Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Co-Creation of Value Practices in Government Agency
Co-Creation of Value Practices in Government Agency
Uploaded by
Journal of ComputingOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Co-Creation of Value Practices in Government Agency
Co-Creation of Value Practices in Government Agency
Uploaded by
Journal of ComputingCopyright:
Available Formats
JOURNAL OF COMPUTING, VOLUME 4, ISSUE 1, JANUARY 2012, ISSN 2151-9617 https://sites.google.com/site/journalofcomputing WWW.JOURNALOFCOMPUTING.
ORG
Co-creation of Value Practices in Government Agency
Imran A. Adeleke, Azizah AbdulRahman
Abstract This paper describes the co-creation of value practices employ by government agencies to interact, share service
experience and understand the customer problem and requirement at any point in time. There is an increasing research on cocreation of value in marketing but few researchers discussed the concept in public sector. For government to provide quality service for citizens, to sustain continuous improvement and service innovation there is need for government to interact more with the citizen, sharing their knowledge and service experience for more improvement and mutual value. In this study, DART building block of value co-creation (Dialogue, Access, Risk management and Transparency) was used to identify the major practices of value co-creation of the government with citizen. The results provide extensive information on the value co-creation practices mechanism adopted by the agencies to interact with customer and share their service experience on one hand and also serves as a source of awareness to the community of service user for ease of communication and experience co-creation. Index Terms Co-creation of value; experience sharing; stakeholder; DART model.
1 INTRODUCTION
HE The traditional way of value cocreation which although had served us so well for over a century has become outdated [1]. The assertion was premised uponthefactthatweliveinachangingworldsuchthat expediency warrant that the approach to issues equally change in order to suit the dynamics of the modern time. Changes and approach manifest as a result of scientific and technological advancement such that it broughtaboutrevolutioninInformationandCommuni cationsectorofthesociety.Ithasfurtherrevolutionized every facet of human relations be it economic, social andpoliticalduetoaccessibilityofavailableinformation which affords customer the opportunity to have global outlook, network with people around the world and experiment with available services. This situation has further prompt customer into becoming active, since they have the chance to interact, compare and contrast service value thereby assisting the customer to make informed decision and choices among several available alternatives.Asaresultofthis,governmentcannolong er have exclusive right of value creation hence the idea of value cocreation which signifies the involvement of the service provider and the customer in cocreating value. The traditional system of assessing government e service application is becoming obsolete and there is
Imran A. Adeleke is a student of Faculty of Computer Science & Infomation Systems, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia. Dr. Azizah AbdulRahman is an Associate professor in the Department of Information Systems, Faculty of Computer Science & Infomation Systems, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia.
need for a new way of exploring the value of these e service applications for continuous improvement and stakeholders mutual value. Cocreation of value in governmenteserviceapplicationisinevitablegivingthe fact that customer rather than isolated are these days connected and have rather than unaware become well informed, and have changed from being passive to ac tive hence government could no longer unilaterally de signservice,deliveryprocessandcontrolchannelwith outtakencustomerintoconsideration[1].Itisthisjoint interaction and mutual reciprocative influence between service provider and customer that inthe final analysis bringsaboutthenewphenomenonorconceptcalledCo creation of value. Government can no longer act auto nomously in designing and delivering service without payingattentiontothecustomerviewandneed.Nowa days, the customer is no more ordinary user of service as they want to interact with service provider to co createvalue. The cocreation of value research in government e serviceisstillinembryoniccomparedtootherresearch field. It is a growing phenomenon in marketing firm where the interaction of service provider and customer areessentialinvaluecocreation.Forthisreason,inor dertoprovideadifferentperspective,thecurrentstudy focuses on evaluating the current practice of govern ment agencies employ to interact and share experience with customer for the improvement of service and mu tualvalue.
JOURNAL OF COMPUTING, VOLUME 4, ISSUE 1, JANUARY 2012, ISSN 2151-9617 https://sites.google.com/site/journalofcomputing WWW.JOURNALOFCOMPUTING.ORG
The paper begins with a brief explanation of co creation of value, followed by description of DART model. The next section discusses dynamic customer roles and cocreation of value practices in government agency was described in section four. The last section compriseconclusion.
DART MODEL
CO-CREATION OF VALUE
Cocreation of value is viewed as a process by which servicesandexperiencesaresharedbyserviceprovider and customer giving way for a new world of conti nuous improvement and mutual value [2], [3]. With thisconceptinmind,Prahaladetaldevelopedamodel forachievingmutualcocreationofvaluebetweenand amongserviceprovidersandtheircustomer.Themod el is called DART, an acronym for Dialogue, Access, RiskassessmentandTransparency[4]. The ten foundational principles of Vargo and Lusch form the basis for the service dominant logic (SD). [5]. Out of these ten foundational principles, the foun dational principle (FP6) emphasizes the importance of customerasacocreatorofvalue.Therefore,FP6isre levant for this study in order to share experience and interact with service provider to cocreate value. This FPsrepresentsadevelopingandcollaborativeeffortto createabetterunderstandingofvalueinuseandvalue cocreation [6]. Value is cocreated when both service provider and customer use their skill, knowledge; ex perience and initiative are very important factors in value cocreation [7]. Today, customers can cocreate value with service providers when engage in service. The cocreation of value is important as it will enable government to identify customer point of view, needs andbenefit. In marketing firm, customer is actively involved intheservicevaluecocreationprocessasresultofem phasis of foundational proposition (FP6) of service dominant logic. In other words, customer is an active participant of cocreation of value. Generally, value is understood in two ways, value inexchange and val ueinuse. The two concepts show various way of thinkingaboutvalueandvaluecocreation.Goodsdo minant logic is referred to as traditional perspective andisbasedonvalueinexchangewhilethealternative view, service dominant logic is known as valueinuse anditisthefocusofthisstudy[8].Inservicedominant logic, the roles of service provider and customers are similar, that is value is cocreated jointly between ser viceproviderandcustomerthroughtheuseofservice.
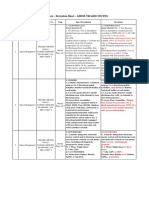
Thebuildingblocksofcocreationofvalueasshownin figure1arethekeytoolsforunderstandingtheprocess or the procedure of value cocreation. The model ac cordingto[1,10])ismadeupofDialogue,Access,Risk management and Transparency. It reveals cocreation practicesthecompanyusetointeractandshareservice experiencewithcustomertherefore,thesemechanisms are very essential for any meaningful interaction to takeplace. 3.1Dialogue:Thisismutualinteractionandengage ment between service provider and customer. Dialogue facilitates sharing of ideas, knowledge as well as cross fertilisingtheideawhichbyandlargeleadstosenseof belongingandloyalty.Itengendersmutualunderstand ingwhichculminatesintomutualinterestandsolidarity. As a result of experience sharing, solution to customer caneasilyberesolvedthroughdialogue.Manycompany todaysuchasDell,eBay,Amazondialoguedirectlywith customerseekingfortheirsuggestions,ideasandexpe rienceandthishasenabledtheDelltobecomeacorpo rateITsupplierintheworldtoday[11] Dialogue Co-creation of value interaction Transparency Access platform Risk Assessment Figure 1: DART model 3.2Access:Accessreferstoaccessibilityofinformation andresourcestoolstocustomer.Bysodoingcompanies would be able to focus on products and services that interest their customers most. Cocreation of value be comessodifficultinasituationwherecompanyhasno resourcestocreateaccessforcustomer.Heobservesfur therthatinternetcafesandbookshopswhicharemaking internetservicesavailabletoeveryoneataverylowcost has opened up several new opportunities in the ever
JOURNAL OF COMPUTING, VOLUME 4, ISSUE 1, JANUARY 2012, ISSN 2151-9617 https://sites.google.com/site/journalofcomputing WWW.JOURNALOFCOMPUTING.ORG
emerging dynamic markets. This access to information, transparent service, dialogue, service personalisation and access resources are some of the features that mi nimizeriskofvaluecocreationandhadhelpedgreatly to remove potential harms to customer. Infact, where such harm are inevitable, they are not borne totally by thecustomerashitherto,theyarerathersharedbetween thecompaniesandtheircustomers[1,4,10]. 3.3RiskAssessment:Byrisk,thepotentialharmofa particular product or service is intended [4] (Prahalad, 2008). Traditionally, the whole of the risk that may be involved in a product and service is exclusively borne by the company. The question now is, if customers are activecocreatorofvalue,shouldtheyshoulderrespon sibilityforriskaswell?ToPrahaladetal[1]thedebate about informed consent and the responsibility of firm and customer may likely continue for several decades. Yet as they assert, it is certain that customer will pro gressively participate in the cocreation of value. They would demand that firm or service provider inform themadequatelyabouttheshortcomingsoftheirservic es, the risk involved not only to individual but to the larger society. This is what we referred to as Risk as sessmentwhichisaimedatmanagingandreducingitto the bearest minimum. This would also assist customer to make informed decisions as well as appropriate choiceofservices. 3.4Transparency:Inthepast,companiesusetoenjoy whatcouldbecalledmonologue,thatis,whatPrahalad and Ramaswamy called Information asymmetry be tweenthecustomerandthefirm.Givingtherevolution in ICT, information asymentarism is rapidly given way such that companies can no longer restrict information to themselves in respect of prices, services and profit margin.Thishadledtoincreasedneedfortransparency. Thedividendofthisisthatitbuildsmutualtrust,loyal tyandsolidarity[1].
tionsaswellastechnologieswhichareequallyeas ily accessible to customer, knowledgeable cus tomercouldthereforemakereasonableinteraction anddecisionwithserviceproviderandtherebyco createmutualvalue. Globaloutlook:Globaloutlookorviewofthecus tomer with revolution that has taken place through Information and Communication tech nology customer could access information about the government eservice valueinuse. The geo graphicalbarrierstoinformationinthetraditional era are fastly disappearing such that rules of business and service competition are also chang ing.Thisisasaresultofaccessibilityofinforma tionaboutgovernmentservicewhichenablecus tomer to scrutinise before taken informed and wisedecisionbasedontheserviceuse. Networking / Linkage: This signifies virtual globalcitizenshipofaglobalcommunityorrather thematic customer communities whereby indi vidual user of government eservice exchange ideas,thought,knowledgeandexperiencesoasto cocreatevaluewithserviceprovider. Experimentation: Customer affords the opportu nity to experiment with and cocreate value with service provider via the eservice, chat online, helpdeskandinternet. Activism: information when processed becomes useful knowledge which enables customer and governmenttomakebetterandinformedchoices and decisions. Based on their knowledge and networking discussed above, customer becomes competenttocreatevaluewhenengageinservice use. Hence, the urge to provide unsolicited feed back to government as well as customer via the internetandwebsitethatfacilitatecustomeractiv ism
DYNAMIC ROLES OF CUSTOMER
CASE STUDY OF GOVERNMENT AGENCY
The impact of the informed, connected, active and reasonable customer is said to be manifested in many ways as necessitating and at the same time facilitating cocreationofvalues.Thechangeincustomerbehaviour andattitudetowardsserviceusecanbeanalysedbased on five distinct manifestations. These manifestations according[1]areinformationaccess,globalviewofcus tomer, customer networking / linkage, experimentation ofservicethroughinternetandlastlyactivism. Accessibility of information: Owing to availability of unprecedented quantum of information about government agencies and their eservice applica
The case study involved one of the government agenciesandtheagencywillonlybereferredtoasAX. Thegovernmentagency(AX)responsibleforcollecting revenue online from various sources. It also gives ser vices in administration, assessment, collection and en forcementofincometaxandothertypesoftaxagreed upon by both governmentand the Board. Tax briefing andeducationforumonhowtocalculatetaxtominim izeerroralsoserveasplatformforthecustomertoex press their opinion regarding the etax filing. The AX performanceindischargingtheirserviceisduetogood interaction, provision of adequate access resources for
JOURNAL OF COMPUTING, VOLUME 4, ISSUE 1, JANUARY 2012, ISSN 2151-9617 https://sites.google.com/site/journalofcomputing WWW.JOURNALOFCOMPUTING.ORG
thecustomertoreachAXatanytime.Thetransparency services cum provision of access tools has earned the AX many awards but there is need for theAX to sus tain interaction and customer experience sharing for continuous improvement. Figure 1 shows a summary ofcocreationpracticesinAX. 5.1Dialogue The government agency AX provides enabling environment to educate the taxpayer, to train the tax payer on efiling. The process start by organizing workshop,seminartogatherthestakeholderstogether to discuss on efiling and how to continue improving their service so that the taxpayer can also be happy with the service. It is a forum forAX to listen to com munityoftaxpayer;itisanopportunityforthetaxpay er to share their knowledge and experience of efiling with the AX. Dialogue enables synchronous interac tions between AX and customer. The AX apart from interacting with customer through workshop, televi sionprogramme,taxeducationandseminar,itaffords the AX to seek for customer opinion and in order to analyze the conflicting results regarding their filing. Thecustomersuggestionsareimportantasitservesas input for improving service and benefit for the stake holders. Dialogue among the stakeholders gives better understandingofcustomerserviceexperience. 5.2Access It is difficult to gather and have the opinion, idea and experience of customer on efiling. The best way to seek the opinion of customer is through the availability of access tools. In order to foster a mea ningfuldialogueandexperiencesharing,AXprovides accesstoolssuchaswebsite,email,facebook,custom er support, blog and others. Cocreation of value among the stakeholders through these access tools enables the organization to have general opinion of their service from the customer. Blog also create offi cialcommunicationbetweentheAXandthecustomer. Customercanmakecomment,complaintthroughthis mediumaswell.ItisausefultoolthatenablestheAX to assess the customer reaction to any new informa tionregardingtheefiling. 5.3Riskmanagement The concept of risk management is a concept that considers how AX manages service risk for the customer.AXenhancestheirservicebygivingproper training to the customer in order to minimize error ratewhenengaginginefiling.Monitoringoftaxpay er by the organization is also put in place to see that correct data is input with access tools provided. The accessresourcesprovidedforthecustomertofiletheir
taxgivethecustomeropportunitytosharetheirexpe rience, it increases interactions and lower the risk of committingerrorwhenfilingtheirtax.TheAXstaffis always available particularly during the peak period when customer engages in efiling.Assisting the cus tomertodocorrectinputalsoreducestherateoferror thecustomerlikelytocommit.
Current practice
Workshop Lecture series Tax Relation officer Briefing Radio programme TV programme Tax Learning prg Website Conference Budget seminar Meetings
Current practice
website E-mail Help desk Blog Telephone Online chat consultation Workshop
DIALOGUE Knowledge and experience sharing, ideas, suggestions takes place among thestakeholders
ACCESS Access are provided for customer. Through this medium they are able to contribute ideas.
Current practice Annual report Open to customer Service consistency Code of conduct Self Assessment System Information dissemination
TRANSPARENCY makes information about the service available for customer
RISK BENEFIT provides necessary training and guidance for the customer
Current practice Provide guidance for service user Quick response to inquiry Provide personalized service Feed back system SSL provision
Figure1:CocreationofvaluepracticeofAX 5.4Transparency The fourth guideline of cocreation of value is transpa rency; in other words shared information. It increases leveloftrustandcooperationamongthestakeholdersin the service system. The organization believes that cus tomerneedmoreinsightintohowtheyshouldfiletheir tax, therefore, a wide range of information was made available to customer through Radio and television, through the organization website, through the work shop and seminar, through tax education and training. The organization website provides the community of taxpayer much opportunity to tell their opinion and problem encounter. The training unit organizes face to face meeting, workshop and make available all neces sary information, all the ideas obtained from the cus tomerarealwayslookedinto.Customercanfiletheirtax by logging in to the website. SelfAssessment System is madeavailable.Soalso,thereportispublishedyearlyto showtheextentofrevenuecollectedfortheyear.
JOURNAL OF COMPUTING, VOLUME 4, ISSUE 1, JANUARY 2012, ISSN 2151-9617 https://sites.google.com/site/journalofcomputing WWW.JOURNALOFCOMPUTING.ORG
CONCLUSION
Cocreation of value is consideredas a joint crea tion of value by the service provider and the customer oracollaborativeinteractionwherevalueiscoinvented between service providers and users. However, the process of value cocreation in public sector is still in embryonic stage though much work from marketing context has been done but we need to provide another perspective. Inthisstudy,wediscussedthecocreationofvalue,the dynamic roles that enable the customer to be active co creator of value. DART model was applied to govern ment agency to explore cocreation of value practices. Fromourcasestudy,wehavelearntcocreationofvalue mechanismsadoptedbythegovernmentagency(AX)to share experience with customer. Many ideas of co creatingvaluewithcustomerwererevealed.Dialogueis themainconceptsthatsmooththeprogressofvalueco creation between the agency and customer. Different training forum, blogs were embarked upon to give in formationtocustomer.Accesswasprovidedtofacilitate communication. These practices enable the agency to havedirectaccessandinteractionwithcustomer,soalso give opportunity to customer to share their experience and ideas with government. These practices improve transparency by allowing the customer through these mediumtointeractwiththeagency.Informationregard ing the service was made available to customer on the website.Quickfeedbackwasalsoimplementedthrough thesefeatures.Italsopaveswayforrelationshipamong thestakeholderduetotheavailabilityofthecocreation ofvaluefeaturesthatareavailableforengagement.
S.L. Vargo and M.A. Akaka, Service Dominant Logic as a Foundation for Service Science: Clarifications, Service Sci ence1(1),pp.3241,2009 [9] L.Batangan,A.PocovnicuandS.Capisizu,EServiceQual ity Management, Journal of Applied Quantitative Method, 4(30),pp.372381,2000. [10] V. Ramaswamy. Cocreating value through customers ex periences: the Nike case, Strategy and Leadership 36(5), pp.914,2008 [11] V. Ramaswamy and F. Gouillart. The Power of cocreation: Power of CoCreation: Build It with Them to Boost Growth, Productivity,andProfits.NewYork:FreePress,2010.
[8]
Imran A. Adeleke is a student of Information systems at the Department of information Systems, Faculty of Computer Science and Information Systems, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia. He received his M.Sc. and B.Sc. in Computer Science at University of Agriculture, Abeokuta and University of Benin, Benin-city, Nigeria respectively. He is a member of AIS and IEEE. Assoc. Prof.Dr. Azizah AbdulRahman is a Senior lecturer in the Department of Information Systems, Faculty of Computer Science and Information Systems, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia. She received her PhD in computer science at Universiti Teknologi Malaysia. She is a member of AIS
REFERENCES
[1] C.K.PrahaladandV.Ramaswamy.Cocreatinguniquevalue withcustomers.JournalofStrategyandLeadership32(3),pp 49,2004 P.M. Di Gangi and M. Wasko, The cocreation of value: ex ploring customer engagement in customergenerated content websites, Proceedings of JAIS Theory Development Work shop. Sprouts: Working Papers on Information Systems, http://sprouts.aisnet.org9(50),2009 V.Ramaswamy.CocreationofValueTowardsanEx pandedParadigmofValueCreation.MarketingReviewSt. Gallen6,2009 C.K. Prahalad and V. Ramaswamy. The future of Competi tion: Cocreating Unique Value with Customers. Harvard businessSchoolPress,Boston,Massachusetts,2004. S.L.VargoandR.F.Lusch,Servicedominantlogic:Continu ingtheevolution,JournaloftheAcademyofMarketingSci ence36(1),pp.110,2008. S.L.Vargo,P.P.MaglioandM.A.Akaka,Onvalueandvalue cocreation:Aservicesystemsandservicelogicperspective, EuropeanManagementJournal(26),pp.145152,2008. S.L.VargoandR.F.Lusch,Servicedominantlogic:Continu ingtheevolution,JournaloftheAcademyofMarketingSci ence36(1),pp.110,2008.
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
[7]
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (843)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Winners Image PDFDocument42 pagesWinners Image PDFUmair Aslam100% (2)
- Common Errors in Parts of SpeechDocument82 pagesCommon Errors in Parts of SpeechMadhu MunagalaNo ratings yet
- ISO 19901-5-2016 Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries. Specific Requirements For Offshore Structures. Weight Control During Engineering and Construction PDFDocument88 pagesISO 19901-5-2016 Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries. Specific Requirements For Offshore Structures. Weight Control During Engineering and Construction PDFMohamad Zularif Ayup100% (8)
- Eric Van Lustbader The Ninja PDFDocument2 pagesEric Van Lustbader The Ninja PDFKrista50% (2)
- 1506 - Pio Reading 1 - A Leader's Guide To Why People Behave The Way DoDocument2 pages1506 - Pio Reading 1 - A Leader's Guide To Why People Behave The Way DoJavadNurIslamiNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Network Coding Peer-to-Peer Content DistributionDocument10 pagesHybrid Network Coding Peer-to-Peer Content DistributionJournal of ComputingNo ratings yet
- Divide and Conquer For Convex HullDocument8 pagesDivide and Conquer For Convex HullJournal of Computing100% (1)
- Business Process: The Model and The RealityDocument4 pagesBusiness Process: The Model and The RealityJournal of ComputingNo ratings yet
- Product Lifecycle Management Advantages and ApproachDocument4 pagesProduct Lifecycle Management Advantages and ApproachJournal of ComputingNo ratings yet
- Decision Support Model For Selection of Location Urban Green Public Open SpaceDocument6 pagesDecision Support Model For Selection of Location Urban Green Public Open SpaceJournal of Computing100% (1)
- Complex Event Processing - A SurveyDocument7 pagesComplex Event Processing - A SurveyJournal of ComputingNo ratings yet
- Hiding Image in Image by Five Modulus Method For Image SteganographyDocument5 pagesHiding Image in Image by Five Modulus Method For Image SteganographyJournal of Computing100% (1)
- Energy Efficient Routing Protocol Using Local Mobile Agent For Large Scale WSNsDocument6 pagesEnergy Efficient Routing Protocol Using Local Mobile Agent For Large Scale WSNsJournal of ComputingNo ratings yet
- Impact of Facebook Usage On The Academic Grades: A Case StudyDocument5 pagesImpact of Facebook Usage On The Academic Grades: A Case StudyJournal of Computing100% (1)
- K-Means Clustering and Affinity Clustering Based On Heterogeneous Transfer LearningDocument7 pagesK-Means Clustering and Affinity Clustering Based On Heterogeneous Transfer LearningJournal of ComputingNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Deployment Issues For The Enterprise SystemsDocument5 pagesCloud Computing: Deployment Issues For The Enterprise SystemsJournal of ComputingNo ratings yet
- An Approach To Linear Spatial Filtering Method Based On Anytime Algorithm For Real-Time Image ProcessingDocument7 pagesAn Approach To Linear Spatial Filtering Method Based On Anytime Algorithm For Real-Time Image ProcessingJournal of ComputingNo ratings yet
- Path Alignment Cross Polarization Parabolic Antennas TP 108827Document7 pagesPath Alignment Cross Polarization Parabolic Antennas TP 108827ginsudksNo ratings yet
- Programcion Nortel-Avaya (Axsa) Aura Con Una PriDocument520 pagesProgramcion Nortel-Avaya (Axsa) Aura Con Una Prirromeros3691No ratings yet
- Rat Re SelectionDocument6 pagesRat Re SelectionshijineshNo ratings yet
- 15 Towers - Deviation Sheet - 149182-TRASH CHUTESDocument2 pages15 Towers - Deviation Sheet - 149182-TRASH CHUTESLi LiuNo ratings yet
- Mendeley Teaching PresentationDocument36 pagesMendeley Teaching PresentationpatrickNX9420No ratings yet
- WSB 12 12 - 12 Software PDFDocument131 pagesWSB 12 12 - 12 Software PDFwigen001No ratings yet
- SML10 SystemDocument33 pagesSML10 SystemgilbertoNo ratings yet
- Marketing's AssignmentDocument9 pagesMarketing's AssignmentAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Dive Into Deep LearningDocument291 pagesDive Into Deep LearningPrasad Ganesh RKaNo ratings yet
- Elton MayoDocument5 pagesElton MayoDIVINE INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT & STUDIESNo ratings yet
- Jharkhand Bijli Vitran Nigam LimitedDocument2 pagesJharkhand Bijli Vitran Nigam LimitednandksrkumarNo ratings yet
- BFP - Clean AgentDocument47 pagesBFP - Clean AgentSamuelJrManatadNo ratings yet
- Carescape v100 BrochureDocument2 pagesCarescape v100 BrochureNirmayati YatiNo ratings yet
- The Teach For India FellowshipDocument31 pagesThe Teach For India FellowshipSynonymousNo ratings yet
- 16F723ADocument286 pages16F723ApexeaiNo ratings yet
- Computational Method To Estimate Single Event Upset Rates in An Accelerator EnvironmentDocument18 pagesComputational Method To Estimate Single Event Upset Rates in An Accelerator Environmentbububu66No ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet For Bechem GreaseDocument1 pageTechnical Data Sheet For Bechem GreaseSandeepNo ratings yet
- GPP Dip in 5Document7 pagesGPP Dip in 5irhana100% (1)
- 2006 Toyota Prius 1.5l Eng P0a3f TestingDocument7 pages2006 Toyota Prius 1.5l Eng P0a3f TestingilkinNo ratings yet
- AUDISON Prima AP8 9 Bit Tech SheetDocument1 pageAUDISON Prima AP8 9 Bit Tech SheetErwin HernandezNo ratings yet
- JawDocument29 pagesJawsudhak111No ratings yet
- Metnet 60G Unlicensed Mmwave Cpe V2: Enabling 5G Self-Organising Mmwave Access and BackhaulDocument2 pagesMetnet 60G Unlicensed Mmwave Cpe V2: Enabling 5G Self-Organising Mmwave Access and BackhaulCyrille N'GUESSANNo ratings yet
- Interest Rate ModelsDocument188 pagesInterest Rate Modelsdoc_oz3298No ratings yet
- Pipe Class 3SDNCDocument4 pagesPipe Class 3SDNCkar78kaviNo ratings yet
- Striking The Right Balance - Pricing in InsuranceDocument102 pagesStriking The Right Balance - Pricing in InsuranceShantanuNo ratings yet