0% found this document useful (0 votes)
113 views5 pagesUniversity of Balamand: Faculty of Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering
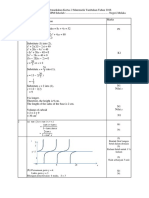
This document contains code for performing cubic spline interpolation. It defines a function that takes in vectors of x and y coordinates (xi and a), finds the coefficients for cubic polynomials between each point, and evaluates these polynomials to interpolate a y value for any given x coordinate. The code is tested by inputting sample x and y vectors and interpolating the y value for x=2.5.
Uploaded by
Jad ChalhoubCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
113 views5 pagesUniversity of Balamand: Faculty of Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering
This document contains code for performing cubic spline interpolation. It defines a function that takes in vectors of x and y coordinates (xi and a), finds the coefficients for cubic polynomials between each point, and evaluates these polynomials to interpolate a y value for any given x coordinate. The code is tested by inputting sample x and y vectors and interpolating the y value for x=2.5.
Uploaded by
Jad ChalhoubCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd