0% found this document useful (0 votes)
79 views1 pageUnderstanding Telescopes and Astronomy Concepts
This document discusses several topics related to astronomy including:
1) Why large telescopes use mirrors and radio telescopes use large dishes - to collect visible light and radio waves, respectively.
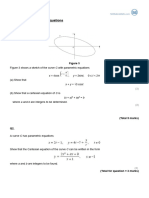
2) Ray diagrams and how they are used to show the path of light through a lens and find the focal length and image location.
3) A diagram labeling the relative positions of the sun, earth, and moon at different times of day and year.
4) Additional concepts like moon phases, parallax angle and parsecs for measuring distance, and how Cepheid variables can be used to calculate distances through their observed brightness and pulsation rate.
Uploaded by
api-27344426Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
79 views1 pageUnderstanding Telescopes and Astronomy Concepts
This document discusses several topics related to astronomy including:
1) Why large telescopes use mirrors and radio telescopes use large dishes - to collect visible light and radio waves, respectively.
2) Ray diagrams and how they are used to show the path of light through a lens and find the focal length and image location.
3) A diagram labeling the relative positions of the sun, earth, and moon at different times of day and year.
4) Additional concepts like moon phases, parallax angle and parsecs for measuring distance, and how Cepheid variables can be used to calculate distances through their observed brightness and pulsation rate.
Uploaded by
api-27344426Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd