0% found this document useful (0 votes)
291 views14 pagesCommon Disease Management Overview
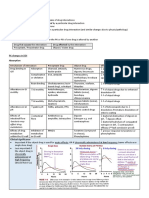
The document summarizes information on the management of common diseases including asthma, COPD, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, depression, infections, and osteoarthritis. It provides details on the indications, dosing, monitoring, and interactions of medications commonly used to treat these conditions, such as warfarin, frusemide, metformin, sulfonylureas, and ACE inhibitors. It also lists the treatment aims and options for conditions like diabetes mellitus type 2 and heart failure.
Uploaded by
cdx25Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
291 views14 pagesCommon Disease Management Overview
The document summarizes information on the management of common diseases including asthma, COPD, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, depression, infections, and osteoarthritis. It provides details on the indications, dosing, monitoring, and interactions of medications commonly used to treat these conditions, such as warfarin, frusemide, metformin, sulfonylureas, and ACE inhibitors. It also lists the treatment aims and options for conditions like diabetes mellitus type 2 and heart failure.
Uploaded by
cdx25Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Common Disease Management
- Warfarin Management
- Frusemide and Osteoarthritis
- Diabetes II
- Heart Failure
- Hypertension