0% found this document useful (0 votes)
63 views10 pagesScience Investigation Questions Guide
This document provides information about the format and content of a science exam, including:
- Section A contains 30 objective questions worth 60% of the exam. Section B contains 4-5 subjective questions based on science process skills worth 40% of the exam.
- The exam covers investigating living things, materials, energy, Earth/universe, and technology.
- Tables show the number of questions per year from 1999-2009 for grades 4-6.
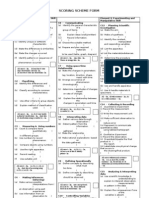
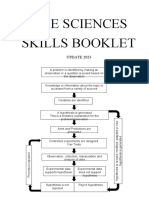
- Key terms and concepts are defined for science process skills like observation, inference, variables.
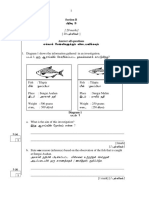
- Examples of questions and answers are provided to illustrate these concepts.
Uploaded by
Ching Chuo TiongCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
63 views10 pagesScience Investigation Questions Guide
This document provides information about the format and content of a science exam, including:
- Section A contains 30 objective questions worth 60% of the exam. Section B contains 4-5 subjective questions based on science process skills worth 40% of the exam.
- The exam covers investigating living things, materials, energy, Earth/universe, and technology.
- Tables show the number of questions per year from 1999-2009 for grades 4-6.
- Key terms and concepts are defined for science process skills like observation, inference, variables.
- Examples of questions and answers are provided to illustrate these concepts.
Uploaded by
Ching Chuo TiongCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd