100% found this document useful (3 votes)
179 views18 pagesECG Course IV: ST-T Deviations & QT Prolongation
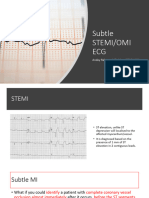
This document discusses ST and QT abnormalities seen on electrocardiograms (ECGs). It aims to help students diagnose ST segment elevation, identify acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and other causes of ST elevation. The document reviews how to diagnose ST depression and understand T wave inversion. It provides information on ECG changes seen in coronary heart disease, how to locate AMI based on which leads show ST elevation, and non-AMI causes of ST elevation like early repolarization and pericarditis.
Uploaded by
api-3757039Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (3 votes)
179 views18 pagesECG Course IV: ST-T Deviations & QT Prolongation
This document discusses ST and QT abnormalities seen on electrocardiograms (ECGs). It aims to help students diagnose ST segment elevation, identify acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and other causes of ST elevation. The document reviews how to diagnose ST depression and understand T wave inversion. It provides information on ECG changes seen in coronary heart disease, how to locate AMI based on which leads show ST elevation, and non-AMI causes of ST elevation like early repolarization and pericarditis.
Uploaded by
api-3757039Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd