100% found this document useful (2 votes)
2K views26 pagesCode of Ethics
The document provides an overview of the code of ethics for nurses. It discusses key topics like the definition and meaning of ethics, the purposes of a code of ethics, terminology used, the evolution of the International Council of Nurses' code, elements of the code including responsibilities towards patients, practice, coworkers and society, ethical principles, and the Indian code of ethics. The code of ethics establishes guidelines for nurses' conduct and responsibilities to patients, other professionals, and society.
Uploaded by
Babita DhruwCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (2 votes)
2K views26 pagesCode of Ethics
The document provides an overview of the code of ethics for nurses. It discusses key topics like the definition and meaning of ethics, the purposes of a code of ethics, terminology used, the evolution of the International Council of Nurses' code, elements of the code including responsibilities towards patients, practice, coworkers and society, ethical principles, and the Indian code of ethics. The code of ethics establishes guidelines for nurses' conduct and responsibilities to patients, other professionals, and society.
Uploaded by
Babita DhruwCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction: Discusses the role and significance of a code of ethics in nursing, emphasizing professional values.
- Definition & Meaning: Explains the formal statement of a group's ideas and values, exploring ethical basics in nursing.
- Purposes: Outlines the objectives of an ethical code including guidelines for nursing actions and protection of rights.
- Terminology: Defines key terms relevant to the nursing profession, including profession, ethics, and law.
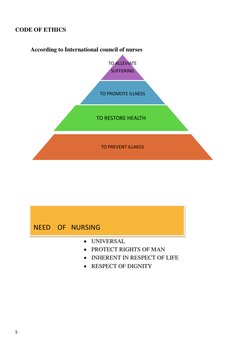
- Code of Ethics: Presents the International Council of Nurses' perspective on ethics and the need for nursing.
- Evolution of Code of Ethics: Describes the adaptation and historical development of nursing ethics codes.
- Elements of Code of Ethics: Highlights primary ethical principles in nursing practice contexts and the role of nurses as advocates.
- Ethical Consideration: Explores various ethical challenges, including uncertainty, distress, and dilemmas, within nursing practice.
- Ethical Principles: Details key ethical principles such as autonomy, beneficence, and confidentiality in nursing.
- Rules: Outlines specific ethical responsibilities including accountability and respect for persons and autonomy.
- Ethical Consideration: Discusses additional ethical considerations relating to veracity, justice, and fidelity in nursing.
- Code of Professional Conduct: Describes the code governing nursing behavior, emphasizing compliance with laws and ethical standards.
- Assertiveness: Defines assertiveness in nursing, advocating for effective communication and legal awareness.
- Legal Considerations: Introduces legal concepts relevant to nursing, such as laws, rights, and responsibilities.
- Legal Principles: Explores legal principles including intentional torts, defamation, and negligence in professional practice.
- Legal Aspects: Discusses broader legal aspects affecting issues like consumer rights and healthcare safety.
- Dos & Don'ts: Lists practical guidelines for nursing conduct, including rights of consumers and legal responsibilities.
- Legal Documents: Details various legal documents and orders crucial to nursing procedures and compliance.
- Visibility of Nurses: Addresses the visibility and professional exposure of nurses within healthcare systems and society.
- Summary: Provides a recap and closing of the document's discussion on ethical codes and professional standards.
- Bibliography: Lists references and sources quoted within the document, indicating scholarly foundation.