0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views1 pageCommon Changes in Reported Speech
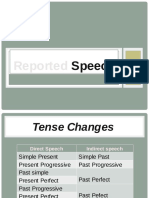
She said that she had seen him today. He said that he had seen him yesterday. He said that he had met her the day before yesterday. He said that he would see him tomorrow. They said that they would come the day after tomorrow. She said that she had an appointment next week. He told us that he had been on holiday last week. He said that he had seen her a week ago. She said that she was getting a new car that week.
Uploaded by
moni_76Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views1 pageCommon Changes in Reported Speech
She said that she had seen him today. He said that he had seen him yesterday. He said that he had met her the day before yesterday. He said that he would see him tomorrow. They said that they would come the day after tomorrow. She said that she had an appointment next week. He told us that he had been on holiday last week. He said that he had seen her a week ago. She said that she was getting a new car that week.
Uploaded by
moni_76Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd