Manufacturing Execution System (MES) Overview
t: 1890 924 155 / +353 21 4536121
f: +353 1 6335872
e: info@esp.ie
w: www.esp.ie
�What is MES
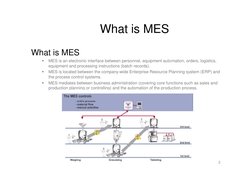
What is MES
MES is an electronic interface between personnel, equipment automation, orders, logistics, equipment and processing instructions (batch records). MES is located between the company-wide Enterprise Resource Planning system (ERP) and the process control systems. MES mediates between business administration (covering core functions such as sales and production planning or controlling) and the automation of the production process.
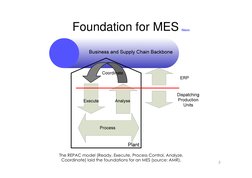
�Foundation for MES
Return
The REPAC model (Ready, Execute, Process Control, Analyze, Coordinate) laid the foundations for an MES (source: AMR).
�Vision of an MES System
Some paper? No Paper
Lights Out, Continuous Batch
�Benefits of MES
Labour avoided and quality enhanced
Data Validation No Blanks (Fields need to be completed to allow process to continue) Value Limits (warning/enforced) Automatic Calculations (eliminate double signature) Eliminate generation, verification and mgt of paper batch record Check the batches by exception
Increased Compliance (inc. 21 CFR Part 11) Reporting across batches or work centres Data Security Archiving and Retrieval Enhanced audit trail Improved traceability Improved Product Information Increased Efficient Information Improved Quality Information Ease of use of Product Information Reporting Reduce/ Remove Paper
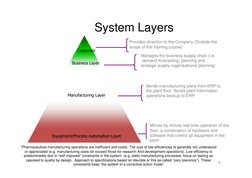
�System Layers
Corporate Business Layer Provides direction to the Company (Outside the scope of this training course) Manages the business supply chain (i.e. demand forecasting, planning and strategic supply organisational planning)
Manufacturing Layer
Sends manufacturing plans from ERP to the plant floor. Sends plant Information operations backup to ERP
Equipment/Process Automation Layer
Minute by minute real time operation of the floor, a combination of hardware and software that control all equipment in the plant
Pharmaceutical manufacturing operations are inefficient and costly. The cost of low efficiencies Is generally not understood or appreciated (e.g. manufacturing costs far exceed those for research And development operations). Low efficiency is predominately due to self imposed constraints in the system (e.g. static manufacturing processes, focus on testing as opposed to quality by design, Approach to specifications based on discrete or this so-called zero tolerance). These 6 constraints keep the system in a corrective action mode
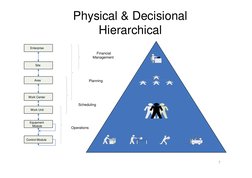
�Physical & Decisional Hierarchical
Enterprise
Financial Management
Site
Area
Planning
Work Center
Scheduling
Work Unit
Equipment Module
Operations
Control Module
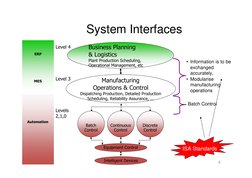
�System Interfaces
Level 4
ERP
Business Planning & Logistics
Plant Production Scheduling, Operational Management, etc
MES
Level 3
Dispatching Production, Detailed Production Scheduling, Reliability Assurance, ...
Manufacturing Operations & Control
Information is to be exchanged accurately, Modularise manufacturing operations Batch Control
Levels 2,1,0
Automation
Batch Control
Continuous Control
Discrete Control
Equipment Control Intelligent Devices
ISA Standards
8
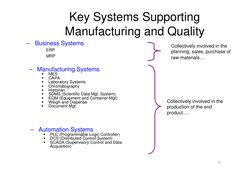
�Key Systems Supporting Manufacturing and Quality
Business Systems
ERP MRP
Collectively involved in the planning, sales, purchase of raw materials
Manufacturing Systems
MES CAPA Laboratory Systems Chromatography Historian SDMS (Scientific Data Mgt. System) EQM (Equipment and Container Mgt) Weigh and Dispense Document Mgt.
Collectively involved in the production of the end product.
Automation Systems
PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) DCS (Distributed Control System) SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition)
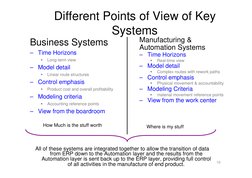
�Different Points of View of Key Systems
Business Systems
Time Horizons
Long-term view
Manufacturing & Automation Systems
Time Horizons
Real-time view
Model detail
Linear route structures
Model detail
Complex routes with rework paths
Control emphasis
Product cost and overall profitability
Control emphasis
Physical movement & accountability
Modeling Criteria
material movement reference points
Modeling criteria
Accounting reference points
View from the work center
View from the boardroom
How Much is the stuff worth Where is my stuff
All of these systems are integrated together to allow the transition of data from ERP down to the Automation layer and the results from the Automation layer is sent back up to the ERP layer, providing full control of all activities in the manufacture of end product.
10
�Overview Functionality of ERP, MES, Automation
ERP
Supply Chain
Enterprise Resource Planning
Inventory Management MRP Asset Management Financial Management
Warehouse Management Equipment/ Container Management Central Recipe & Configuration Management
Scheduling & Planning LIMS /SPC Weighing & Dispensing (Electronic) Batch Record Data Historian Equipment Control
Console Controller Corrective And Preventive Action Tracking
Personnel Qualification & Training
MES
Document Management CAPA
Material Tracking (Genealogy)
Reporting/ Information
Automation
PLC/Intelligent Device
SCADA
DCS
Console Controller
PLC/Intelligent Device
including system integration
11
�IT View of System Landscape
ERP
Level 4
Business Process Information Network
ERP, APO, Logistics Systems
MES
Level 3
Operations Information Network
MES, LIMS, WMS, CMM Systems
Level 2
Automation
HMI, SCADA, Batch Systems
Automation Network
PLC, DCS, Packaged Systems
Discrete & Process Device Communication Networks
Level 1
I/O, Devices, Sensors
12
�Typical MES Architecture
13
�Modules/Benefits of MES
Typical Modules of an MES System EBR/MBR Weigh & Dispense Warehouse Mgt Material Flow Control Equipment & container Mgt Finite Scheduling
14
�Standard MES Functionality
Manufacturing Order (ERP)
Work Order (MES)
SFO1
SFO2
SFO3
SFO4
SFO5
15
�Material Mgt Within Production Controlled by MES
Blending Compression Coating
Electronic control of all materials in production (Order and Stock)
16
�Visual Production Status/Tracking
Sign off clean sheet
Line clearance
Tablet filler set-up
labeller
Checkweigher
Vision system
Take first retain sample
production
17
�Automatic Recording of Daily balance checks in EQM
Paper Log Book Paperless EQM
18
�Automatic Complete Check of Room and Setup Parts
Paper BMR Paperless EBR
Plausibility Check Electronic Signature Check by System
19
�Packaging Line Batch Details
Product: Tablet 800mg Market; IE/ UK Batch No: 123 Exp date: SEP 2006
20
�Barcode Identification and Scanning
Room and equipment Pack room 1 Checkweigher Bottle unscrambler Auto cartoner Vision system GMP No.
F-05 CW-001 BUS-001 CRT-001 PVS-003
Verified By
Room F-05
BUS-001
CW-001
CRT-001
PVS-003
21
�Barcode Identification and Scanning
Scanned
Room and equipment Pack room 1 Checkweigher Bottle unscrambler Auto cartoner Vision system Set-up checks GMP No.
F05 CW-001 BUS-001 CRT-001 PVS-003
Verified By
Not Necessary
variables
John Smith 30 Sep 05 Verified by:______________________________Date:___________________________________
22
th
�Automatic Calculation of water to add for Granulation
Paper BMR Paperless EBR
23
�Automatic Downloading of setpoints to control equipment (e.g. Granulator PLC)
Paper BMR Paperless EBR
MES
Control Network
Granulator
Blender
Coaters
Presses
24
�Execute EBR for Electronic Batch Recording
Steering of RSBatch execution by using EBR and monitor batch execution. Real-time process and data presentation using RSVIEW and process control using RSBatch.
25
�Execute EBR for Electronic Batch Recording
Return
Create Batch Report
Analyse, review and approve batch report for real-time Release
26
�Standards & Best Practises
(and FDA Current Initiatives)
Regulation/Compliance 21 CFR Part 11 (Electronic Records & Signature)
Validation of Systems Copies of records Protection of records Limitations on access Computer Time stamped records Operational system checks (permission of sequencing) Authority checks Use of devices for determination of checks Qualified personnel Adherence to written policies Use of appropriate control Control for open systems EBRs (unique and attached to the executed record) Periodic testing of controls
Standards/ Best Practises PAT
Reduction of cycle times Less batch failures Faster batch release time Improved management change control Reduced start-up time Improved speed of deployment
GAMP4 EMEA (European Medicines Agency) ISPE (International Society of
Pharmaceutical Engineers)
Lean Manufacturing S95 standard S88 standard
FDA (Food and Drug Administration) IMB (Irish Medicine Board) Annex (11 & 15)
27
�Future Requirements & Standards
Competitive markets is forcing the need to have accurate,timely information on which to make business decisions. The data already exists on the manufacturing floor. The issue is accessing the data and turning that into useful information. The need is to leverage standards to help move forward.
28
�Any Questions?
t: 1890 924 155 / +353 21 4536121
f: +353 1 6335872
e: info@esp.ie
w: www.esp.ie