0% found this document useful (0 votes)
88 views2 pagesTherapeutic Actions: Indications
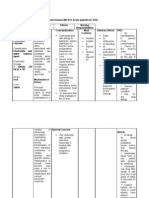
Potassium is an important intracellular cation that participates in many physiological processes like maintaining intracellular tonicity, nerve impulse transmission, and muscle contraction. It can be indicated to treat potassium deficiency from conditions like vomiting, diarrhea, or prolonged diuretic use. Potassium should not be used in cases of severe renal impairment, untreated Addison's disease, hyperkalemia, acute dehydration, or GI disorders that delay passage. Slow K is a extended-release formulation meant to provide a gradual release of potassium to minimize high localized concentrations in the GI tract, and it should never be added to an IV bag that is hanging. Close monitoring of IV sites and cardiac rhythm is needed with IV potassium.
Uploaded by
Chinju CyrilCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
88 views2 pagesTherapeutic Actions: Indications
Potassium is an important intracellular cation that participates in many physiological processes like maintaining intracellular tonicity, nerve impulse transmission, and muscle contraction. It can be indicated to treat potassium deficiency from conditions like vomiting, diarrhea, or prolonged diuretic use. Potassium should not be used in cases of severe renal impairment, untreated Addison's disease, hyperkalemia, acute dehydration, or GI disorders that delay passage. Slow K is a extended-release formulation meant to provide a gradual release of potassium to minimize high localized concentrations in the GI tract, and it should never be added to an IV bag that is hanging. Close monitoring of IV sites and cardiac rhythm is needed with IV potassium.
Uploaded by
Chinju CyrilCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd