade 9 Chemistry Review ExerciseDocument6 pagesGrade 9 Chemistry Review ExerciseJacqueline LaiNo ratings yet
- A3 ReactionsDocument3 pagesA3 ReactionshaNo ratings yet
- Ricardo Obregon Martinez - Macromolecules - Dehydration Synthesis Gizmo - 13867984Document6 pagesRicardo Obregon Martinez - Macromolecules - Dehydration Synthesis Gizmo - 13867984Ricardo ObregonNo ratings yet
- Bio 7Document58 pagesBio 7Prince SanjiNo ratings yet
- Test 2 CHM 572 DEC 2021Document5 pagesTest 2 CHM 572 DEC 2021NUR AINA SYAHMINA MOHD AMRANNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Prefinal PaperDocument4 pagesChemistry Prefinal Paperkuldeep9034.patelNo ratings yet
- TestbankDocument6 pagesTestbankRen H. RoxasNo ratings yet
- Valence Bond Theory (VBT)Document67 pagesValence Bond Theory (VBT)Kehkashan GhauriNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties and Identification of Acid-Base Properties of Representative Organic Compounds Using Simple Solubility TestsDocument6 pagesPhysical Properties and Identification of Acid-Base Properties of Representative Organic Compounds Using Simple Solubility TestsMatthew SA100% (1)
- Experiment 3 - Determination of Mixed AlkaliDocument2 pagesExperiment 3 - Determination of Mixed AlkaliPeter BrayNo ratings yet
- Goc Iit Jam MaterialDocument15 pagesGoc Iit Jam MaterialjagannivasNo ratings yet
- Mathematical ProblemsDocument4 pagesMathematical ProblemsbkmmizanNo ratings yet