0% found this document useful (0 votes)
206 views8 pagesValue Analysis and Engineering Guide
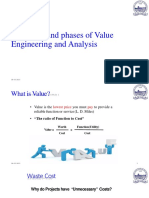
Value analysis and value engineering are systematic techniques to identify the function of a product or service and provide that function at the lowest cost. Value analysis is applied to existing products, while value engineering is applied during the design stage of new products. The techniques aim to simplify products, use better materials, modify designs, make processes more efficient, reduce costs, and increase product utility in an economical way. Value analysis should be considered when a company's sales are declining, prices are too high, costs are rising disproportionately, or profits are falling. It evaluates performance and value as a ratio of utility to cost.
Uploaded by
Anonymous DQGLUZxHCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
206 views8 pagesValue Analysis and Engineering Guide
Value analysis and value engineering are systematic techniques to identify the function of a product or service and provide that function at the lowest cost. Value analysis is applied to existing products, while value engineering is applied during the design stage of new products. The techniques aim to simplify products, use better materials, modify designs, make processes more efficient, reduce costs, and increase product utility in an economical way. Value analysis should be considered when a company's sales are declining, prices are too high, costs are rising disproportionately, or profits are falling. It evaluates performance and value as a ratio of utility to cost.
Uploaded by
Anonymous DQGLUZxHCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Value Analysis / Value Engineering
- DFM: An Example
- Aims
- When to Apply Value Analysis
- Value Definition
- Types of Value
- Value Engineering Procedure