0% found this document useful (0 votes)
52 views2 pagesDouble Inverted Pendulum Control Methods
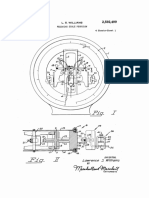
This document provides an introduction to an integral type-2 fuzzy logic type double inverted pendulum. It defines an inverted pendulum as a pendulum with its mass above its pivot point. A double inverted pendulum combines an inverted pendulum with a double pendulum, making it inherently unstable and requiring active balancing. The document explains that a double inverted pendulum can be controlled by moving its base or applying torque between the two pendulums. It includes a figure showing the systemic diagram of a double inverted pendulum.
Uploaded by
Ankit AgrawalCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
52 views2 pagesDouble Inverted Pendulum Control Methods
This document provides an introduction to an integral type-2 fuzzy logic type double inverted pendulum. It defines an inverted pendulum as a pendulum with its mass above its pivot point. A double inverted pendulum combines an inverted pendulum with a double pendulum, making it inherently unstable and requiring active balancing. The document explains that a double inverted pendulum can be controlled by moving its base or applying torque between the two pendulums. It includes a figure showing the systemic diagram of a double inverted pendulum.
Uploaded by
Ankit AgrawalCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd