Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Indian Astro House System
Uploaded by
vcrbabuOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Indian Astro House System
Uploaded by
vcrbabuCopyright:
Available Formats
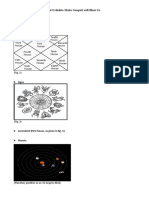
In almost all traditional practice, the twelve houses (bhva) of an astrological chart have the same boundaries as the
twelve signs in the chart; in other words, each sign is a house in the chart. The beginning of each house is the 0th degrees of the sign and the end is the 30th degree of the sign. What varies from chart to chart is the enumeration of these houses, i.e., which sign is the first house, which is the second, and so forth. This is determined by the position of the Lagna (the Ascendant, or the longitudinal point of the zodiac that was rising in the East at birth.) The house in which the Lagna falls is always the first house of the chart, and the other houses follow it, counter-clockwise, in the sequence of the zodiac. Each of the twelve houses signifies a region of the concerns of life, and the identity of the sign of that house colors what may be expected from that life. More than one system to align houses with signs are recognized in Jyotisha. The most common method is described above, a method that Western astrologers call the whole sign house system; another is Sripathi, introduced by Sripati, akin to a Porphyry house system. The modern Krishnamurti Paddhati also incorporates a Placidus house system. The principle of House Division introduced in Sripathi Bhva System is described as follows: "In the Sripathi system the 1st house cusp is the Lagna, and the 7th house cusp is the Descendant opposite it, the 10th house cusp is at the MC (Medium Coeli or Madhya Lagna), i.e. Zenith, and the 4th house cusp is at the IC (Imum Coeli or Patala Lagna) i.e. Nadir. The four quarters divided thus should be divided into three equal parts each, and thus we find the 12 house cusps in Sripathi system. To find the Bhava Sandhis (meeting points of houses) we should divide the distance between the house cusps into halves."[2]
[edit] The houses
The names of the 12 houses and the areas of life represented by them are:[3] 1. Lagna - Nature of Native, Appearance, Health, Character, Purpose of Life, behavior,[4] birth,[5] limbs,[6] head[7] 2. Dhana - Wealth, Family, Domestic Comforts, Early Education, Inheritance, Speech[8], moveable asssets[9] 3. Parakrama - Younger Brothers and Sisters, Communication (Talking, Writing, Business Documents),[10] Intelligence, fine arts[11] Short Journeys, "great prowess (physical and mental)," [12] hands, arms, shoulders [13] 4. Suhda - Mother, Emotions, Education, Home, Property and Land, Surrounding in Old Age, vehicles,[14] the chest[15] 5. Suta - Children, Lovers, Recreation[16] Devotion[17], Speculation and Gambling,[18] the belly,[19] accumulated karma[20] 6. Ripu/Roga - Diseases,[21] Maternal uncle and aunt, Litigation, Servants, Mental Worries, Enemies, Foreigners, small intestine,[22] 7. Kma - Spouse, Business Partner, Death,[23] Respect,[24] passion,[25] groin [26] 8. Mtyu - Death & Longevity, Obstacles,[24] Suffering, Sexual organs and sexual attractiveness,[27] Occult, Dowry, Inheritance, Imprisonment, Excretory organs,[28] accidents[29] 9. Bhgya - Father, Luck, Higher learning, Philosophy & Religion, Mentor or Guru, Prosperity, Travel, "deeds of virtue"[30]
10. Karma - Profession, Status & fame, Power, Father, Mother-in-law, Government, Clothes,[31] Commerce,[32] knees[33] 11. ya - Friends, Hopes, Earnings, Club or Social Activities, Elder Brothers and Sisters, Daughter/Son-in-law, calves, shins and ankles[34] 12. Vyaya - Expenses, Sleep (and convalescence), Sexual pleasures,[35] Spirituality, Travel & Pilgrimage, Secret Enemies, Imprisonment, Hospitals, Asylums, Liberation, loss[36] foreign residency,[37] feet[37]
You might also like
- Astrology For Layman: The most comprehensible book to learn astrologyFrom EverandAstrology For Layman: The most comprehensible book to learn astrologyRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- The 12 Rasis and Their CharacteristicsDocument12 pagesThe 12 Rasis and Their CharacteristicsJyothi VadhirajNo ratings yet
- English Summary NotesDocument4 pagesEnglish Summary NotesHasim AliNo ratings yet
- KP Fundamental Principles (AstroSage)Document39 pagesKP Fundamental Principles (AstroSage)G100% (1)
- KP Learning Home Tutorial Chapter 2 Fundamental PrinciplesDocument20 pagesKP Learning Home Tutorial Chapter 2 Fundamental PrinciplesaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- The Basic Components of Vedic AstrologyDocument4 pagesThe Basic Components of Vedic AstrologyRahan RRahanNo ratings yet
- AstronomyDocument20 pagesAstronomyAjay Kumar DasNo ratings yet
- Horary AstrologyDocument3 pagesHorary Astrologyabhi16No ratings yet
- Karak AsDocument8 pagesKarak AsDADI PRASANNANo ratings yet
- Karak AsDocument8 pagesKarak AsDADI PRASANNANo ratings yet
- Chakras and astrology: Astrology/Jyotish, #1From EverandChakras and astrology: Astrology/Jyotish, #1Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Chapter 2 - Fundamental Principles - KP AstrologyDocument22 pagesChapter 2 - Fundamental Principles - KP Astrologybabu reddy100% (1)
- Before We Start: The Horoscope ExplainedDocument16 pagesBefore We Start: The Horoscope Explainedraokvkp100% (1)
- 12 Houses SignificationDocument5 pages12 Houses Significationvinayak bhalekarNo ratings yet
- 1 HouseDocument4 pages1 Housejitendra mishraNo ratings yet
- Re BirthDocument4 pagesRe BirthRanjit bhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- KP BasicsDocument3 pagesKP BasicsKrishna CH100% (3)
- Stella AstrologyDocument30 pagesStella AstrologyVenkatadurgaprasad Gopam100% (1)
- Jo TishaDocument4 pagesJo TishamwbarveNo ratings yet
- Horary astrology is an ancient branch of horoscopic astrology in which an astrologer attempts to answer a question by constructing a horoscope for the exact time at which the question was received and understood by the astrol.docxDocument5 pagesHorary astrology is an ancient branch of horoscopic astrology in which an astrologer attempts to answer a question by constructing a horoscope for the exact time at which the question was received and understood by the astrol.docxgauranimaidasaNo ratings yet
- KP AstroguDocument23 pagesKP AstroguSaini Varun100% (1)
- Astrological HousesDocument5 pagesAstrological HousesMaría Goldstein100% (1)
- Observations on the 6th House and its Role in PredictionsDocument6 pagesObservations on the 6th House and its Role in Predictionsvbindu_150% (2)
- Astrological Analysis of Planet, House and RashiDocument4 pagesAstrological Analysis of Planet, House and RashiAstrologerAnjaanNo ratings yet
- 12 Astrological Houses ResumeDocument26 pages12 Astrological Houses ResumeCarlos FairfieldNo ratings yet
- Vedic Astrology Lesson - 8: More On KarakathwaDocument4 pagesVedic Astrology Lesson - 8: More On KarakathwaNagendra KrishnamurthyNo ratings yet
- The 12 Houses of Astrology and Their SignificationsDocument10 pagesThe 12 Houses of Astrology and Their Significationsmujibar rahamanNo ratings yet
- Understanding KP AstrologyDocument13 pagesUnderstanding KP AstrologyRavi Goyal100% (3)
- Karakas-Parijaata.com.docDocument11 pagesKarakas-Parijaata.com.docKrishna Das CNo ratings yet
- Notes On AstrologyDocument17 pagesNotes On Astrologyramaphanik2729No ratings yet
- Fundamental Principles KP Punit PandeyDocument13 pagesFundamental Principles KP Punit PandeyAshish100% (2)
- Astrology Secrets RevealedDocument5 pagesAstrology Secrets RevealedDebashis GhoshNo ratings yet
- Before We Start: The Horoscope ExplainedDocument18 pagesBefore We Start: The Horoscope ExplainedrrajeshdashNo ratings yet
- Tanu Bhava Base of Your HoroscopeDocument24 pagesTanu Bhava Base of Your Horoscoperajesh.shirwal382No ratings yet
- House (Astrology) : The Four Bhavas of Hindu AstrologyDocument2 pagesHouse (Astrology) : The Four Bhavas of Hindu AstrologymackNo ratings yet
- A Study of 10Th and Bhava and SignificanceDocument3 pagesA Study of 10Th and Bhava and SignificanceSugar SugarNo ratings yet
- KP Astrology Basics PDFDocument19 pagesKP Astrology Basics PDFbadriaa_182% (11)
- Congenital Disceases A Study From Trimsamsa VargaDocument5 pagesCongenital Disceases A Study From Trimsamsa VargaRaman KrishnanNo ratings yet
- KP Astrology TextbookDocument117 pagesKP Astrology Textbooklalitbhushan gotan100% (7)
- JKR Astro Research Foundation Astroclass Material Till Oct 11Document20 pagesJKR Astro Research Foundation Astroclass Material Till Oct 11jeydownloadNo ratings yet
- Before We StartDocument17 pagesBefore We Startanand rangaNo ratings yet
- Shri LagnaDocument6 pagesShri Lagnaharikrishan108No ratings yet
- 11 HousesDocument38 pages11 HousesSatyanneshi ER100% (2)
- April 2014 1396444394 131fa 08Document3 pagesApril 2014 1396444394 131fa 08Sagar ShindeNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Guide to KP Astrology - Understanding Horoscopes, Planets, Houses & MoreDocument14 pagesThe Ultimate Guide to KP Astrology - Understanding Horoscopes, Planets, Houses & Morepriyantha_yapa67% (3)
- KP Astro Basic 1Document5 pagesKP Astro Basic 1Darsh SoniNo ratings yet
- KP Horoscope ExplainedDocument29 pagesKP Horoscope Explainedravikpillai0% (1)
- Astrology Short NoteDocument7 pagesAstrology Short Notehsmanian100% (2)
- Chapter 2: Fundamental PrinciplesDocument45 pagesChapter 2: Fundamental Principlesmadhu77100% (1)
- Chapter 2: Fundamental Principles: KP Learning Home TutorialDocument21 pagesChapter 2: Fundamental Principles: KP Learning Home TutorialShanmugam GobinathNo ratings yet
- Lesson #1 - 1. Mantras For Learning Astrology. 2. Introduction To Vedic Astrology (Basic Concepts) .Document2 pagesLesson #1 - 1. Mantras For Learning Astrology. 2. Introduction To Vedic Astrology (Basic Concepts) .Leo Jones100% (2)
- The Art of Vedic AstrologyDocument79 pagesThe Art of Vedic AstrologyBrij PatwariNo ratings yet
- Karakas PlanetsDocument11 pagesKarakas PlanetsKrishna CH100% (2)
- KP AstrologyDocument87 pagesKP Astrologyanandrai2100% (3)
- Application of Jeeva Sareerain Nadi Astrology ColorDocument18 pagesApplication of Jeeva Sareerain Nadi Astrology ColorSunil Rupani100% (1)
- BTR (PDF Library)Document2 pagesBTR (PDF Library)raokvkp100% (1)
- 17 IndexDocument5 pages17 IndexvcrbabuNo ratings yet
- Tables of Houses, Placidus System: A Sample Page FromDocument1 pageTables of Houses, Placidus System: A Sample Page FromvcrbabuNo ratings yet
- Barack ObamaDocument4 pagesBarack Obamavcrbabu100% (1)
- Everything You Need to Know About Centrifugal FansDocument65 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Centrifugal Fansahmed100% (1)
- Florence Nightingale: The Lady with the LampDocument18 pagesFlorence Nightingale: The Lady with the LampsrinivasanaNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet FINAL LipidDocument3 pagesAnswer Sheet FINAL LipidFaridah MagumparaNo ratings yet
- PENERAPAN ARSITEKTUR TROPIS PADA HOTEL RESORT DI PANTAI KRAKALDocument12 pagesPENERAPAN ARSITEKTUR TROPIS PADA HOTEL RESORT DI PANTAI KRAKALleo adoNo ratings yet
- Biology Standard XII Human Reproduction WorksheetDocument10 pagesBiology Standard XII Human Reproduction WorksheetPriya SinghNo ratings yet
- Calculator For SW Density Changes - Effect of List On Ships DraftDocument3 pagesCalculator For SW Density Changes - Effect of List On Ships DraftHein Thurein KyawNo ratings yet
- Kultura I InteligencijaDocument15 pagesKultura I InteligencijaToni JandricNo ratings yet
- Function and Definite Integrals ExplainedDocument7 pagesFunction and Definite Integrals Explainedana maharaniNo ratings yet
- ArtsDocument5 pagesArtsRhovi Christine AbandoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.5: Measurements of Directions and Angles: Unit IDocument12 pagesLesson 1.5: Measurements of Directions and Angles: Unit ICarlo CabanusNo ratings yet
- Psychopathology: Dr. Shafqat Huma MBBS, FCPS (Psychiatry) Fellowship in Addiction Psychiatry (USA)Document48 pagesPsychopathology: Dr. Shafqat Huma MBBS, FCPS (Psychiatry) Fellowship in Addiction Psychiatry (USA)sfrtr100% (1)
- Briefing Paper No 4 CV Electrification 30 11 17 PDFDocument5 pagesBriefing Paper No 4 CV Electrification 30 11 17 PDFAlex WoodrowNo ratings yet
- AWWA M28 Rehabilitation of Water Mains 3rd Ed 2014Document133 pagesAWWA M28 Rehabilitation of Water Mains 3rd Ed 2014millini67% (3)
- Nsf-Ansi 55 PDFDocument56 pagesNsf-Ansi 55 PDFJawwad AhmedNo ratings yet
- BASIC IMMUNOLOGY TERMSDocument2 pagesBASIC IMMUNOLOGY TERMSAnnicoldjohn LariozaNo ratings yet
- What Is RTN/Microwave TechnologyDocument27 pagesWhat Is RTN/Microwave TechnologyRavan AllahverdiyevNo ratings yet
- 03-Mechanical Seal &seal System Basics-REV01Document39 pages03-Mechanical Seal &seal System Basics-REV01Fayez Al-ahmadiNo ratings yet
- Ross 308 AP Broiler PO2019-EN PDFDocument16 pagesRoss 308 AP Broiler PO2019-EN PDFJORGE GALVISNo ratings yet
- Schneider Power Supply PhaseoDocument26 pagesSchneider Power Supply PhaseoScott EnnisNo ratings yet
- Motherboards Tuf z270 Mark 2Document70 pagesMotherboards Tuf z270 Mark 2Jonah HexNo ratings yet
- Elimination - Nursing Test QuestionsDocument68 pagesElimination - Nursing Test QuestionsRNStudent1100% (1)
- National Leprosy Control Program For CHNDocument18 pagesNational Leprosy Control Program For CHNNaomi Cyden YapNo ratings yet
- ChecklistsDocument1 pageChecklistsnotme2120No ratings yet
- Multi Purpose StadiumDocument130 pagesMulti Purpose StadiumEmmanuel SolomonNo ratings yet
- Evolis User ManualDocument28 pagesEvolis User ManualIonmadalin1000No ratings yet
- WIP CaseStudyDocument3 pagesWIP CaseStudypaul porrasNo ratings yet
- The Role of Women in The Livelihood Strategies of The House Hold: Case of Geressie Woreda, Gamo Zone, EthiopiaDocument95 pagesThe Role of Women in The Livelihood Strategies of The House Hold: Case of Geressie Woreda, Gamo Zone, Ethiopiaermias eshetu100% (3)
- Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate: Riefing - Nfrared BsorptionDocument4 pagesTenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate: Riefing - Nfrared BsorptionMostofa RubalNo ratings yet
- Journal of Cleaner Production: S.M. Ashekuzzaman, Patrick Forrestal, Karl Richards, Owen FentonDocument10 pagesJournal of Cleaner Production: S.M. Ashekuzzaman, Patrick Forrestal, Karl Richards, Owen FentonSenthil KumarNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ghusoon Mohsin Ali: Al-Mustansiriya University College of Engineering Electrical Engineering DepartmentDocument89 pagesDr. Ghusoon Mohsin Ali: Al-Mustansiriya University College of Engineering Electrical Engineering Departmentهمام الركابي100% (1)