0% found this document useful (0 votes)
735 views50 pagesExcel VBA Macro Programming
This document provides an overview of Excel VBA macros and programming. It discusses declaring variables, data types, arrays, constants, modules, functions, subroutines, conditional statements, loops, functions, dialogs, the Excel object model including the Application, Workbook, Worksheet, Window, and Range objects. Key methods and properties are described for tasks like saving, closing, printing, protecting sheets, and more.
Uploaded by
natee8632Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
735 views50 pagesExcel VBA Macro Programming
This document provides an overview of Excel VBA macros and programming. It discusses declaring variables, data types, arrays, constants, modules, functions, subroutines, conditional statements, loops, functions, dialogs, the Excel object model including the Application, Workbook, Worksheet, Window, and Range objects. Key methods and properties are described for tasks like saving, closing, printing, protecting sheets, and more.
Uploaded by
natee8632Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
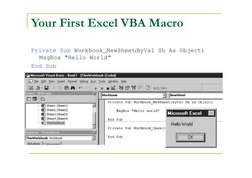
- Your First Excel VBA Macro: Introduces writing and executing a simple macro with 'Hello World' example.
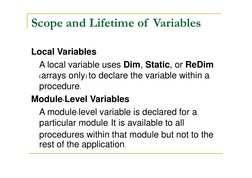
- Variables, Constants, and Data Types: Details how to declare and use variables, constants, and data types in VBA programming.
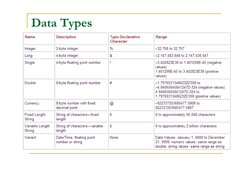
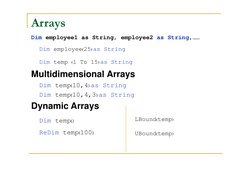
- Data Handling: Provides an overview of different data types and how arrays are managed.
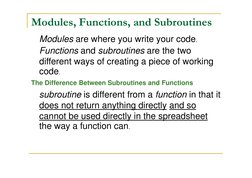
- Modules, Functions, and Subroutines: Covers the concepts of modules, functions, and subroutines, highlighting differences and applications.
- Programming Basics: Introduces basic programming logic in VBA, including decisions and looping with examples.
- Functions: Introduces functions available in VBA, explaining commonly used functions with examples.
- User Interface Commands: Discusses commands affecting the VBA interface such as SendKeys, Dialogs, and PopUp menus.
- The Excel Object Model: Explains different Excel objects and their properties, crucial for manipulating Excel from VBA.

![Variables, Arrays, Constants, and Data
Types
declare a variable using the Dim statement
Dim variablename [As type]
Example](https://screenshots.scribd.com/Scribd/252_100_85/178/381123968/3.jpeg)