Facebook,
Inc.
The
Initial
Public
Offering
Niranjan
Zende
Prof.
Trevor
Larkan
FI
627
Bentley
University
th
July
7
2015
�I.
Introduction
Facebook is a social networking website that allows you to connect and share
memories with your family and friends online. Originally designed for college
students, Facebook was created in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg while he was
enrolled at Harvard University. By 2006, anyone over the age of 13 with a
valid email address could join Facebook. Although Facebook did face
competition in its early stages from incumbents within the industry on a
national as well as international level, it kept growing rapidly.
Based on the data provided and analysis done, I would like to bring to light
some key concerns and suggest some recommendations for an Investment in
the IPO.
II.
Facebook Inc. Business Model
Facebook primarily generated revenues by advertising. Advertising
accounted for 98%, 95% and 85% of Facebooks revenues in 2009, 2010 and
2011 respectively. Since all user data is available to Facebook and is owned by
the company, Advertisers on Facebook were provided with the opportunity
of selecting target segments based on user data, expressed interests, social
connections and other demographics. The remainders of Facebooks revenues
were generated through their payments business, which was exponentially
growing since 2009; this unit generated $13 million, $106 million, $557 million
in the years 2009, 2010 and 2011 respectively.
�Facebook had quite a few competitive advantages; large user base, Business
model built around data, ease and simplicity of use, mobile app for user
engagement and an aggressive stance towards an inorganic growth strategy.
III.
US IPO Market - Technology Industry
At the time of the Facebook IPO, the US economy was still recovering from
the 2007-09 economic crises and the global economy including Europe and
developing economies were in crisis or were faltering.
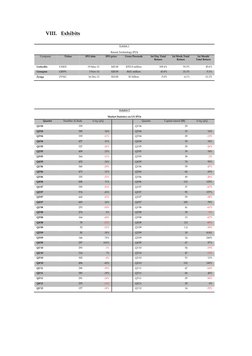
According to data in Exhibit 1, It can be observed that IPO fundraising (in
dollar terms) in the first quarter of 2012 witnessed a 70.2% decrease Year-onYear as compared to the first quarter of 2011. Also IPO fundraising (in # of
IPO terms) activity in the first quarter of 2012 witnessed a 46.9% decrease
Year-on-Year as compared to the first quarter of 2011.
Also, Exhibit 2, depicts the recent technology IPOs in the US markets whose
performance was being analyzed by Mr. McNeils Team, It is very evident
that the stock price of the companies in the industry had witnessed a pop on
the first day of being traded. Companies such as Groupon and LinkedIn sold
at a price above their initial price range. It was the overvalued intrinsic value
of the stock that made the prices fall gradually. As far as the IPO for Zynga
goes, even though their IPO price was within their price range, its
performance wasnt sustaining.
�IV.
Purpose of the Facebook IPO
Today, Facebook is the world's largest social network, with more than 1 billion
users worldwide. The goal stated in the 2011 Facebook prospectus was that
Facebook intended to connect all the 2 billion global Internet users.
In 2011, Facebook Inc. made the decision of going public after noticing the
increasing popularity and presence of social media companies. Facebook
decided to go for the IPO as it would allow existing shareholders and
investors to participate in the public markets and also allow Facebook to make
use of the public equity markets for future fundraising. It was pre-determined
that the proceeds from the IPO would be used for working capital and general
corporate purposes.
V.
Valuation of the Share
The intrinsic value of a company is the actual value of a company or an asset
based on an underlying perception of its true value including all aspects of
the business, in terms of both tangible and intangible factors. This value may
or may not be the same as the current market value.1
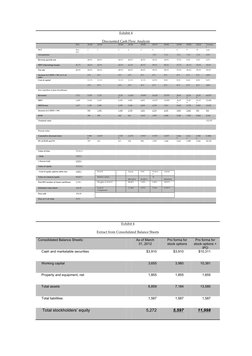
In the case is given a Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) approach to evaluating the
intrinsic value of the company and the shares. Exhibit 3 shows the analysis of
the DCF keeping all the baseline assumptions in line with the analysis
performed by Prof. Aswath Damodaran. The only thing that has been taken
into account is the additional number of shares, which may be floated into the
public market post-IPO. This has led me to value the share at $32.47. This
�price is below the price talk of $34 to $38 per share and may indicate the stock
to be overvalued if all the stocks held by the stakeholders may be traded in
the open market in the short to medium term.
Another method by which we may be able to determine the value of the stock
by using Exhibit 4, which is given below, the extract from the consolidated
balance sheet gives us the pro forma values for the pro forma for stock
options and pro forma for stock options+IPO. The difference between these 2
figures i.e. $11,998million and $5597million would give us $6,401million.
Therefore, Value of Issue/No. of shares issued = 6,401/180 = $35.56 per
share. This price is between the price range of the price talk of $34 to $38
which was updated by the underwriters as this estimation would value the
stock at $35.56 .
VI.
Key Concerns
There are a number of major concerns that an investor such as CXTechnology
Fund must pay attention to before being exposed to unknown risks. Few of
the concerns that are more important than others are as follows:
Shareholding structure completely in favor of Mark Zuckerburg Since
Mark Zuckerburg is entitled to 56% of the voting rights because of the
class B shares, the decision making power in the organizational is too
concentrated and a small mistake at the hands of Mr. Zuckerburg may
deteriorate a lot of firm value.
Sales revenue is forecasted to increase only marginally in the medium to
long term The DCF model proposed by Prof. Aswath of NYU stern
assumes that sales growth will increase at a decreasing rate and increasing
number of DAUs and MAUs are critical to sustain any substantial
growth.
At the time, Facebook wasnt able to advertise on platform on the mobile
devices, which was increasingly being adopted by users this would
hamper the sales revenue as the advertisers would be less inclined to use
Facebook as a medium for reaching out to users who access their accounts
using mobile devices.
User engagement This is one of the most important factors in keeping
the MAUs and DAUs high always, and only if these numbers are seen to
be increasing and promising would advertisers pay Facebook for
advertisements. A roadmap must be in place to keep user engagement at
satisfaction at an all time high.
User data security and privacy Facebook has taken a lot of heat in the
recent years and even years preceding the IPO in regard to the social
values of the social media behemoth. Underage users and Social
experiments on users are only some of the proven accusations on the
company and such incidents would only erode shareholder value.
If a potential institutional investor does not pay attention to critical issues in
the industry such as these before investing, it may lead to negative returns
and also erode significant value from their portfolio.
�VII.
Recommendation
As the importance or social media rises in the day-to-day operations of
corporations, it has encouraged a lot of companies to invest in social media.
Also, the previous Tech IPOs relating to the social media sub-category did
perform very well indeed and also allowed short-term traders to make money
on the first day of trading after a spike in the price.
The Facebook IPO has potential to deliver returns given their growth
trajectory and aggressive growth model. Investors may view Facebooks
positive cash flows as a good signal in the future of the company.
CXTechnology Fund should make the investment on the first day of the IPO
in Facebook in two phases at various price points. They should do so in order
to sell part of the shares and capitalize on the initial spike in share value in
intraday trades and secure some returns and the other part in order to stay
invested in the company for the long term, as it seems to be a promising
investment from the analysis.
�VIII. Exhibits
Exhibit 1
Recent Technology IPOs
Company
Ticker
IPO date
IPO price
Gross Proceeds
1st Day Total
Return
1st Week Total
Return
1st Month
Total Return
LinkedIn
LNKD
19-May-11
$45.00
$352.8 million
109.4%
91.9%
Groupon
GRPN
3-Nov-11
$20.00
$621 million
43.0%
21.3%
45.6%
-5.3%
Zynga
ZYNG
16-Dec-11
$10.00
$1 billion
-5.0%
-6.1%
-11.3%
Exhibit 2
Market Statistics on US IPOs
Quarter
Number of deals
Q1'04
339
Q2'04
385
Q3'04
339
Q4'04
457
Q1'05
327
Q2'05
409
Q3'05
364
Q4'05
452
Q1'06
Q2'06
%chg QoQ.
Quarter
Capital raised ($B)
%chg QoQ.
Q1'04
29
14%
Q2'04
33
14%
-12%
Q3'04
29
-12%
35%
Q4'04
39
34%
-28%
Q1'05
29
-26%
25%
Q2'05
39
34%
-11%
Q3'05
38
-3%
24%
Q4'05
74
95%
360
-20%
Q1'06
39
-47%
473
31%
Q2'06
66
69%
Q3'06
355
-25%
Q3'06
49
-26%
Q4'06
608
71%
Q4'06
112
129%
Q1'07
395
-35%
Q1'07
37
-67%
Q2'07
574
45%
Q2'07
95
157%
Q3'07
442
-23%
Q3'07
59
-38%
Q4'07
603
36%
Q4'07
105
78%
Q1'08
253
-58%
Q1'08
41
-61%
Q2'08
274
8%
Q2'08
39
-5%
Q3'08
164
-40%
Q3'08
13
-67%
Q4'08
78
-52%
Q4'08
2.0
-85%
Q1'09
52
-33%
Q1'09
1.4
-30%
Q2'09
82
58%
Q2'09
10
614%
Q3'09
146
78%
Q3'09
34
240%
Q4'09
297
103%
Q4'09
67
97%
Q1'10
293
-1%
Q1'10
54
-19%
Q2'10
314
7%
Q2'10
47
-13%
Q3'10
302
-4%
Q3'10
53
13%
Q4'10
484
60%
Q4'10
132
149%
Q1'11
296
-39%
Q1'11
47
-64%
Q2'11
383
29%
Q2'11
66
40%
Q3'11
291
-24%
Q3'11
29
-56%
Q4'11
255
-12%
Q4'11
29
0%
Q1'12
157
-38%
Q1'12
14
-52%
�Exhibit 4
Discounted Cash Flow Analysis
DCF
2011
2012E
2013E
2014E
2015E
2016E
2017E
2018E
2019E
2020E
2021E
Termina
l
Base
year
10
year
7.6%
7.6%
7.6%
7.6%
7.6%
0.0%
Assumptions:
Revenue growth rate
40.0%
40.0%
40.0%
40.0%
40.0%
32.4%
24.8%
17.2%
9.6%
2.0%
2.0%
EBIT (Operating) margin
45.7%
44.6%
43.5%
42.5%
41.4%
40.3%
39.3%
38.2%
37.1%
36.1%
35.0%
35.0%
Tax rate
40.0%
40.0%
40.0%
40.0%
40.0%
40.0%
39.0%
38.0%
37.0%
36.0%
35.0%
35.0%
Increase in CAPEX + WC as % of
sales
67%
67%
67%
67%
67%
67%
67%
67%
67%
67%
100%
Cost of capital
11.1%
11.1%
11.1%
11.1%
11.1%
10.5%
9.8%
9.2%
8.6%
8.0%
8.0%
67%
67%
67%
67%
67%
67%
67%
67%
67%
67%
100%
Free cash flow to firm ($ millions):
Revenues
3,711
5,195
7,274
10,18
3
14,256
19,959
26,425
32,979
38,65
1
42,36
2
43,20
9
44,073
EBIT
1,695
2,318
3,167
4,325
5,903
8,051
10,377
12,599
14,35
3
15,27
9
15,12
3
15,426
EBIT(1-tax)
1,017
1,391
1,900
2,595
3,542
4,830
6,330
7,811
9,042
9,778
9,830
10,027
Increase in CAPEX + WC
995
1,392
1,949
2,729
3,821
4,333
4,391
3,800
2,486
568
864
FCFF
396
508
646
813
1,010
1,997
3,420
5,242
7,292
9,262
9,162
Terminal value
152,707
Present value:
Cumulative discount factor
0.900
4
0.8107
0.729
9
0.6572
0.5917
0.5357
0.4877
0.446
5
0.411
1
0.380
6
0.3806
PV of FCFF and TV
357
412
471
534
598
1,070
1,668
2,341
2,998
3,526
58,128
Equity
Debt
Preferre
d
Capital
Value of firm
72,101.2
- Debt
1,587.0
+ Excess Cash
2,000.0
Value of equity
72,514.2
- Cost of equity options (after tax)
3,088.5
WACC
Value of common equity
69,425.7
Market values
$81,247.8
$1,587.0
Post-IPO number of shares (millions)
2,138.1
Weights in WACC
98.08%
1.92%
0.00%
100.0%
Estimated value /share
$32.47
Cost of
Component
11.24%
2.37%
7.14%
11.07%
Price talk
$38.00
Price as % of value
117%
$$82,834.8
Exhibit 4
Extract from Consolidated Balance Sheets
Consolidated Balance Sheets:
$3,910
$3,910
Pro forma for
stock options +
IPO
$10,311
Working capital
3,655
3,980
10,381
Property and equipment, net
1,855
1,855
1,855
Total assets
6,859
7,184
13,585
Total liabilities
1,587
1,587
1,587
5,272
5,597
11,998
Cash and marketable securities
Total stockholders equity
As of March
31, 2012
Pro forma for
stock options
�IX.
References
1. Intrinsic Value Definition | Investopedia. (2003, November 23).
Retrieved July 3, 2015, from
http://www.investopedia.com/terms/i/intrinsicvalue.asp
Mark, K., Compeau, D., Dunbar, C., & King, M. (2014).
Facebook, Inc: The Initial Public Offer (A). In (W12453 ed.). Ivey
Publishing.