Implement an eBGP based solution, given a network design and a set of requirements Determine network resources needed for
implementing eBGP on a network Create an eBGP implementation plan Create an eBGP verification plan Configure eBGP routing Verify eBGP solution was implemented properly using show and debug commands Document results of eBGP implementation and verification plan
�Border Gateway Protocol Used to exchange routes/prefix between different autonomous systems (AS) Use TCP port 179 Require IGP, network cant route with only BGP Only one process per router Need neighbors but doesnt run on interfaces Neighbors doesnt need to be directly connected iBGP: In the same AS (AD 200) eBGP: In different AS (AD 20) Hello 60 seconds / Dead 180 seconds BGP Autonomous System Set of routers under a unique technical administration AS range: Public: 1 64511 Private: 64512 65535
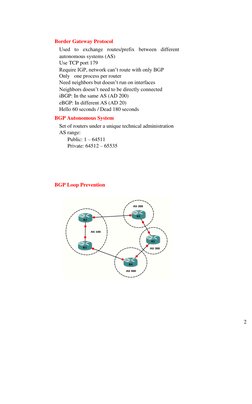
BGP Loop Prevention
�Design of BGP, when to use it? Connection with multiple AS Implement complex routing When you are a transit AS Multihoming Connection to two different ISPs via BGP Verify that your networks are correctly advertised Be careful not to become a transit AS Filter networks not originated from your AS
Design of BGP, what routes should i receive? Only a default route Some routes plus a default Full routes (more than 200.000) Impact Memory CPU Route selection
�BGP Messages OPEN KEEPALIVE UPDATE NOTIFICACION BGP Tables Neighbor table BGP table IP routing table
BGP Neighbor States IDLE: Looking for neighbors CONNECT: TCP session complete ACTIVE: Trying to establishing a neighborship OPEN SENT: BGP open message has been sent OPEN CONFIRM: Response of an open message ESTABLISHED: Neighbor is up, routes exchange start
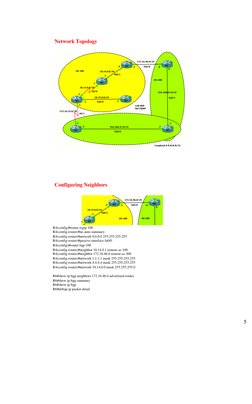
�Network Topology
Configuring Neighbors
R4(config)#router eigrp 100 R4(config-router)#no auto-summary R4(config-router)#network 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 R4(config-router)#passive-interface fa0/0 R4(config)#router bgp 100 R4(config-router)#neighbor 10.14.0.1 remote-as 100 R4(config-router)#neighbor 172.16.46.6 remote-as 200 R4(config-router)#network 1.1.1.1 mask 255.255.255.255 R4(config-router)#network 4.4.4.4 mask 255.255.255.255 R4(config-router)#network 10.14.0.0 mask 255.255.255.0 R6#show ip bgp neighbors 172.16.46.4 advertised-routes R6#show ip bgp summary R6#show ip bgp R6#debup ip packet detail
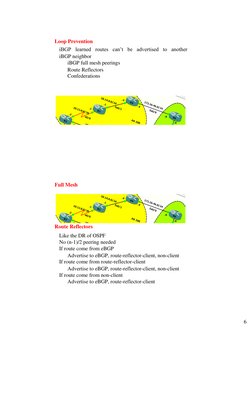
�Loop Prevention iBGP learned routes cant be advertised to another iBGP neighbor iBGP full mesh peerings Route Reflectors Confederations
Full Mesh
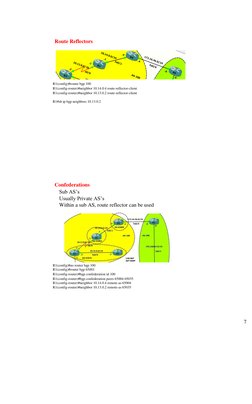
Route Reflectors Like the DR of OSPF No (n-1)/2 peering needed If route come from eBGP Advertise to eBGP, route-reflector-client, non-client If route come from route-reflector-client Advertise to eBGP, route-reflector-client, non-client If route come from non-client Advertise to eBGP, route-reflector-client
�Route Reflectors
RR
R1(config)#router bgp 100 R1(config-router)#neighbor 10.14.0.4 route-reflector-client R1(config-router)#neighbor 10.13.0.2 route-reflector-client R1#sh ip bgp neighbors 10.13.0.2
Confederations Sub ASs Usually Private ASs Within a sub AS, route reflector can be used
R1(config)#no router bgp 100 R1(config)#router bgp 65001 R1(config-router)#bgp confederation id 100 R1(config-router)#bgp confederation peers 65004 65035 R1(config-router)#neighbor 10.14.0.4 remote-as 65004 R1(config-router)#neighbor 10.13.0.2 remote-as 65035
�Next Hop Processing eBGP change the next hop iBGP doesnt change the next hop How to change the next hop: Static route Running a IGP Option next-hop-self Via route-map
Option next-hop-self
R4(config)#router bgp 100 R4(config-router)#neighbor 10.14.0.1 next-hop-self
Via Route Map
R4(config)#route-map NEXTHOP permit 10 R4(config-route-map)#set ip next-hop 10.14.0.4 R4(config-router)#neighbor 10.14.0.1 route-map NEXTHOP out
�Redistribution When you redistribute an IGP to BGP, BGP can propagate to another AS. Routing loops may occur because external IGP routes may be originated in another AS When redistributing from BGP to an IGP it could cause high CPU and memory usage, there are more than 200.000 routes in the internet Well see an example on synchronization rule
Update Source and Multihop By default the TCP packet is sent via the closest interface In some occasions its a good idea that the TCP packets are originated from another interface. eBGP must be directly connected, if not, use multihop
R4(config)#neighbor 6.6.6.6 remote-as 200 R4(config)#neighbor 6.6.6.6 ebgp-multihop 255 R4(config)#neighbor 6.6.6.6 update-source Loopback0 R4(config)#ip route 6.6.6.6 255.255.255.255 172.16.46.6
�Peer Groups Easier administration In occasions a more efficient way to configure BGP Lot of neighbors with the same configuration Locally significant
R3(config)#router bgp 100 R3(config-router)#neighbor GROUP peer-group R3(config-router)#neighbor GROUP remote-as 100 R3(config-router)#neighbor GROUP route-reflector-client R3(config-router)#neighbor 10.35.0.5 peer-group GROUP
Summarization Used in AS border Advertise a single route CPU Memory Cisco way says that is better to aggregate than redistribute static routes connected to null
R4(config)#ip route 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 null 0 R4(config)#router bgp 100 R4(config-router)#network 10.0.0.0 mask 255.0.0.0 R4(config-router)# aggregate-address 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 or R4(config-router)# aggregate-address 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 summary-only
10
�Authentication Only MD5 is supported Very little ISPs wants to run authentication with its clients
R4(config)#router bgp 100 R4(config-router)#neighbor 10.14.0.1 password cisco
Filter Access list Prefix list Route maps Access Lists
Send only summary route to R6 R4(config)#access-list 10 permit 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 R4(config)#router bgp 100 R4(config-router)#neighbor 172.16.46.6 distribute-list 10 out
Prefix Lists
Send only summary route to R6 R4(config)#ip prefix-list SUMMARY permit 10.0.0.0/8 R4(config)#router bgp 100 R4(config-router)#neighbor 172.16.46.6 prefix-list SUMMARY out
11
�Route Maps
Deny only summary route to R6 and permit all other routes R4(config)#ip prefix-list SUMMARY permit 10.0.0.0/8 R4(config)#route-map FILTER deny 10 R4(config-route-map)#match ip address prefix-list SUMMARY R4(config)#route-map FILTER permit 20 R4(config-router)#neighbor 172.16.46.6 route-map FILTER out
What are BGP Attributes The BGP metric is not simple Attributes are ways that you can tag incoming or outgoing BGP routes Some attributes are WELL KNOWN (everyone supports) while others are OPTIONAL Some attributes are MANDATORY (must be in the update) while others are DISCRETIONARY Some attributes are TRANSITIVE (travel from router to router) while others are NON-TRANSITIVE
12
�WELL KNOW Attributes Autonomous system path AS_PATH (Mandatory) Next-hop-address (Mandatory) Origin (Mandatory) Local Preference (Discretionary) Atomic Aggregate (Discretionary) OPTIONAL Attributes Aggregator (Transitive) Multi-exit Discriminator (Non-Transitive)
BGP Path Selection
13
�BGP Path Selection
Influence BGP Path Select ion: Weight Influence the OUTBOUND traffic Apply INBOUND Local to the router Default value 0
R4(config)#router bgp 100 R4(config-router)#neighbor 172.16.46.6 weight 200 R4(config)#ip prefix-list LOOBACK2 permit 2.2.2.2/32 R4(config)#route-map WEIGHT permit 10 R4(config-route-map)#match ip address prefix-list LOOBACK2 R4(config-route-map)#set weight 200 R4(config)#route-map WEIGHT permit 100 R4(config)#router bgp 100 R4(config-router)#neighbor 172.16.46.6 route-map WEIGHT in
14
�Influence BGP Path Select ion: Local Preference Influence the OUTBOUND traffic Apply INBOUND Local to AS Default value 100
R4(config)#router bgp 100 R4(config-router)#bgp default local-preference 150 R4(config)#ip prefix-list LOOPBACK2 permit 2.2.2.2/32 R4(config)#route-map LOCAL_PREFERENCE permit 10 R4(config-route-map)#match ip address prefix-list LOOPBACK2 R4(config-route-map)#set local-preference 150 R4(config)#route-map LOCAL_PREFERENCE permit 100 R4(config)#router bgp 100 R4(config-router)#neighbor 172.16.46.6 route-map LOCAL_PREFERENCE in
Influence BGP Path Select ion: AS Path Influence the INBOUND traffic Apply OUTBOUND Shortest is better
R4(config)#ip prefix-list LOOPBACK4 permit 4.4.4.4/32 R4(config)#route-map AS_PATH permit 10 R4(config-route-map)#match ip address prefix-list LOOPBACK4 R4(config-route-map)#set as-path prepend 100 100 100 100 R4(config)#route-map AS_PATH permit 100 R4(config)#router bgp 100 R4(config-router)#neighbor 172.16.46.6 route-map AS_PATH out
15
�Influence BGP Path Select ion: MED Influence the INBOUND traffic Apply OUTBOUND Only compare MED if prefix is advertised from two sources from the same AS, if not: (config-router)#bgp always-compare-med
R3(config)#ip prefix-list LOOPBACK3 permit 3.3.3.3/32 R3(config)#route-map MED permit 10 R3(config-route-map)#match ip address prefix-list LOOPBACK3 R3(config-route-map)#set metric 2300418 R3(config)#route-map MED permit 100 R3(config)#router bgp 100 R3(config-router)#neighbor 172.16.32.2 route-map MED out
R3(config-router)#default-metric x
Synchronizat ion Rule Prevents traffic to be black holed Reduces traffic that will be drop / Ensure consistency Turn off when Redistribute BGP into IGP BGP is running in all routers of the AS Routes learned via BGP must be validated by the interior routing table before they can be advertised to remote peers
16
�Synchronizat ion Rule
R3(config)#router bgp 100 R3(config-router)#synchronization R4(config)#router bgp 100 R4(config-router)#synchronization
How to fix it 1. BGP running in all routers of the AS or 1. Turn off synchronization on R3 and R4 and:
R4(config-router)#router eigrp 100 R4(config-router)#redistribute bgp 100 metric 1 1 1 1 1
Communities To tag routes in the BGP topology Consistent filtering in the AS domain
se n d t ag
r ou t es
R5(config)#route-map COMMUNITY permit 10 R5(config-route-map)#set community 123456 local-AS R5(config)#router eigrp 100 R5(config-router)#no network 5.5.5.5 0.0.0.0 R5(config-router)#router bgp 100 R5(config-router)#network 5.5.5.5 mask 255.255.255.255 R5(config-router)#neighbor 10.35.0.3 route-map COMMUNITY out R5(config-router)#neighbor 10.35.0.3 send-community
17
�Verifying and Troubleshooting BGP ACL blocking TCP 179 eBGP not directly connected, use multihop AS mismatch Troubleshooting
R1#show ip bgp R1#show ip bgp summary R1#show ip neighbors R1#clear ip bgp * R1#clear ip bgp * in R1#clear ip bgp * out R1#debug ip bgp
BGP Design Peer Review Implementation Plan Detail (configuration and notes) Based on the network topology, configuration of peers, route reflectors, filters BGP Implementation Peer Review Question that can be Asked Why route reflectors and no confederations? Possible Answers There is only one route reflector in the network, the solution is simple
18