0% found this document useful (0 votes)
129 views1 pageUnderstanding the Normal Curve Properties
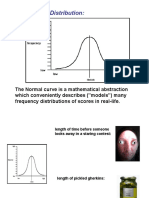
The normal curve is a bell-shaped, symmetrical distribution with the mean, median, and mode at the center. It gradually decreases in frequency as you move away from the center and has the same proportion of scores under the curve for standardized scores (z-scores) across all normal distributions. The normal distribution table can be used to find the proportion under the curve for any given z-score.
Uploaded by
Leung YiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
129 views1 pageUnderstanding the Normal Curve Properties
The normal curve is a bell-shaped, symmetrical distribution with the mean, median, and mode at the center. It gradually decreases in frequency as you move away from the center and has the same proportion of scores under the curve for standardized scores (z-scores) across all normal distributions. The normal distribution table can be used to find the proportion under the curve for any given z-score.
Uploaded by
Leung YiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd