GoodPracticeFramework
Performance Management
�GoodPracticeFramework
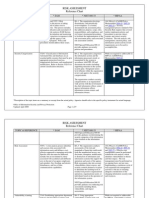
Decision Gatewa y Strategic Planning STRATEGIC
PLANNING
PolicyContext Needs Assessment Strategic Review Outcomes CurrentService &Demand Contract Review Benchmarking Market Assessment& Stimulation Options Development &Resourcing Pricing Model CommissioningPlan andBusinessCase
Stakeholder Engagement
Continuous Improvement
Str at yD eg
em en
Performance Measurement
ev
ag
an
STRATEGICCOMMISSIONING
e lo en pm
Co n
Contract Startup
Toidentifythehealthneedsofthe populationandmakeprioritised decisionstosecurecaretomeetthose needswithinavailableresources
Decision Gatewa y
ct
tra
ACQUISITION PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT
Contract Award Provider Selection Tendering Standard Contracts Evaluation Plan Market Sounding Consultation
Procurement
Stakeholder Engagement
Procurement Initiation Procurement Route Specification Development
Decision Gatewa y
�Performance Management Overview
This stage starts after the contract has been awarded to the successful bidder. Managing the contract efficiently ensures that: Targets agreed in the contract are adhered to and measures can be put in place early to improve performance if they are not being met. You can measure performance against key outcomes linked to strategic targets including care improvement and adjust the service according to changing circumstances and demands Getting the information that you need on the performance of the contractor can be achieved firstly by setting up systematic methods of measuring and reviewing performance throughout the life of the contract and secondly by maintaining an open and constructive relationship with your service provider. By achieving such clarity you are in a better position to make informed decisions about the future of the service. While ensuring that levels of service set out in the contract are met, you should not necessarily regard the contract as a rigid set of stipulations which cannot be changed should circumstances and demand change. By maintaining an open dialogue with your provider, you can achieve a level of service which not only realises planned improved patient outcomes but which could potentially exceed them. The steps in this stage look firstly at managing the transition from award of contract to contract start-up and then at how you can set up a firm foundation for reporting and Performance Management, as well as providing a framework for continuous improvement.
�Performance Management
Decision Gateway Strategic Planning The steps in this stage will contribute towards developing your competencies in the following areas
Strategic Review
Continuous Improvement
Performance Management
Co n
Contract Start up
tra
ct
an
ag
em en
Performance Measurement
helpingcommissionersdevelopcompetencies
�Performance Management Step 1: Contract start up
Strategic Planning
Prerequisites Provider selected Contract agreed
1
Performance Management
Summary The terms and conditions of the contract will have been established during the tendering process. This stage describes the period between contract signature and the commencement of service The purpose of this stage is to ensure a smooth transition of services provided by the provider, and a common understanding of how the management of the contract will be carried out in practice. The primary output of this will be a Statement of Readiness. In setting up the contract you should be aiming to establish working practices that will provide a constructive commercial relationship with your service provider. To do this you will need: A clear understanding of the business objectives on both sides of the contract Effective governance and administration of the contract, including regular Performance Management and reporting and the appointment of a contract manager. On the PCT side, the contract manager must have an in-depth knowledge of the care area for which the contract is being provided. A commitment to continuous improvement A thorough understanding of the contract and services specified Flexibility over unforeseen circumstances, particularly in long-term contracts and a commitment to manage a change in the contract should requirements or scope change. A broad perspective of the contract which looks critically at outcomes as well as outputs. Information/Dataset
contract
Who is involved? Project/Contract Managers Clinical Governance Commercial Legal Service specifiers
Source
�Performance Management Step 1: Contract start up
Keyactivitiest To ensure that the transition from contract award to service commencement is clearly defined, be clear about allocation of responsibilities, including knowing and agreeing who funds the transition. After the contract is signed, you next need to work with your service provider to ensure that you are ready for the start of the new service. The key steps you will need to address during the implementation stage may include: Planning and setting up mobilisation meetings with appropriate stakeholders as early as possible Delivering the change through disciplined project management. Plan carefully to minimise disruption to ongoing business requirements. Transition of staff and assets. Designated resources need to be in place for transition (e.g. communications, HR, contract, finance, IT) Identification of key risks and issues Building key interfaces between relevant (internal and external) stakeholders Establishing an appropriate culture within the retained organisation Building the relationship with the provider. Clear communication is a key factor. Clear and formal methods of reporting progress must be agreed. Ensuring that services are safe and meet contractual requirements before patients are seen Identifying and realising any quick wins needed to justify the commercial case and demonstrate success. Depending on nature, size and complexity of the service being provided, the implementation stage will vary enormously. It is important to ensure that there is a team in place to manage the contract throughout its life
�PerformanceManagementStep1:Contractstartup
ToolsandTemplates Transition to safe toolkit from the Mental Health Road map Statements of Readiness template http://www.dh.gov.uk/en/Procurementandproposals/Procurement/ProcurementatPCTs/DH_ 081031
Linkstofurtherguidance Good Practice contract management framework (OGC December 2008) http://www.ogc.gov.uk/procurement_documents_best_practice_guidance_.asp Contract Management Guidelines (OGC 2003) www.ogc.gov.uk/documents/Contract_Management.pdf
WCCCompetency 10 Effectively manage systems and work in partnership with providers to ensure contract compliance and continuous improvements to ensure sustainable development and value for money
�Performance Management Step 2: Performance Measurement
Strategic Planning
Prerequisites Contracts National and local targets Specification
1
Performance Management
Summary An effective performance measurement regime should ensure that the provider is delivering against the targets stated within the contract. This involves not only measuring agreed quantitative targets, for example volume and timeliness, but also working with your provider to ensure that the contract is continuing to deliver the desired outcomes for patients. Contract management activities can be broadly grouped into three areas: service delivery management ensures that the service is being delivered as agreed, to the required level of performance and quality. relationship management keeps the relationship between the two parties open and constructive, aiming to resolve or ease tensions and identify problems early. contract administration handles the formal governance of the contract and changes to the contract documentation.
Whoisinvolved? Thisprocessshouldbeledbytheperformanceimprovement/managementteamwithinputfrominformationanalysts,contractand servicemanagers.
�PerformanceManagementStep2:Performance Measurement
Key activities
1. Measurements In order to achieve this step you need to consider the following: Confirm with your service provider the key performance indicators set out in the contract. These will typically cover: Service standards Service activity Financial activity Service quality. Agree the means of measurement and how the evidence will be acquired as described in the specification development you should be seeking to collect a wide range of evidence including data on patient safety , clinical effectiveness and workforce standards. When it comes to the agreed review time you need to complete your assessment of the performance. At the same time, your service provider should be given the opportunity to make their own assessment. Make sure that you have a balanced set of indicators but it is advisable not to have too many. You need to consider the cost and difficulty of collecting data. 2. Review process Ensure that you have a timetable of reviews that meets those outlined in the specification Gather your information analyse activity and financial data Review feedback and information from patient groups Make an assessment against your KPIs. You can score your assessment these can be weighted according to the priorities of your benefits or targets. You should not allow a part score for a performance indicator that has not been fully met. Scoring your performance will allow you to present the performance report in a graphical format Discuss results with provider and give them the opportunity to make a separate assessment Review joint performance assessment and produce report Reflect on the results of the report with the provider and within the PCT Report any concerns to customer departments Agree a written improvement plan with the provider Prioritise areas for future review Ensure stakeholders see results of performance reviews
�PerformanceManagementStep2:Performance Measurement
Key activities continued 3. Managing Poor performance How you deal with poor performance can depend on a number of factors. By fostering a constructive relationship with your provider you should be able to spot problems early and put in place an improvement plan before the issue becomes serious and before the matter has become serious. In determining how punitive your action will be you need to consider the risk of any failure to patients and the consequent severity of the situation, whether there has been a breach of contract and the providers previous record and response to poor performance. To deal with a problem effectively you need to: Analyse the reasons behind the problem Make clear to the provider the problem that has been caused Give managers the time to develop a corrective action plan
�Performance Management Step 2: Performance Measurement
Tools and Templates Performance review timetable Customer review template Examples
For examples of KPIS see http://www.dh.gov.uk/en/Publicationsandstatistics/Publications/PublicationsPolicyAndGuidance/DH_4137271
Links to further guidance http://www.ogc.gov.uk/procurement_documents_best_practice_guidance_.asp OGC Contract Management Guidelines www.ogc.gov.uk/document/contract_management.pdf OGC Category management toolkit http://www.ogc.gov.uk/documents/SupplierCustomer_Performance_measurement.pdf http://www.ogc.gov.uk/documents/Performance_Indicators(1).pdf Mental Health Road Map Contract Management Toolkit http://www.pasa.nhs.uk/PASAWeb/PCTzone/mentalhealthservices/HowdoIcontractform entalhealthservices/Procurementtoolkit.htm
WCC Competency 10 Effectively manage systems and work in partnership with providers to ensure contract compliance and continuous improvements to ensure sustainable development and value for money
�Performance Management Step 3: Continuous Improvement
Strategic Planning
Prerequisites Understanding of national, regional, organisational and contract targets Who is involved? This process should be led by the performance improvement/management team with input from service managers, clinicians including Clinical governance and patients.
1
Performance Management
Summary The whole commissioning relationship is based on one of continuous improvement. It is essential that every effort is taken to ensure that both stakeholders and service providers seek and exploit any opportunity to improve the level and quality of the service to the patient. This will be done initially by Performance Management and improving performance and compliance with the provider. Throughout the life of the contract, it is important to work jointly with the provider to identify and explore innovation as a means to improve service, quality, cost-effectiveness, etc. as well as seeking service and cost improvement and containment opportunities. This can be achieved through the use of service reports, patient feedback and market developments and enabled by establishing principles for continuous improvement as part of the tender specification, which can then act as a lever for ongoing development throughout the contract term.
Informationrequired Information/Dataset KPIs Patient experience data Source
Patient satisfaction surveys
�PerformanceManagementStep3:ContinuousImprovement
Key activities
In addition to managing and measuring performance against the contract. You need to maintain a dialogue with your providers so that both sides can respond to changing demand this includes: Monitoring and managing development plans Involving your provide in joint improvement efforts that will continue to meet the PCTs key strategic objectives Ensuring that there is resource and assistance in place to develop new opportunities Employing knowledge management to continue to track the provider market, to analyse spend history changes in the health economy Where you have more than one provider competing for services it is important to monitor the impact of that competition on price and quality of services Involving clinicians is an important aspect of achieving continuous improvement. New innovations or the impact of improvements is related care areas could have an effect of the service required in the future perhaps introducing new ways of improving patient care or changing the emphasis of the service provided. Involving all key stakeholders in regular discussions about service provision will help foster an environment of continuous improvement.
�PerformanceManagementStep3:ContinuousImprovement
WCC Competency 8. Promote and specify continuous improvement in quality and outcomes through clinical and provider innovation and configuration 10 Effectively manage systems and work in partnership with providers to ensure contract compliance and continuous improvements to ensure sustainable development and value for money
Tools and Templates http://www.institute.nhs.uk/wo rld_class_commissioning/dat a_into_information/tools_and _templates.html
Further Guidance For supporting information for benchmarking http://www.connectingforhealth.nhs.uk/systemsandservices/sus
�Performance Management Step 4: Strategic Review
Strategic Planning
Prerequisites Contract Strategic targets
1
Performance Management
Summary The strategic review aims to provide an assessment of the services commissioned based on the specific characteristics of the performance levels agreed in the contract. This is an ongoing process that should ensure that the strategic need continues to exist for the commissioned service and that contracts in place remain fit for purpose and deliver value for money. However, there should be an annual assessment that will report whether or not the service in place is still fit for purpose and that the funding and resources associated with that service are still beneficial. Of particular importance is to continue to check the patient demographic and environment to ensure that the service is still meeting demand and the impact of related programmes. For example, how is the performance of the management of obesity affecting demand for diabetes care?
Whoisinvolved? This process should be led by the project sponsor and the performance improvement/management team with input from: PCT Board Performance management team Contract managers Service managers Clinicians Patients.
�PerformanceManagementStep4:StrategicReview
Information required Information/Dataset Activity information Source PCT
Performance metrics
PCT
Financial cost of the service
PCT
National & Local (LDP) targets
PCT
Performance against key metrics Performance against national standards
PCT PCT/DH
�Performance Management Step 4: Strategic Review
Key activities
There are three elements to the strategic review: Service performance How is the service performing against the CSFs in the contract? How is the service performing against national and local targets? How is the relationship with the service provider? Is it conducive to providing the best service possible? Value for money How do resources and costs compare against local comparators? Service demand Is there still the same level of need for this service? Is the same approach to demand management still relevant?
Yourcommissioningstrategyreviewneedstoconsider: Anymajorexternalfactorsthatinfluencedtheperformanceoftheserviceinadefinedperiodoranyfactorsthatarelikely toinfluenceprioritiesinthecomingperiod. Revieweachofyouroutcomesandspecifyprogressagainsteachofthekeyperformanceindicatorsandanyactionsthat havebeentakenasaresultoftheperformancemeasured. Recordanychangesthathaveoccurredthatmightaffectthepriorityoftheserviceincludingtheimpactofprogresson relatedcarepathways forexamplehavethesuccessofpublichealthcampaignsreduced thenumberofpatientsrequiring treatmentinsomeareasandhowdoesthisaffectthesupplyofthattreatment. Reviewyouroriginalobjectivesmeasuresandactionsandproposechangeswhereapplicable
WCC Competency 10. Effectively manage systems and work in partnership with providers to ensure contract compliance and continuous improvements to ensure sustainable development and value for money