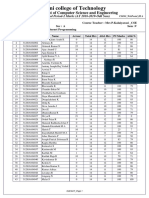
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
115 views6 pagesComputing Technologies and Concepts Overview
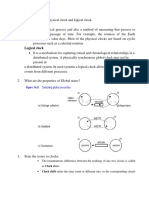
1. The document defines key computing concepts including RFID, GPS, IoT, cloud computing, ubiquitous computing, degrees of parallelism, and cyber-physical systems.
2. It also defines computing paradigms and models such as centralized, parallel, distributed, and cloud computing. Cluster computing, single system image, computational and peer-to-peer grids are also described.
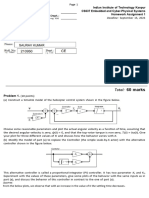
3. The motivation behind the Open Grid Services Architecture (OGSA) is to facilitate resource sharing and management across distributed environments through open standards.
Uploaded by
jayanthikrishnanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
115 views6 pagesComputing Technologies and Concepts Overview
1. The document defines key computing concepts including RFID, GPS, IoT, cloud computing, ubiquitous computing, degrees of parallelism, and cyber-physical systems.
2. It also defines computing paradigms and models such as centralized, parallel, distributed, and cloud computing. Cluster computing, single system image, computational and peer-to-peer grids are also described.
3. The motivation behind the Open Grid Services Architecture (OGSA) is to facilitate resource sharing and management across distributed environments through open standards.
Uploaded by
jayanthikrishnanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd