0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views2 pagesSimulation of Profits from Put Options
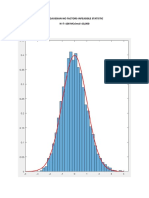
The document simulates put option payoffs over multiple time periods using randomly generated standard normal variables. It calculates profits over 10,000 periods for 10,000 simulations and plots the distribution of profits for one simulation and the evolution of cumulative profits over time. The plot shows it can take many periods before cumulative profits go negative.
Uploaded by
Alain-Philippe FortinCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views2 pagesSimulation of Profits from Put Options
The document simulates put option payoffs over multiple time periods using randomly generated standard normal variables. It calculates profits over 10,000 periods for 10,000 simulations and plots the distribution of profits for one simulation and the evolution of cumulative profits over time. The plot shows it can take many periods before cumulative profits go negative.
Uploaded by
Alain-Philippe FortinCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd