0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes) 1K views8 pagesSegment Proofs Key PDF
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content,
claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online on Scribd
2-7 Practice
Proving Segment Relationships
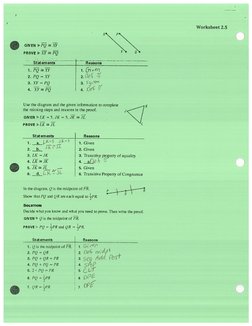
Complete the following proof. eK
1. Given: 4B = DE eens
Bis the midpoint of AC *
Raney = enone
Prove: BC = EF fo:
Proof:
peers [eecons
3, ABEOE BLSaN
Bis mida af AC
Eis midyt of OF
b. AB= DE b. Wa =a
¢. Definition of Midpoint
«Sub
aaa
2. TRAVEL Refer to the figure. DeAnne knows thatthe distance Grayson__Apex_-Redding_ Pine Blt
from Grayson to Apex isthe same asthe distance from Redding -
to Pine Bluf, Prove that the distance from Grayson to Redding is z
equal to the distance from Apex to Pine Bluff. VROVE
0 6a-ae OGven
R PB
eR-ArP
© GAIFR= GR @SAP
ARIBL=A 6
@® BPHAR=CA @Sve
@ Gere @ Sve
Chopter2 46 Glencoe Geometry�Worksheet 2.5
xX Ps
@ GWEN > 70 =
PROVE > XY = PO. Ne a
“~Heasons
‘Statements —
1, PQ = XY 1. Given
2. PQ = XY Dine
3. XY = PQ 3, 54m |
4. XY = PO 4, Dek
Use the diagram and the given information to complete x
the missing steps and reasons in the proof. u
GIVEN > LK = 5, JK = 5, IK = JE
Prove >LK = JL t
Statements Reaso:
ieee
3 2. Given
3. LK =JK 3, Transitive property of equality
4. k= 4 Per =
@ :x-7,- 5. Given
eae
6, Transitive Property of Congruence
Im the diagram, Q is the midpoint of FIR. aa
Show that PQ and Q# are exch equal 14
Soustion
Decide what you know and what you need to prove. Then vite the proof.
GIVEN » Qs the midpoint of PR.
PROVE» PO =
4. Qis he midpoint of PR. 1, Cov?
2. PO-OR | 2 72 midget
3. PQ +OR=PR i 5eg Add Pe:
4.7Q+PQ=PR ; 4 sAC
5.2°P0=PR Neal
6. ro = LR ia 0CE
O22�@Paovine THEOREM 2.1 Copy and completa the proof fortwo of the
cases ofthe Properties of Segment Gongruence Thaerem.
6, Reflexive Property of Segment Congruence
GIVEN > EF js a line segment oe
Prove » EF = EF
Statements
VEF=EF
2,_ 2 BFSEr
2. Definition of congruent segments
7, Transitive Property of Segment Congmuence
GIVEN © AB
PROVE > AB = ST
2. AB OeF ©
Dd Bacco arans
D dye 24a-h ee
% lazax Qs!
2 orE
@ x=6 6
16. © Devecorina Proor Write a complete proof by rearranging the
reasons listed on the pieoes of paper.
GIVEN > fi = XV, VAV = WY,
Prove > (iV =
Statements
We=tZ
2. VW FZ
3. UV = X¥, WZ
5.�17. GIVEN > XY = 8, XZ = 8, XY = 7
PROVE » XZ= ZY
@ \
(TOE EET o oe
© xyex2 ore x
Oa. @ Sve re
6 0et =
18. GIVEN > NK = NZ.NK=13
PROVE > NL = 13
@ Merwe wie [0G
® heme ee
® iene oe
® wrz3 syn�_____|Reteaching Worksheet 3 :
Two-Column Proots with Segments
Proofs in geometry follow the same format that you used in
Lesson 2-4. The steps in a two-column proof are arranged in a
step-by-step order so that each step follows logically from the
Preceding one, The reasons can be given information, definitions,
postulates of geometry, or rules of algebra. You may also use
information that it is safe to assume from a given figure
Example: Write a two-column proof, spe *
Given: BC=DE —-—_____{
Prove: AC = AB + DE 2
—___s
Statements
a, BC=DE a. Given
b. BC b. Definition of congruent segments
e. AC =AB+BC ¢, Segment addition postulate
d. AC=AB+DE d. Substitution property of equality
Complete each proof by naming the property that justifies
each statement.
1. Given: Mis the midpoint of AB,
Bis the midpoint of MD. Apert arses,
Prove: MD = 2MB
Statements Reasons
a, Mis the midpoint of AB. a. Gen seit ene
Bis the midpoint of MD. .
b. AM = MB b. ROC Siri pia satan ee
©. MD = MB+ BD e Hed AU hiss ae Oa
d. MD=MB+MB a _2Ub
e. MD = 2MB e.
2 Given: A, B, and C are collinear, °
AB = BD
BD = BC
Prove: Bis the midpoint of AC, * ee
Statements Reasons
a. A, B, and C are collinear, a iver
AB = BD
¢. Bis the midpoint of AC.
Glencoe Divison, MacmulaniMeGraw-Hit�1.Given: Kis between Jand L. JK = 6, KL = 10 ‘ i
Prove: JL = 16 A —__.____.
Proof Statements Reasons
3.JL=JK+ KL :
4.JL = 6 +10 4.2
5.JL = 16 SSO Tee a eS eS
Complete each proot. : 5
1, Given: AD = 248 + BC ae
AB = CD ; 5
Statements Reasons
a. AD = 24B + BC a NEN VET eRanRC ree
b. AD=AB+ BC + CD bp, SAP
© 24B+BC=4B+BC+CD |e, Co) Sameera
d. AB=CD 4 3te
e. AB = CD eel RARER
2. Given: B is between A and D.
Cis between A and D. aS
er AB +BD ~~ AC+CD oS
Proof:
Statements | Reasons
a. Bis between A and D, a ver
is between A and D.
b. AB + BD = AD
©. AC +CD=AD
d. AD = AC +CD
e. AB+BD=AC+CD
Write a two-column prot.
3. Given: B is the midpoint of AC.
Proves AB © C= BD” teh
Proof: ee
Statements | Reasons
O6%S the mdpyOrRe lOGNen
@ ABreC=pc ONE
© h6-8c HA Midgt
® 8c+C0260 SAC
° © A®iCp=B0 5v0�muy Mrioys
19. Copy and complete the proof.
Fa mR
Hons
Prove: [G= MA
Given:
Statements
Copy and complete each proof.
20. Given: DA = EL
Prove: DE = AL
Statements
DA-EL
21.
AB=CD
Mis the midpoint of AB,
Nis the midpoint of CD.
Prove: AM = CN
emer
i5= cD on
Mis the midpoint of AB,
Nis the midpoint of CD.
- ae cD pm
Na.
ee
CN+ND=CD
Ais b= CNN
dike Ai Cn «cn
2AM =2CN
h. AM = CN
®
i
a. Given
» Hef 2
0
aSAt
d. Addition property of equality
¢. Substitution property of equality
anor FP
. Substitution property of equa
z
io
Reasons
» Gen
» OE =
. Definition of midpoint
« BAP
« Sub.
« Bub
4. Substitution property of eq:
i. AM= CN�Peg) ovis ¢
nsenutOn()
as @ ay=0n+Ny
Ss AW sYS
ON =4S
ans 8 U/
VANS :n01g
AN =¥S ‘on -cz
=4d@Q, 422 *°
gsQ ré-a¥@
aS Deksax- uo?)
KAtxX= HD
oo oe arene
dvs Q) ¥< 284048) pet
ae Eee
Bs 40Q| x=) @ “age ay sang
et xpeW xZ = OV
van) 0! xkKE4O ARP OF ‘emg 97
2sQ 07-79
5) 04 B= 29+
{ 41a = 29 8H |
G78 @Q) vinasany 475 IN=0W 0)
oy =a +20 a Ow = NY 4471
3YS@ > a x : seit wuhs
YOY iy ay |
on eng) tae | Mea | ates@
l= 9S
Gat (bey) oe
2 vent
dG = Og :2n01g
av = av d= IST = 1H :9n01g
= OY wang yz dW any IS = SY mag zz
*yoosd uumnjoo-ory & anna