0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views2 pagesCrosstab Analysis of Sanitation and Prevalence
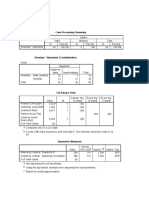
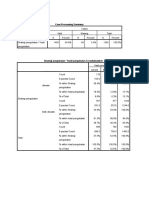
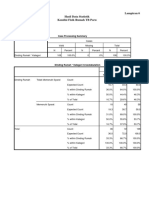
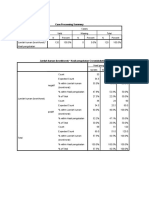
This document presents the results of a cross-tabulation analysis examining the relationship between sanitation (sanitasi) and prevalence (prevalensi). It found that 47 cases had adequate sanitation and positive prevalence, while 20 cases had inadequate sanitation and negative prevalence. A chi-square test revealed a statistically significant relationship between sanitation and prevalence with a p-value of 0.035. The odds ratio also indicated those with adequate sanitation had lower odds of positive prevalence compared to those with inadequate sanitation.
Uploaded by
fathim zahroCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views2 pagesCrosstab Analysis of Sanitation and Prevalence
This document presents the results of a cross-tabulation analysis examining the relationship between sanitation (sanitasi) and prevalence (prevalensi). It found that 47 cases had adequate sanitation and positive prevalence, while 20 cases had inadequate sanitation and negative prevalence. A chi-square test revealed a statistically significant relationship between sanitation and prevalence with a p-value of 0.035. The odds ratio also indicated those with adequate sanitation had lower odds of positive prevalence compared to those with inadequate sanitation.
Uploaded by
fathim zahroCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd