0% found this document useful (0 votes)
895 views2 pagesMarket Failure
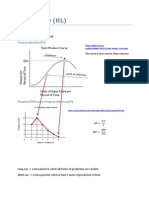
This document discusses market failures such as the lack of provision of public goods, externalities, unequal income and wealth distribution, and monopoly power. It defines externalities as costs or benefits experienced by third parties as a result of market transactions. Externalities can be positive or negative. Positive externalities provide public benefits from private actions while negative externalities impose public costs. The document includes graphs illustrating how externalities can lead to deadweight loss through over or underproduction relative to the socially optimal level.
Uploaded by
Betty BavorováCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
895 views2 pagesMarket Failure
This document discusses market failures such as the lack of provision of public goods, externalities, unequal income and wealth distribution, and monopoly power. It defines externalities as costs or benefits experienced by third parties as a result of market transactions. Externalities can be positive or negative. Positive externalities provide public benefits from private actions while negative externalities impose public costs. The document includes graphs illustrating how externalities can lead to deadweight loss through over or underproduction relative to the socially optimal level.
Uploaded by
Betty BavorováCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Market Failure: Explains the circumstances under which markets fail, including the issues with public goods, externalities, and monopoly power related to efficiency and distribution.
- Externalities: Describes externalities, their impact on third parties, and provides examples of both positive and negative externalities with visual graphs.