0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views2 pagesPediatric Pneumonia Nursing Assessment
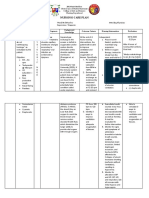
The mother reported that her baby was having difficulty breathing due to coughing. On examination, the baby had tachycardia, dyspnea, and a temperature of 37.7°C. The diagnosis was impaired gas exchange due to secretions affecting oxygen exchange in the lungs. The planned nursing interventions were to monitor vital signs, elevate the head of the bed and change positions frequently, limit visitors, and assess the lungs every 4 hours to ensure timely resolution of the current infection without complications.
Uploaded by
_garonCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views2 pagesPediatric Pneumonia Nursing Assessment
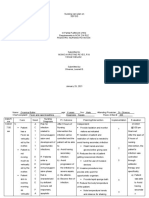
The mother reported that her baby was having difficulty breathing due to coughing. On examination, the baby had tachycardia, dyspnea, and a temperature of 37.7°C. The diagnosis was impaired gas exchange due to secretions affecting oxygen exchange in the lungs. The planned nursing interventions were to monitor vital signs, elevate the head of the bed and change positions frequently, limit visitors, and assess the lungs every 4 hours to ensure timely resolution of the current infection without complications.
Uploaded by
_garonCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Rationale: Provides reasoning behind each planned intervention, linking actions to expected outcomes.
- Diagnosis: Presents the clinical diagnosis based on assessment findings, focusing on respiratory conditions.
- Evaluation: Discusses criteria and results for assessing the effectiveness of interventions and patient outcomes.
- Planning: Outlines planned interventions, goals, and timeliness to address patient diagnosis.
- Intervention: Lists actions and measures to be taken to achieve the planned outcomes, such as monitoring and evaluating progression.
- Assessment: Details subjective and objective assessment findings including patient symptoms and vital signs.
- Scientific Explanation: Explains the scientific rationale for the observed symptoms and diagnosis, emphasizing pathophysiology.