100% found this document useful (4 votes)
962 views52 pagesBusiness Model Canvas Guide
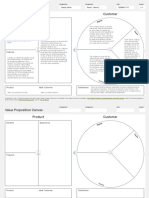
The document discusses business model generation and the business model canvas. It provides an agenda that covers the differences between a business model and business plan, an overview of the business model canvas, business model patterns, business model design, and the business model design process. The bulk of the document then explains each of the nine blocks of the business model canvas - customer segments, value proposition, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, key resources, key activities, key partnerships, and cost structure.
Uploaded by
cetetCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (4 votes)
962 views52 pagesBusiness Model Canvas Guide
The document discusses business model generation and the business model canvas. It provides an agenda that covers the differences between a business model and business plan, an overview of the business model canvas, business model patterns, business model design, and the business model design process. The bulk of the document then explains each of the nine blocks of the business model canvas - customer segments, value proposition, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, key resources, key activities, key partnerships, and cost structure.
Uploaded by
cetetCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd